Selecting a Greenhouse Heating System and Installation Instructions
Content
Which system to choose?
Heating a greenhouse is beneficial if growth occurs year-round, or if the gardener begins planting in early spring. Furthermore, heating commercial greenhouses is essential for achieving high yields year-round.
The choice of heating method will depend on the materials used to construct the greenhouse, its size, and its location on the site. The first parameter is important because every material has a thermal conductivity coefficient. For example, plastic film has a higher thermal conductivity coefficient than polycarbonate, meaning a polyethylene greenhouse will require more intensive heating.
The choice of heating for a greenhouse in winter is influenced by the size of the room: larger areas require more extensive and carefully planned heating, which includes additional insulation of the structure.
Heating for a greenhouse can be chosen depending on the location of the building on the site, since a gardener does not always have the opportunity to install electricity, gas, or water systems.
In any case, the final choice of winter heating method depends on the individual preferences and expectations of each property owner. The material costs of installing insulation also cannot be ruled out. A factory-made system is a more expensive option, while a DIY heater is less expensive.
The most popular types of thermal equipment are:
- infrared;
- water;
- wood-burning;
- air.
Less common in homes are steam heating and heating using alternative energy sources. Mixed-mode heating devices are also used.
Video: Installing a Soil Heating System in a Greenhouse
This video will show you how to properly install the Heatline soil heating system in a greenhouse.
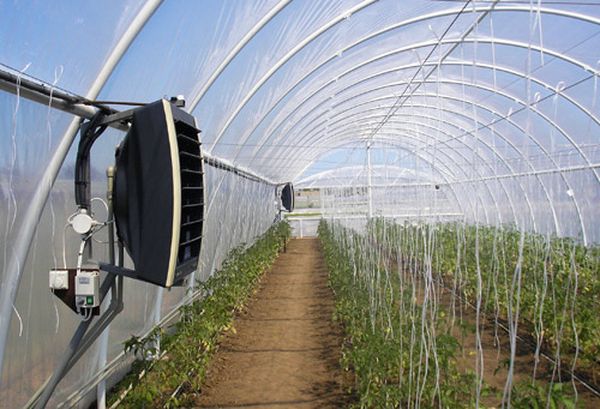
Infrared heating
To heat a greenhouse, you can use infrared heating, either with infrared lamps or heaters. Both systems consist of plates with heating elements suspended from the ceiling above the plants.
Infrared systems work by heating the vegetables and soil without heating the air, allowing for targeted heating. Furthermore, soil itself has a low thermal conductivity, allowing heat to be retained within the soil itself, warming plants from root to tip.
However, infrared heaters have a controversial reputation. On the one hand, they are an environmentally friendly way to heat a room, as they don't release combustion waste into the air. On the other hand, they require electricity to operate, which is expensive.
You can solve the greenhouse heating problem by installing a solar heat accumulator, better known as a solar panel. You can install as many of these panels in the roof of your house or greenhouse as needed to heat the entire complex.
How to install
Heating lamps and heaters are difficult to manufacture, but they can be installed by hand. For a standard greenhouse 6 meters long and 3 meters wide, 3-5 lamps are typically installed (depending on the size of the equipment). For installation, you'll need electrical cable, insulation materials, fasteners, a shut-off system, and, if necessary, a temperature sensor that will automatically regulate the equipment.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantage of this design is its high efficiency and the ability to heat both small greenhouses and large industrial spaces. However, the equipment remains expensive both in terms of installation and operation (high electricity costs). Furthermore, installing the lamps requires a preliminary design that includes the number of electrical appliances required for the building volume; a ceiling that is too low can lead to soil overheating.
Air heating
Both large and small spaces can be heated using air heating, achieved by installing convectors of any type:
- Electric. They operate using electricity and require the installation of an additional electrical cable connected to a high-voltage line;
- Solid fuel. These are based on the Buleryan type of stoves, which operate by burning solid fuel and then allowing the resulting gases to burn out. This is a quick and economical way to heat a greenhouse;
- Gas and diesel convectors differ from other convectors in the fuel type they use.
In any case, all equipment operates on the principle of distributing warm air throughout the entire perimeter of the room. On average, the temperature in the greenhouse can be raised from +5 to +25°C in just one hour.
How to install
Convector installation depends on its configuration and technical specifications. Many factory-made designs require insulation of the installation site. Furthermore, to construct the system, it is necessary to install pipes (made of metal or perforated polyethylene) from the convector to distribute the air masses.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantage of this method is its high efficiency and relative ease of maintenance (especially for convectors using purchased fuel). However, the entire structure can take up a significant amount of space in the greenhouse (this does not apply to cannons and electric convectors installed in polycarbonate greenhouses near the vents). Warm air significantly reduces humidity in the room, requiring the installation of an automated vegetable spraying system.
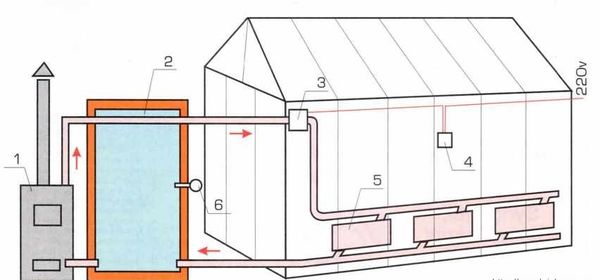
Water heating
Hydronic heating is well known to most city apartment dwellers. In this system, water is heated by a boiler, passes through pipes and radiators, and returns to the boiler—a closed-loop system. Typically, radiator and pipe installation diagrams recommend installing the elements around the entire perimeter of the greenhouse. Occasionally, the system is supplemented with underground pipes that heat the soil.
How to install
Even a novice builder can install piping correctly using fasteners, metal-plastic pipes, and threaded fittings. Choosing a boiler to heat the water is a much more challenging process. It depends on your needs, budget, and timeframe.
The most commonly recommended boilers for installation are condensing gas boilers, electric boilers, liquid fuel boilers, and solid fuel boilers, which can be either factory-made or hand-made.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantage of this type of heating system is its relative ease of installation and the low cost of its handmade construction (including the boiler). However, choosing a boiler can be challenging and require significant resources. It is recommended to use a hydronic system continuously, as freezing water in winter and then turning it on again can lead to burst pipes.
Wood heating
Both hydronic and forced-air heating systems require specialized equipment—convectors and boilers—that operate on one of several fuel types (gas, liquid, or solid fuel). Firewood, an inexpensive and readily available fuel, is often used as a solid fuel. Furthermore, wood-burning equipment can also be fueled by organic waste—paper, husks, sawdust, old boxes, etc. Stoves are sometimes used for wood heating, effectively replacing boilers.
How to install
The installation method will depend on the overall heating system, which you can read about above. If you decide to install a stove, you'll need the help of a professional stove builder.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantage of wood-burning equipment is its low cost and the ability to substitute wood with anything. This is especially true for units made from readily available materials, such as potbelly stoves, bubafoni stoves, and ovens. However, open-fire designs require additional safety precautions—the damper must be closed to prevent a fire hazard and the spread of gases throughout the room. Wood-burning equipment is virtually impossible to automate—you'll have to manually maintain the correct temperature and add fuel to the boiler at the right time.