Secrets of spring apple tree grafting for beginners
Content
When to start grafting an apple tree
A common question among beginning gardeners: when is the best time to graft? In fact, apple trees can be grafted at any time of year (indoor grafting is done in winter), but the best time is spring. This is when the scion takes root best, and the rootstock is less susceptible to damage from the procedure.
Moreover, if the procedure is unsuccessful, it can be repeated in the summer. Therefore, spring grafting is the most suitable time for beginners. It is better to graft an apple tree when the sap begins to flow and the buds swell. The timing of grafting may vary depending on the climate zone: in central Russia, for example, in the Moscow region, grafting can begin in March or April. Many prefer to choose a favorable day according to the lunar calendar, during the waxing moon (for example, in 2025, the optimal days were in April, from the 27th to the 30th). Finally, the optimal time for the procedure is early morning or evening, in good, dry, and warm weather.
Selecting scion and rootstock
When asking the question, "How to graft an apple tree in spring?", choosing the right scion and rootstock is crucial. They should be compatible, ideally from closely related varieties. A cultivated tree can be transplanted onto a wilding. The rootstock must be hardy: resistant to drought, excess moisture, low temperatures, and so on. It must be suitable for the local climate (for example, Arm-18, Ural 1 and 5, and R-60 perform well in the Urals).
There are special "rootstock" varieties for grafting that, in addition to being hardy, have a very high compatibility rate. The tree itself must be healthy and strong. Mature apple trees are most often used, but saplings are also acceptable. Even an older tree can be grafted, as long as it is healthy. The scion must have good fruiting qualities. The scion should be taken from an apple tree that is already bearing fruit and has proven itself, so that its yield and the taste of the apples can be assessed.
Choosing the best grafting method
There are different grafting methods. When deciding how to graft an apple tree in the spring, you need to choose the best one for your conditions.
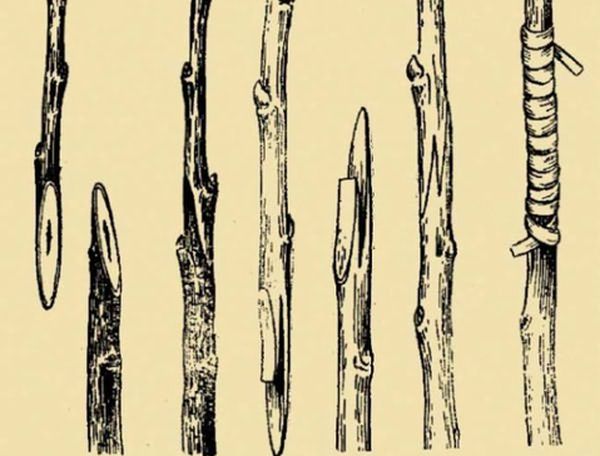
Standard copulation
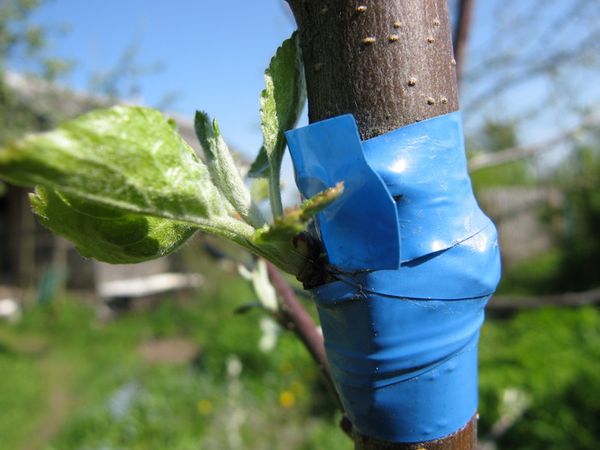
This method has a good survival rate, but it's not always available, as it only allows scion and rootstock to be grafted with the same diameter and perfectly aligned cuts. It works well if both apple trees are young. To graft, make identical 2-3 cm diagonal cuts and press them tightly together—this should be done within a minute.
Wrap the cut with electrical tape or film. Some experts recommend placing the scion in a bag secured to the branch until grafting occurs—this will protect the buds from drying out. Another method, called improved copulation, involves making longitudinal cuts (tongues) in the cuts, one-third the depth of the diameter. These cuts ensure better adhesion when joined. This method is well suited for grafting apple trees onto the crown.
Into the cleft
A fairly easy and effective method. It's suitable for grafting apple trees onto thick rootstock branches (including onto an old tree). After carefully sawing off the rootstock branch (to create a stump-like structure), it's split. Make 2-3 cm diagonal wedge-shaped cuts on two scion shoots and insert them into the gap. The cambium of the rootstock and scion should be tightly adjacent. After treating the cut with garden pitch, secure the scion with electrical tape or film. This method is also suitable for grafting a scion onto a stump of a felled tree.
Budding
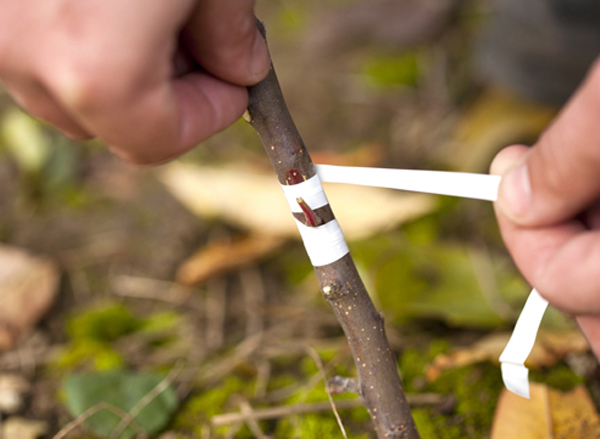
Bud grafting. This method is slightly more difficult, but minimally traumatic for the tree. When and how to bud graft?
The sap should already be actively flowing (in Russia, this is usually late April - early May). A T-shaped incision is made in the scion bark. Layers of the upper tissue, including the bud, are cut from the scion scion and inserted into the incision. The grafting site is secured (the bud should remain exposed). Another variation of this method is the "butt" method: a cut in the bark on the rootstock is made to form a "pocket," and the bud is removed from the scion scion with its "shield" and inserted into the incision. The upper part of the "pocket" should be removed so that it does not obscure the bud.
In the side cut
A diagonal cut is made on the rootstock branch, but the branch itself is not removed. Two diagonal cuts are made on the scion to form a wedge, and it is transplanted into the cut so that it and the "receiving" branch form a fork. The cambia should be in close contact. Finally, treat and secure the junction.
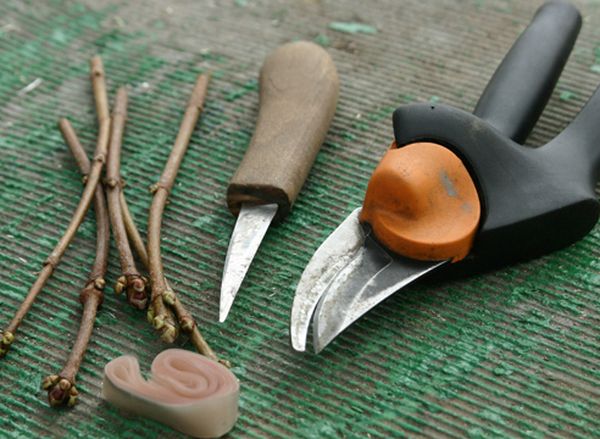
With grafting shears
Grafting apple trees with grafting shears is a great way to do it. The cuts they make are very even and perfectly aligned on the rootstock and scion. Any gardener who has grafted will appreciate this convenience.
Suitable for cuttings from 4 to 13 mm. Most models have interchangeable blades (V-, Ω-, and U-shaped). When deciding which pruning shears to buy, it's best to choose models with a band spring and a 1.5–2 mm blade.
Other methods
There are other grafting methods. If needed, you can find step-by-step descriptions of how to graft apple trees in spring, as well as visual diagrams of any method. Bridge grafting involves inserting the scions in an arch under the bark of the rootstock. Under-bark grafting involves inserting a scion cut with the stump into a cut in the rootstock's bark. Ablactation grafting involves grafting the rootstock with a branch from a nearby tree, rather than a cut scion.
Further care of the tree
Since properly grafting an apple tree in spring isn't everything, let's learn how to care for the grafted tree. Ten to fifteen days after spring grafting, check to see if the rootstock has taken root. If the scion is grafting properly, it should have viable buds and smooth bark. The wound should heal normally. If the scion has dried out, the rootstock wound should be treated with tar. Since grafting can also be done in summer, you have time to correct any mistakes and try again.
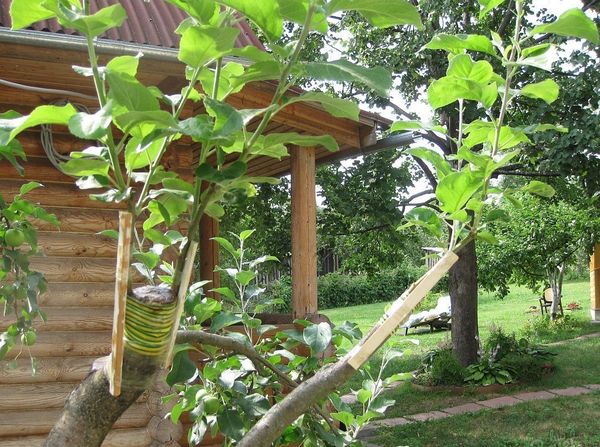
The grafting should be loosened periodically to prevent it from compressing the growing scion. Spring grafting of apple trees allows for the final removal of the grafting as early as the second or third month. Any shoots that appear under the graft should be cut off with a sharp knife, otherwise they will draw the sap. If they are broken, many new shoots will emerge.
After the buds awaken, pruning is necessary. If several buds have sprouted, the rules require leaving the strongest one (preferably the top one). The lower bud is shortened, and the side shoots are cut back to a ring. Since the mechanical connection is still weak, it is best to tie up the scion shoot after it has grown 20 cm. The staking should be renewed as it grows and continued for 2-3 years. During the first few years, abundant watering is especially important for the grafted plant.
Tips from an experienced gardener
It is advisable to attach a label with the names of the scion and rootstock varieties to the grafting site (especially if you have many trees).
To deter birds, you can use brightly colored strips. Experimenters may wonder: is it possible to graft apple trees onto other trees (pear trees, etc.)? Generally speaking, yes, but the survival rate will be lower, the scion will have a shorter lifespan, and the fruit may be smaller.
Video: "Spring Grafting of Apple Trees"
This video will show you how to properly graft an apple tree in the spring.