How to choose equipment and organize lighting for greenhouses
Content
Requirements for the quantity and quality of light
Plants are static elements of living nature. This characteristic has given them the ability to adapt to environmental conditions, extracting maximum resources from available sources. This is precisely what makes garden crops sensitive to light. They lack the flexibility and adaptability of humans, as evidenced by their close dependence on ultraviolet radiation, the source of which has been the sun since the dawn of life on the planet.
Current advances in agricultural science make it possible to equip greenhouses with phytolamps that create conditions as close to natural as possible, thanks to a wide range of light wavelengths. Their wavelength and color influence various stages of plant life:
- blue-violet parts of the spectrum are beneficial for general strengthening and also stimulate photosynthesis;
- yellow and green have the opposite effect;
- The red-orange color scheme is good for flowering and crop development, but only in moderate light conditions;
- Monochromatic parts of the spectrum are good for growing flowers;
- ultraviolet – to acquire resistance to cold and the accumulation of useful microelements.
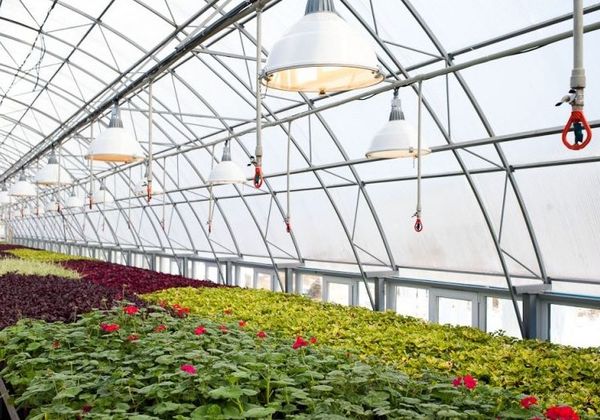
Greenhouse conditions are created to accelerate the growth of crops, as well as to control their development, regardless of the current season and weather. In some cases, adequate lighting for greenhouses can be challenging due to the structure's location. This requires the use of a lamp or reflective tape to provide the necessary supplemental lighting. However, moderation is key – plants need rest, and 24-hour lighting will only exhaust them.
Video: "Greenhouse Lighting"
In this video, an expert will explain how to properly apply lighting to greenhouses.
Types of lighting modes
Like all living things, different crop species and varieties have their own characteristics and growth cycles, which dictate the amount and intensity of light needed. However, there are two basic regimens, based on daylight hours:
- Winter and spring periods.
- Summer and autumn.
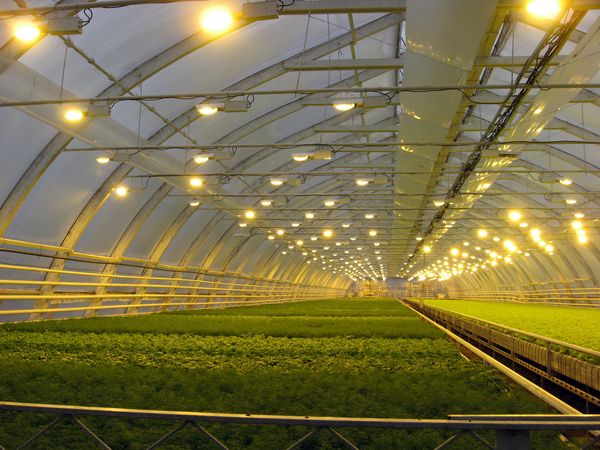
Since greenhouse-grown plants require 8 to 12 hours of continuous light, supplemental lighting is always necessary in winter. Furthermore, the various primary lighting modes and their application may depend on the greenhouse's design. For example, lighting for glass winter greenhouses will differ from that for polycarbonate structures, while industrial structures are often equipped with sodium phytolamps.
Choosing a lamp
Lighting fixtures equipped with bulbs operating under different operating principles each have their own unique purposes. Some have a broad range of effects, while others are more specific. However, whether they benefit or harm crops depends on the application.
Incandescent lamps
They are characterized by a warm light spectrum and the ability to warm the surrounding space. If used for a long time and placed improperly, they can adversely affect not only plants but also the soil. However, grow light manufacturers have improved incandescent bulbs, reducing the harmful red light with a blue filter. They are best suited for illuminating greenery during forcing.
Fluorescent
Known as greenhouse fluorescent lamps, these models come in a variety of lighting options:
- Cold – universal. Such lamps can be used in the background anywhere;
- warm – ideal for growing flowers;
- combined – combines the properties of the previous positions;
- special – aimed at achieving specific goals.
Fluorescent lighting does not affect heat and humidity levels, but it is dependent on the electrical network and has a small illumination radius.
Gas discharge
They are characterized by good light output, a beneficial effect on greenhouse greenery, and a high cost. Due to their power and efficiency, they are often used by industrial facilities. High-pressure lamps fall into this category.
Energy saving
Small, energy-efficient, and designed to fit standard socket threads, these greenhouse lights are typically used in conjunction with reflectors. Some fluorescent lights are also energy-saving.
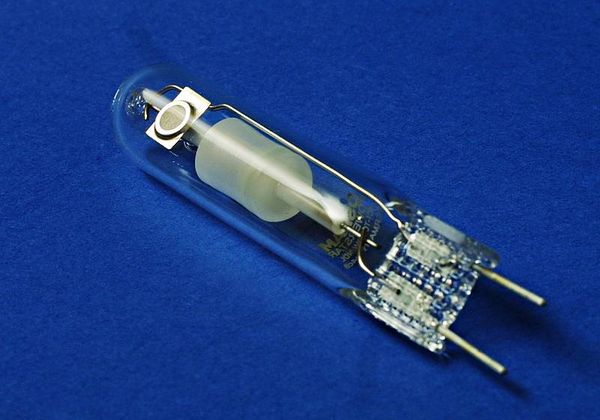
Metal halide
Specialized equipment that mimics the light typical of spring. Blue light is beneficial for plants during the early growing season, stimulating growth. These lamps are sensitive to placement, short-lived, and require a significant investment.
High-pressure mercury lamps
This invention specializes in inhibiting plant growth. This seemingly counterintuitive purpose proves useful when sprouted crops begin to stretch. This effect is achieved through a shock dose of ultraviolet light.
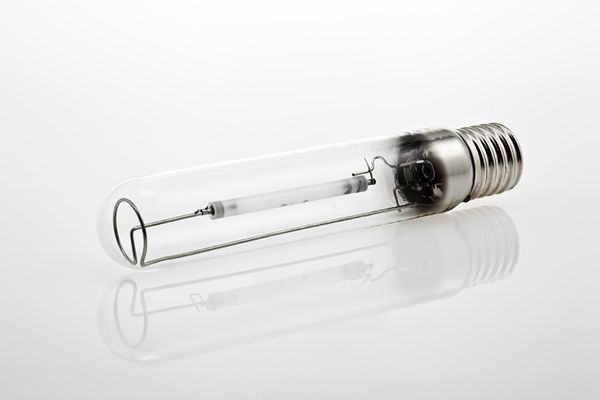
High-pressure sodium lamps
Because they emit red light, sodium lamps are ideal for greenhouses growing heat-loving crops that are untypical for the gardener's climate. They are also useful during flowering and fruit set. However, sodium phytolamps are inappropriate for seedlings and may attract pests. Difficulty in manual installation makes the equipment suitable only for industrial purposes.
LED lighting
A technique gaining widespread popularity is lighting plantings with LED elements. This method has already been tested and proven effective due to:
- flexibility in forming the required spectrum;
- environmental friendliness;
- economy;
- at reasonable prices;
- ease of installation.
In addition, LED greenhouse lamps do not have the side effect of heating, which means they can be placed almost right next to the plants.
How to electrify a greenhouse
Before wiring the greenhouse, it's necessary to calculate the optimal number of lamps. This can be done using measuring instruments, a calculator, and the formula F = E x S / Ki, where:
- F is the light flux required for the effective development of crops. Calculated in lumens;
- S – illuminated area of the room;
- Ki is a coefficient that determines the luminous flux utilization. The Ki varies for different lamps. If the equipment has an external reflector, the Ki coefficient will be 0.4; if it's built-in, it'll be 0.8.
Based on the descriptions of various lamps, LED lights are ideal for greenhouses due to their versatility and ease of installation. However, before introducing seedlings to the beneficial effects of LEDs, the greenhouse must be connected to the main electrical grid using cables. This can be done in two ways:
- Underground. A trench about a meter deep is dug. Its route should avoid any potential drainage systems. The cable leading from the home's electrical panel must be insulated with corrugated conduit.
- Aerial method. The main recommendation for its use is a rational approach to pulling wires so that they do not intersect with tree branches.
The next steps are the same regardless of the chosen method. They involve wiring and then connecting components such as switches and outlets. If the greenhouse owner lacks specialized skills, it is strongly recommended to hire an electrician.