What type of polycarbonate is best for covering a greenhouse?
Content
Description and properties of the material
Many gardeners, when considering building a greenhouse, face the challenge of choosing a covering material. While previously they had to choose between film and glass, today polycarbonate is the optimal choice. Polycarbonate greenhouse plastic offers many positive characteristics:
- durability, strength and resistance of the carbonate film to mechanical impacts;
- excellent light transmittance;
- low thermal conductivity of polycarbonate;
- safety during operation, no difficulties during installation of the coating;
- resistance to weather and climate conditions (heavy rainfall, increase or decrease in air temperature, etc.);
- light weight compared to other commonly used covering materials;
- wide selection (brand, thickness, color, density, size, structure, etc.).
According to reviews from gardeners who have worked with polycarbonate, this material has a number of disadvantages, which it is recommended to familiarize yourself with before building a greenhouse. For example, polycarbonate has low resistance to abrasives and alkaline and highly acidic household chemicals. Some manufacturers deliberately inflate the cost of carbon and polycarbonate films.
After weighing the pros and cons and carefully studying comparison tables describing the characteristics of popular covering materials, most gardeners prefer to use durable, high-quality polycarbonate.
Video: "Polycarbonate for Greenhouses"
In this video, an expert will discuss the advantages of polycarbonate greenhouse coverings.
Main types
The main purpose of a greenhouse is to provide a comfortable microclimate for growing various crops. Before choosing the material for the greenhouse structure and its covering, it's important to determine the structure's intended purpose—whether it will be used year-round or only during the growing season.
Polycarbonate comes in cellular and solid varieties. Let's explore the differences between solid and cellular polycarbonate for greenhouses.
Cellular
Cellular polycarbonate consists of two or more sheets joined by a large number of ribs. Now the origin of this type of polymer plastic's name becomes clear. Cellular polycarbonate is characterized by flexibility, lightness, and good thermal transfer.
The cellular structure diffuses light, preventing direct sunlight from hitting the plants growing in the greenhouse. Covering a greenhouse frame with cellular polycarbonate requires little experience or skill in working with this material.
Monolithic
Compared to cellular plastic, monolithic polymer plastic has no hollow cells, weighs more, and looks significantly more expensive. Despite its aesthetic appeal, monolithic material does not maintain the temperature and humidity conditions necessary for growing crops. It may be recommended for greenhouse structures that do not require additional framing.
What to consider when choosing
Today, gardeners have a huge selection of polymer plastics to choose from. What should you consider when choosing polycarbonate, you ask? Experienced gardeners with years of greenhouse cultivation say it's important to consider UV protection, density, color, and thickness of the polycarbonate used in greenhouses.
Thickness and density
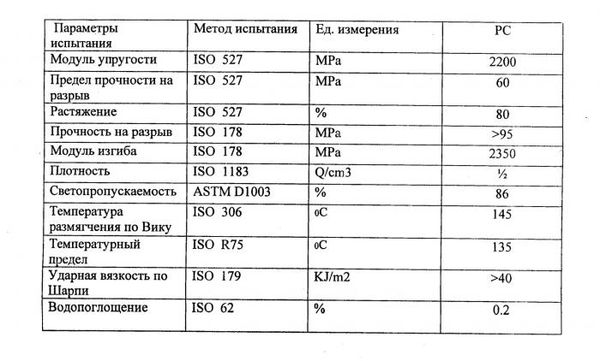
The main criteria responsible for the functionality and strength of polycarbonate are density and thickness.
Polycarbonate density can vary depending on the sheet thickness and the number of internal cavities. For example, the optimal polycarbonate density for greenhouses is 4 mm. However, this density is not suitable for collapsible structures or for regions with harsh weather conditions. It's better to choose a more durable material with a thickness of 6, 8, or even 10 mm.
Color
Polymer plastic manufacturers offer transparent, opaque, and colored sheets. The choice of coating color depends on the regional climate and the crops grown in the greenhouse. For example, brown, green, and red sheets are best for berries and mushrooms. In warmer climates, yellow polycarbonate is most often used.
Some gardeners install removable colored blocks on the roof of the greenhouse, which can be replaced if necessary.
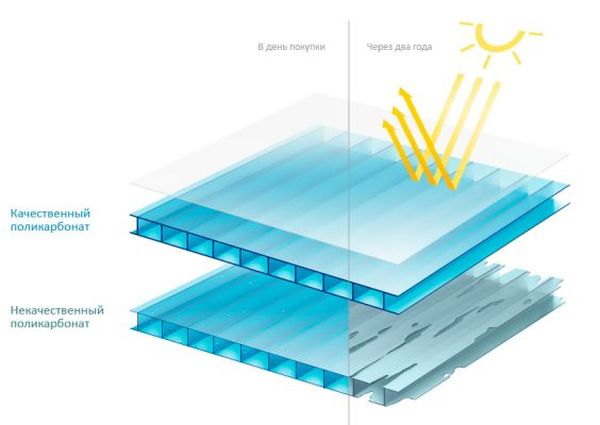
Availability of protection from UV radiation
According to manufacturers, UV film protects polycarbonate from deterioration and significantly extends its service life. When exposed directly to sunlight, after a certain period of time, microcracks begin to appear in the greenhouse covering. These cracks rapidly grow and intertwine, leading to sagging and deterioration of the polymer plastic.
UV protection is often located on the inner side of the sheet. However, some polycarbonate sheets have UV protection built into the plastic sheet itself. The recommended UV protection percentage for this layer should be between 30 and 46 units.
How to extend the service life
Despite good wear resistance and excellent technical characteristics, polycarbonate, like any other material, loses its properties over time.
Please note that the lifespan of the covering material depends on how well it is selected. Choose reputable manufacturers who stand behind the quality of their products, and carefully review the technical specifications and properties of the material you are purchasing.
Polymer plastic should be washed periodically and cleaned of accumulated dust and dirt. It is not recommended to use household chemicals when washing. Use clean water and a soft cloth.
Any mechanical damage (scratches, cracks, etc.) leads to heat loss. To maintain the thermal conductivity of the polycarbonate and prevent damage to the UV protection, prune the branches of trees and shrubs growing near the greenhouse promptly.
During snowfall, remember to clear snow from the greenhouse roof. Snowdrifts can break the roof sheets and damage the integrity of the greenhouse structure.