How to build a warm underground greenhouse yourself
Content
Advantages and disadvantages of an underground greenhouse
Underground greenhouses built with your own hands have the following advantages:
- year-round use of the structure;
- no dependence on weather;
- high efficiency;
- efficiency of solar energy use (used for additional heating of the building);
- in such a design, it is possible to grow even crops that are exotic for a particular area;
- durability and reliability;
- excellent light transmittance parameters of the roof;
- good thermal insulation properties of the room;
- versatility.
These are the advantages of a greenhouse in the ground, both without heating and with it.
The ruined greenhouse type has only two drawbacks: relatively high labor intensity and the need for a reliable ventilation system. But if you approach the work correctly, these design flaws won't cause much trouble.
Video: "Greenhouse-dugout for year-round gardening"
This video will show you how to build a dugout greenhouse for year-round gardening.
Design Features
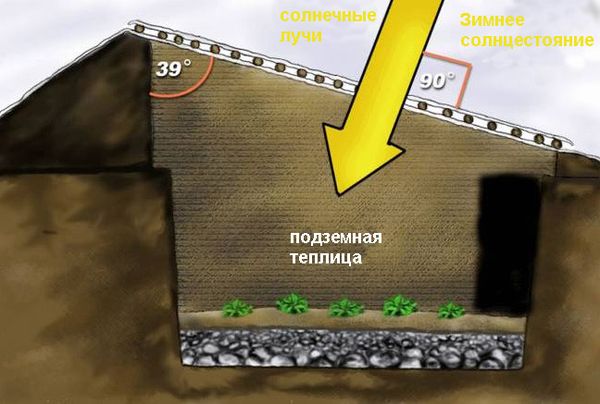
An underground greenhouse is a structure partially built into the ground. This design creates a thermos effect. This occurs if the greenhouse is buried at least 1 meter into the ground. In this case, the temperature inside such a dugout will range from +3 to +14°C.
If the structure is buried 2.2–2.4 meters deep, the temperature inside will remain virtually constant throughout the year. The primary objectives in such structures are temperature maintenance and irrigation.
If you're planning to build an underground greenhouse, you need to accurately calculate the depth of the greenhouse's burial depth. This is determined based on the depth of the groundwater table and the winter freezing point. Based on these parameters, you can easily determine whether this type of greenhouse is feasible. In marshy areas or areas with a low groundwater table, the underground greenhouse option is not suitable.
It's worth noting that soil freezing has a major impact on plant growth. Crop beds in such structures should be located below the seasonal freezing level in the region. Therefore, the bottom of the pit should be located between the groundwater level and the freezing point.
Today, there are two types of earthen greenhouses:
- Underground. In this case, the depth chosen allows for the maintenance of the plant beds completely underground. The greenhouse should have a ladder along the entrance wall, as well as walkways between sections (where specific plant groups are grown) that allow a person to move around without bending over;
- Recessed. Here, the structure is serviced without a ladder, from the ground surface. The roof is raised.
Depending on the terrain and available space, a DIY underground greenhouse can be horizontal (with all walls the same height) or inclined. These greenhouses can be trench-type (considerable length with minimal width) or pit-type, depending on the footprint.
An in-ground greenhouse can be used to grow fruits, berries, mushrooms, vegetables, seedlings, and flowers. Thanks to its design, such a greenhouse can be installed in Siberia or anywhere else in our country.
How to make it yourself
A DIY sunken greenhouse is built in several stages. You'll need the following tools:
- hammer drill;
- hammer;
- Bulgarian;
- shovel;
- construction mixer and vibrator for concrete;
- electric drill;
- hacksaw, knife and scissors;
- trowel;
- spatula;
- paint brush;
- level, plumb line and tape measure.
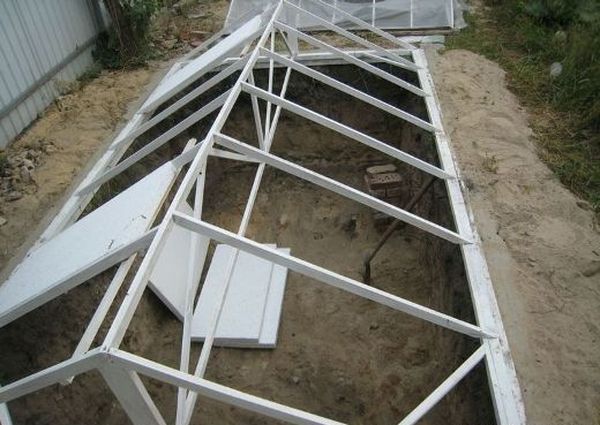
The Scottish (recessed) type of greenhouse begins with digging a pit.
pit
To create a greenhouse effect inside the greenhouse, the pit depth should be 1.9–2.2 (2.5) m. The width of the structure should not exceed 4.8–5.2 m. If the structure is too wide, insolation parameters will deteriorate and the need for heating will increase.
The length is determined by the available space on the site for construction. The amount of space you allocate for the greenhouse will determine its length.
It is recommended that the excavated pit be oriented east-west. The sides of the pit should be leveled as much as possible. This is necessary to ensure high-quality walls. Each side of the structure must be properly aligned to avoid problems with the roof.
Foundation and walls
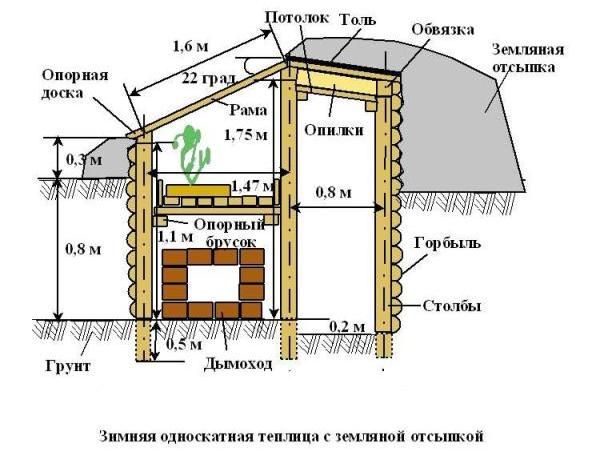
Once you've dug the foundation pit for your greenhouse, you can begin pouring the foundation. Typically, the foundation is poured around the perimeter of the structure and forms a strip. Reinforced concrete should be used for this type of foundation. The optimal thickness of the foundation is 30–50 cm (depending on the size of the greenhouse). This ensures that the center of the structure remains earthen.
The side walls can be constructed from wood, expanded polystyrene blocks, or aerated concrete blocks. These materials offer excellent thermal insulation properties and are lightweight.
If gardening is to be done year-round, the walls should be raised at least 0.5 m above the snow cover. The optimal wall height for such structures is determined individually for each region.
Roof installation
To create a roof for a sunken greenhouse, supports must be installed in the center of the structure. Wooden beams will be laid on these supports and the walls. A ridge beam should be installed in the center of the structure. Cross ribs are then assembled from the beams. Honeycomb polycarbonate sheets are installed on the resulting frame.
The covering material is secured to the beams using special thermal washers fitted with rubber seals. During installation, use a steady hand to prevent gaps. To improve the thermal insulation of the greenhouse in cold regions, the roof should be constructed from two layers of polycarbonate.
Insulation and heating
To insulate a sunken greenhouse, the wall surface should be covered with a waterproofing membrane. Thermal insulation is then installed on top of this membrane. Polystyrene foam or mineral wool are most commonly used as insulation. Special polymer thermal insulation films with a foil layer can also be used. These films help accumulate heat inside the greenhouse by reflecting sunlight. If heat-loving plants are needed, underfloor heating can be installed.
This is how a sunken greenhouse is constructed. When built correctly, such a structure will have all the advantages described above. Once completed, the greenhouse can be used immediately for its intended purpose.