Planning and building a polycarbonate greenhouse yourself
Content
What type and shape of greenhouse should I choose?
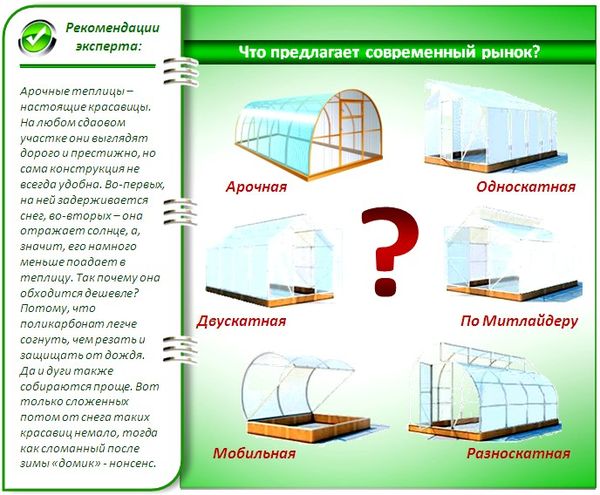
Among the various types of greenhouses, the most popular ones are:
- arched, which have a semicircular shape;
- single-pitched - one side can be attached to some building on the garden plot and have a common wall side with it;
- hipped, having a gable roof in the shape of a triangle;
- Greenhouses, which don't allow for growing plants directly on the ground, use racks and shelves to hold boxes of vegetable, herb, and flower seedlings;
- greenhouses with removable panels that can be easily removed if necessary;
- greenhouses of non-standard shape;
- Winter greenhouses must have heating pipes connected to a central heating system;
- A summer greenhouse is a budget option for a cheap and simple seasonal structure at the dacha.
These examples of polycarbonate greenhouses can be easily built independently.
Video: "DIY Polycarbonate Greenhouse"
This video will show you how to build a polycarbonate greenhouse yourself.
Creating a project
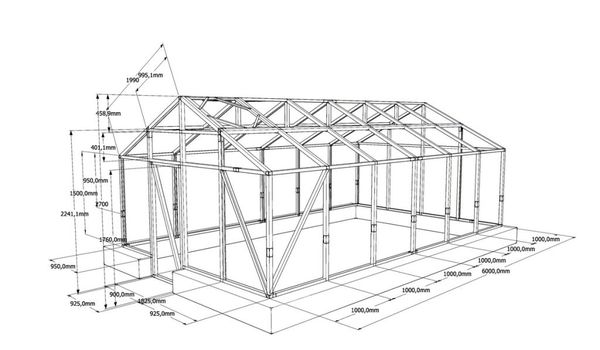
Before building a greenhouse or hothouse, decide on the installation location and dimensions. Once you've determined that, you can begin creating the design. Your plan should include the following points:
- the type and quantity of materials required for construction;
- detailed drawing of all parts and elements;
- diagram of the connection and fastening of the structural units;
- arrangement of interior space;
- detailed diagram of artificial lighting, heating, and power supply systems.
Take our advice: when calculating the dimensions of your future greenhouse, consider the size of standard polycarbonate sheets. This size will determine the size of the foundation and base.
Selecting and preparing a site
What should be considered when choosing a good location for polycarbonate greenhouses and hothouses:
- Cardinal Direction. The greenhouse location is chosen correctly if it is aligned with the cardinal directions. Seedlings will receive the maximum amount of sunlight if the structure faces east to west.
- The chosen location should be relative to buildings. It is important to avoid daytime shading from other objects.
- Terrain. Uneven surfaces and lowlands are unsuitable for construction. A slightly elevated, flat surface is ideal.
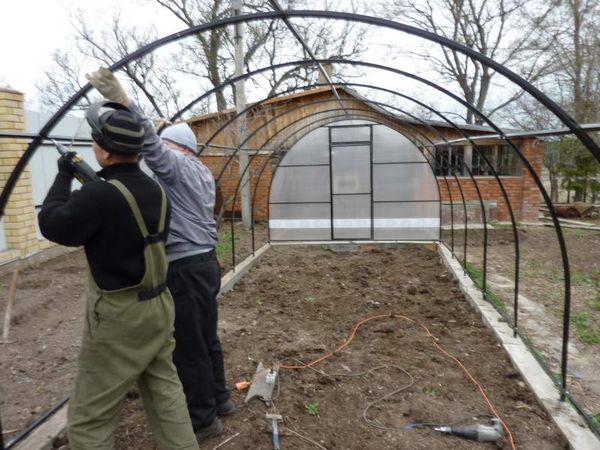
Creating a framework
After the foundation is erected, we move on to the crucial and crucial stage: installing the frame for the polycarbonate greenhouse. The following materials are used for its construction:
- Wooden beam. Building a wooden frame is not difficult, but joining the pieces together requires some knowledge and practice. You can also secure them with a metal bracket, ensuring a right angle.
- Metal pipes, metal profile. This homemade frame is quite strong. However, its installation is impossible without specialized tools for cutting and welding metal. The metal pipes can be assembled during the production process using couplings, but this structure can be assembled only after pre-threading.
- Plastic (polymer) pipes. They are durable, rust-resistant, and mold-resistant. Their disadvantages include poor impact resistance (brittleness) and insufficient frost resistance.
- Aluminum guides. Aluminum is a relatively lightweight yet durable material that's easy to saw by hand and screws into easily.
Material
- Wood is a natural, environmentally friendly material. When constructing the frame, the timber is treated with an outdoor preservative. The parts that come into contact with the soil are also treated. This will not only protect the wooden parts of the greenhouse but also prevent plant diseases.
- Metal (steel pipes or profiles) has increased rigidity compared to other materials. Square pipes are best for welding. However, before assembling such a heavy frame, a strong foundation is required.
- Galvanized profile. The material is simple and easy to install, and despite its lightweight construction, it is strong and reliable.
Assembly process
The frame assembly must be carried out in accordance with the drawing and calculations. Carefully plan the process steps in advance. Prepare the necessary tools. Assembling the frame elements will take several steps:
- We cut the profile for one element, according to the calculations performed.
- We assemble it using self-tapping screws for rigid fastening.
- Carefully measure the resulting structure and make sure that its dimensions correspond to the sample in the drawing.
- Once you've made sure everything is in order, feel free to start cutting the remaining parts and assembling them one by one.
- The final step is to assemble the entire structure.
We are creating a foundation
Let's ask ourselves: is a foundation really necessary when constructing a simple and lightweight greenhouse structure?
Let's not forget that the creation of a foundation for greenhouses is associated with its main and essential functions, namely:
- to give rigidity and integrity to the frame;
- protection of the interior space of the premises from the aggressive influence of the external environment.
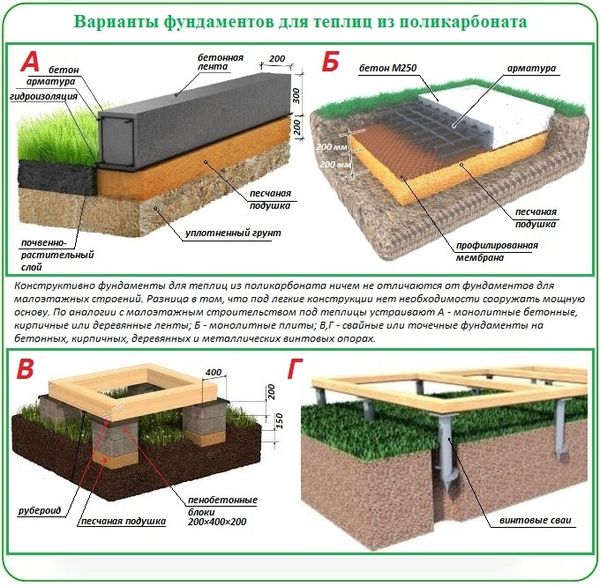
Types of foundation
Site preparation begins with clearing the area of vegetation and marking out the future foundation:
- Strip foundation. The most reliable, durable, and, of course, expensive. When the greenhouse is in operation year-round, the foundation should be set slightly below the frost line.
- Timber. Used for seasonal use. It is simpler to construct and significantly less expensive. Timber can serve as a foundation for greenhouses used for a limited period (a few years).
- Pile-and-grillage foundation. Similar to strip foundation. The difference is that the concrete strip is installed on a sand bed and reinforced with reinforced piles driven into the ground. Durable and high-quality, but does not provide frost protection.
- Point. The simplest and cheapest. The frame is supported by piles made of timber, brick, or other durable material.
- Foundation made of timber.
How to pawn
The simplest and cheapest option is a wooden foundation with a short service life.
Curbstone, aerated concrete, brick – remove the top layer of soil (200 mm), add a gravel bed, and pour concrete. Lay a layer of roofing felt before laying the bricks.
Monolithic reinforced concrete is an expensive but stable and durable option. For installation, a trench at least 400 mm deep must be dug and filled with gravel. Formwork is installed and concrete is poured.
Compared to industrial polycarbonate greenhouses, homemade ones have a number of advantages:
- cheaper than their industrial counterparts;
- can be adjusted to any size;
- simple and easy to use.
Polycarbonate coating
Polycarbonate is the most suitable material for greenhouse construction. It offers several advantages:
- perfectly transmits natural light, which is essential for the development and growth of plants;
- polycarbonate has a special coating that reliably protects seedlings from the ultraviolet spectrum of sunlight;
- high-quality, durable material, tested in practice;
- Carbonate sheets have increased thermal insulation;
- shock-resistant;
- long service life – about 10 years;
- withstands temperature fluctuations;
- resistance to weather loads (snow, wind, hail).
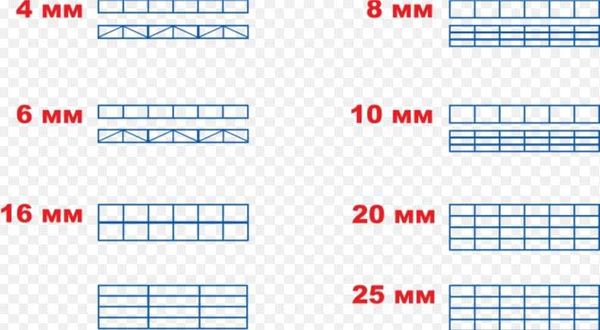
Types of polycarbonate
The industry produces three types of polycarbonate:
- monolithic;
- profiled;
- cellular.
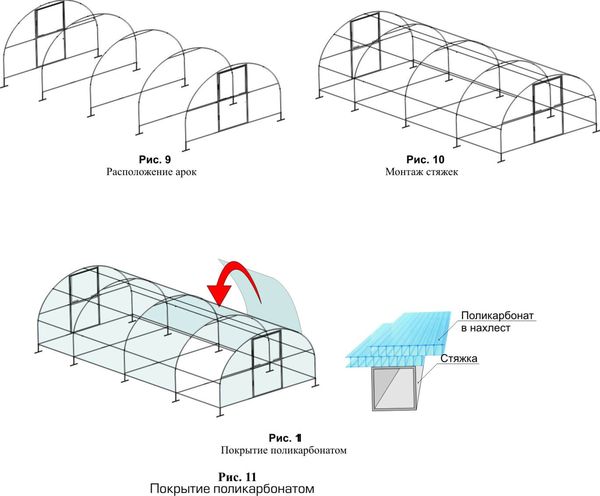
Installation instructions
The construction of a greenhouse, like any structure, includes several stages:
- Foundation construction. First, formwork is installed on a leveled surface using pre-treated planks. Reinforcement is added at the corners to ensure rigidity and stability.
- Install reinforcement bars around the entire perimeter to a depth of more than 50 cm and then reinforce them.
- We place pre-prepared and adjusted length plastic pipes onto the installed rods.
- We attach them to the wooden base with metal loops.
- Join several pipes together so that the length of the resulting pipe is equal to the length of the structure.
- Stretch the film.
- Secure the door and formugi.
A polycarbonate greenhouse should be built with your own hands in strict accordance with the installation instructions.