How to plant and grow a honey apple tree of the Medunitsa variety in your garden
Content
- 1 History and characteristics of the Medunitsa apple tree
- 2 Varieties of the variety
- 3 Video "A Brief Overview of the Medunitsa Apple Tree"
- 4 Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- 5 Features of planting and growing the Medunitsa apple tree
- 6 Protection from diseases and pests
- 7 Reviews from gardeners
History and characteristics of the Medunitsa apple tree
In the 1930s, Sergei Ivanovich Isaev, a professor and biologist well known in horticultural circles, began developing a new fruit crop. By selectively crossing the Welsi and Cinnamon Striped apple varieties, he succeeded in developing a frost-resistant apple variety, which was named Medunitsa. Other popular names for this fruit crop include Medovka, Medovitsa, and Medovaya.

Description of the tree
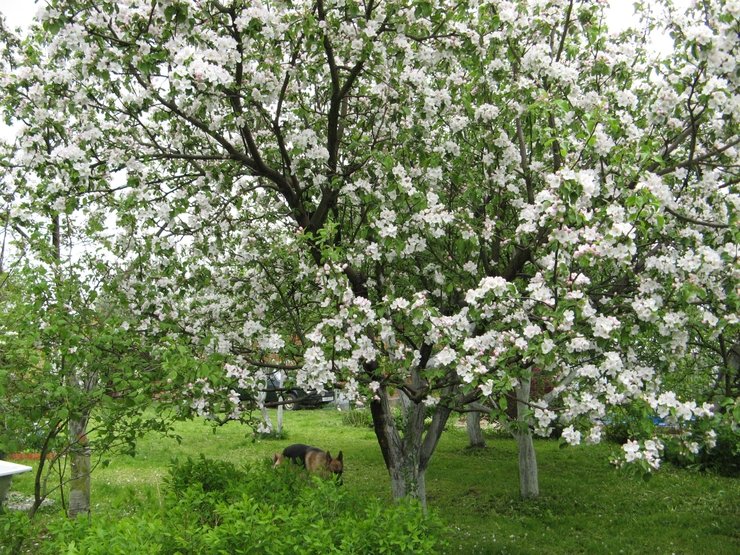
Grown on seedling rootstock, this apple tree is characterized by vigorous growth. A mature tree can reach 7 meters in height, with a spreading, pyramidal crown. The variety boasts above-average foliage and shoot production.
The robust, slightly drooping branches are densely covered with foliage. The bark of the shoots is a gray-olive shade. The leaves are dark green, elongated oval in shape with a central sag. The apple tree is particularly striking during flowering, with large white flowers covering almost the entire crown. Lungwort is highly ornamental, making it a popular choice for garden design.
Commercial and taste qualities of fruits
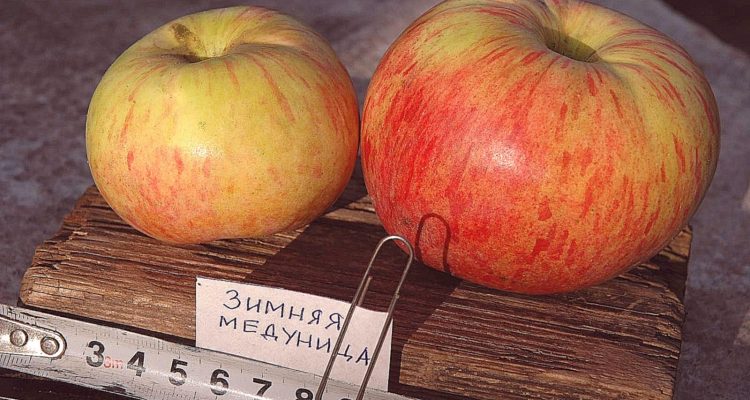
Medunitsa apples have a regular round shape. Conical apples are much less common. A ripe apple weighs 100–150 g. At maturity, the skin is yellow-green with distinct red-orange stripes. When fully ripe, the fruit is bright red or deep yellow with a characteristic scarlet blush.
The pulp of this variety is dense and juicy. Medunitsa apples have a delicately sweet flavor with virtually no tartness. A distinctive feature of this variety is its pleasant honey aftertaste.
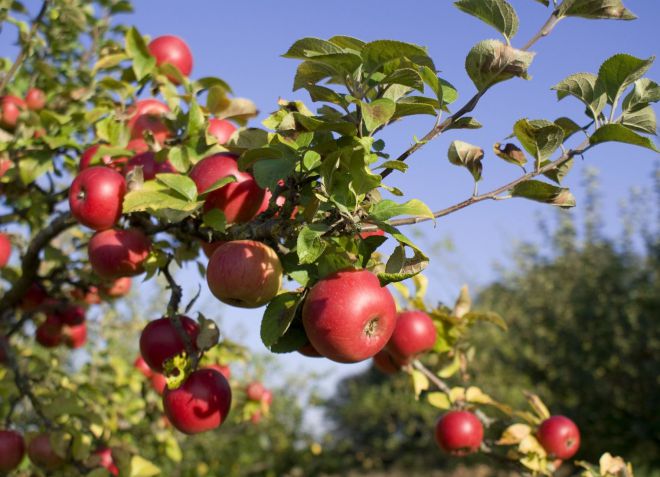
Ripening and fruiting
Due to the dense canopy, uneven ripening of the fruit is observed. Thus, the summer apple tree bears fruit from August to September, while the winter apple tree bears fruit from late September to mid-October.
Lungwort is a self-fertile variety. However, to increase fruiting, experienced gardeners recommend cross-pollination. The following varieties are used as pollinators: Pobeda (Victory), Korichnoye Polosatoye (Cinnamon Striped), and Anis Sverdlovsky (Sverdlovsk Anise).
The variety bears fruit late. The first harvest from an apple tree grown on seedling rootstock is not harvested until the fifth or sixth year. The tree bears fruit actively for 50–60 years.
Productivity and application of fruits
The Medunitsa apple tree traditionally produces approximately 120–170 kg of edible fruit. The average shelf life in a cellar or basement is up to 3–4 months. Note that the honey aroma and aftertaste linger for no more than 2 weeks after harvest.
Juicy and aromatic, these apples are eaten fresh. The fruit is used in cooking to make compotes, juices, preserves, marmalades, and marmalades.
- The variety has a high yield
- Winter variety
- Summer variety
Varieties of the variety
There are several varieties of the Medunitsa apple tree: summer, winter, and those grown on dwarf rootstock. Let's look at the main characteristics of each type of fruit tree.
Summer lungwort
It is characterized by a high yield—a single tree can yield approximately 80 kg of fruit. The apples are sweet and juicy, with a pleasant honey aroma. Unfortunately, fruits harvested between August and September quickly lose their flavor and marketability. The shelf life is no more than 1.5 months.

Winter lungwort
The winter variety is popular with gardeners in southern regions. This fruit tree produces a late harvest of juicy, sweet apples. The fruits are suitable for long-term storage and long-distance transportation.
Lungwort on a dwarf rootstock
In small garden plots, cultivation on dwarf rootstocks is used. The fruit tree grows to a height of no more than 2.5 m. Fruiting occurs early, approximately three years after grafting. The yield and consumer quality of the fruit are high.
Video "A Brief Overview of the Medunitsa Apple Tree"
This video presents the main characteristics of the variety.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- the impressive appearance of the tree;
- high survival rate of seedlings;
- self-pollination;
- abundant harvest;
- absence of fallen fruit;
- high consumer qualities of fruits;
- good transportability;
- resistance to scab and various types of rot.
- the need for frequent crown pruning;
- uneven ripening of fruits;
- loss of characteristic honey aroma during storage;
- short shelf life.
Features of planting and growing the Medunitsa apple tree
The Medovitsa apple tree is highly adaptable and easy to care for. However, knowing certain planting and growing guidelines will help increase fruiting and yield.
How to plant an apple tree
In the central and southern regions of Russia, seedlings are planted outdoors in the fall, approximately 2–3 weeks before the onset of frost. In Siberia, the Urals, and the Far East, it's best to postpone planting until spring.
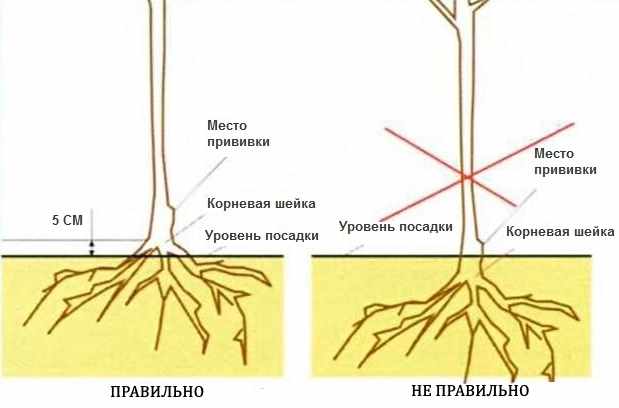
A sunny, well-heated area of the garden is ideal for planting and growing fruit trees. Building walls and fences can provide protection from wind and drafts. When planting multiple seedlings, maintain a certain distance between holes and rows:
- apple trees on dwarf rootstocks – 4–5 m between rows and 1.5–2.5 m between holes;
- apple trees on vigorous rootstocks – 6–8 m between rows and 4–6 m between holes.
Suitable soil is well-drained, permeable loam. To improve the fertility of the substrate, apply a pre-planting fertilizer, mixing peat, humus, leaf mold, and turf soil in equal proportions.
Caring for fruit crops
Lungwort is characterized by high drought tolerance. In the absence of extremely high temperatures, the tree is watered no more than once every 7-10 days. If the summer is hot, the frequency of watering is increased to once every 4-5 days. 20 to 40 liters of settled water are poured under each apple tree.
Young, non-fruit-bearing apple trees are fed with urea and nitrogen-containing fertilizers. Fruit-bearing trees are fertilized with potassium chloride (0.5 cup per 10 liters of water) and superphosphates (2 tablespoons per bucket of water). Complex mineral fertilizers, such as Kemira Lux, are often used for fruit tree nutrition.
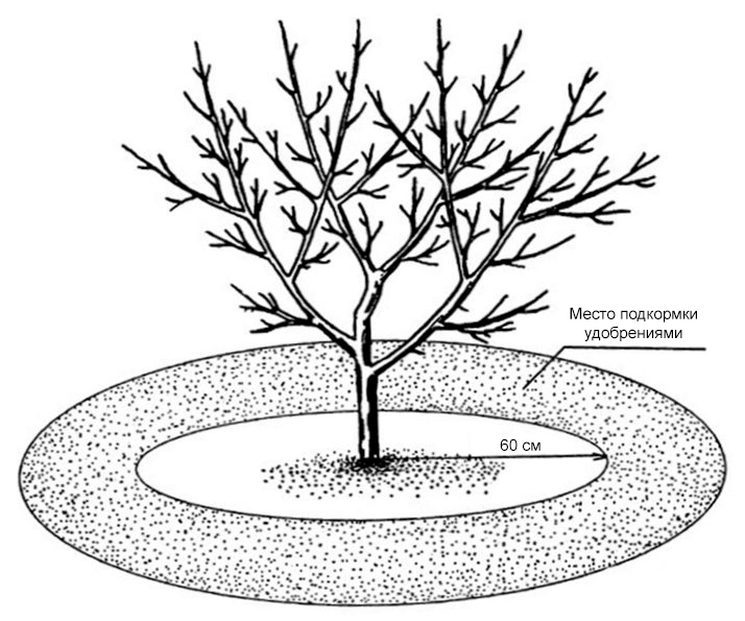
Rejuvenating and shaping pruning is carried out in early spring, before buds begin to open. Branches weakened by winter and those growing inward are removed. No more than 5-7 healthy, fruiting shoots are left on the tree.
Every fall, after the harvest, the crown is pruned. Dry and damaged branches are cut back to living tissue, and the cuts are sealed with garden pitch.
Wintering of a tree
Lungwort has a high winter hardiness threshold—around -33°C. This fruit crop is grown in gardens in Siberia and the Urals. The plant is only insulated during winters with little snow. The trunk area is generously mulched with peat, dry fallen leaves, and small spruce branches.

Protection from diseases and pests
A unique feature of the Medunitsa apple tree is its high resistance to harmful insects and various diseases, including scab. For prevention, the plant is periodically sprayed with a 3% Bordeaux mixture solution or colloidal sulfur diluted in water.
Reviews from gardeners
"Every garden should have an apple tree. We chose the winter variety Medunitsa. Its advantage is the late harvest of juicy and flavorful apples. We eat the fruit fresh and also use it to make compotes and juices for the winter."
"The Medunitsa apple tree is a unique fruit crop because it can be grown even in regions with harsh climates. The plant withstands severe frosts, recovers quickly in the spring, and delights with a bountiful harvest of delicious apples."
The Medunitsa variety is suitable for growing by beginning amateur gardeners. The plant does not require abundant watering or frequent fertilizing. Timely pruning and preventative spraying to prevent diseases and insects are the main care for this fruit crop.



