The main stages of planning and arranging a greenhouse
Content
Preparation and planning
Greenhouses are created for growing a variety of heat-loving crops, both for consumer purposes (fruits, vegetables, herbs) and for decorative purposes (flowers).
Before preparing for indoor installation, you need to determine what crops will be used in the space and how they will be maintained (in pots, boxes, or beds). Setting up a greenhouse indoors requires addressing several important issues:
- Creating a water supply system (irrigation). Installation of the plant water supply system must begin early, as some system components may be located underground. It's important to consider the number of water intake points, which is directly proportional to the greenhouse area. Water pressure should be approximately equal throughout the system to ensure efficient and economical irrigation. Drip irrigation is the most efficient and beneficial method for plants.
- Install a proper ventilation system. Ventilation and fresh air are essential for optimal crop growth. If polycarbonate is used for the greenhouse covering, creating opening sections is easy. The installation locations should be planned before beginning work.
- Provide heating for the greenhouse during the winter. The following methods and devices are used for this purpose:
- small stove (garden stove, potbelly stove);
- heat gun;
- infrared heater;
- hot water heating of a greenhouse;
- heating with the creation of a warm floor (this system extends over the entire area; special thermal insulation is required below the heating circuit so that the heat spreads upward).
- The greenhouse must have an artificial lighting system inside. For this purpose, it is better to use fluorescent, LED or gas-discharge lamps, which have the entire spectrum necessary for seedling growth.
Video: "Interior Design of a Greenhouse"
This video will show you how to properly set up a greenhouse inside.
Insulation of the premises
The main thing in insulation is high-quality execution of work and the choice of appropriate materials.
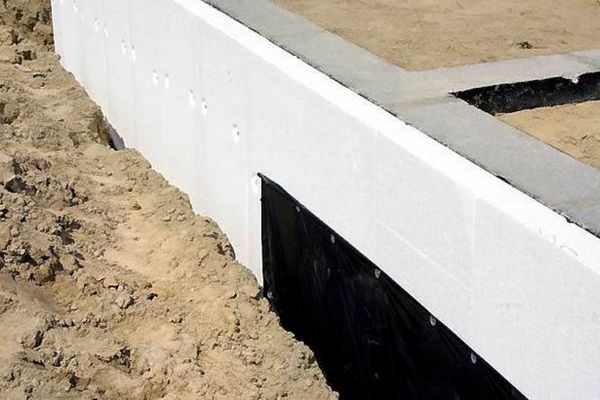
Insulating the foundation is key to further heat retention. Its base should be below the frost line, and adobe blocks, which are non-conductive, are the preferred material. They are covered with roofing felt. The interior is insulated with foam plastic and sand.
Heat loss not only has a financial impact but also poses a threat to plant life. Using polycarbonate, a special plastic construction, minimizes heat loss. However, when assembling the sheets, the use of rubber gaskets is essential; otherwise, all the benefits of this material will be negated.
More heat will be retained in the soil if they are raised by 400–500 mm.
Once all insulation issues have been resolved, it's time to figure out how to furnish the inside of the greenhouse.
Space design
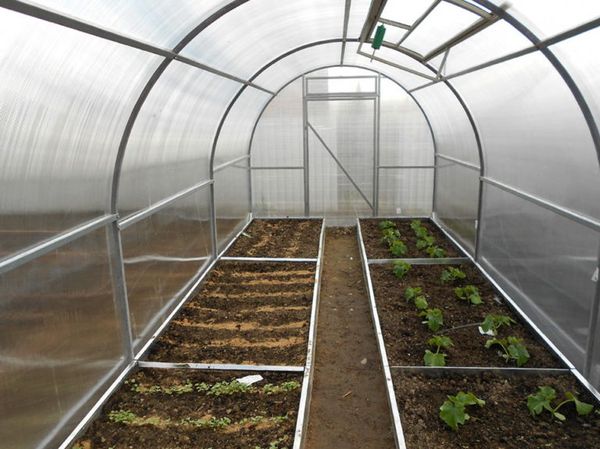
The key to setting up a greenhouse interior is creating the beds. To do this, certain rules must be followed:
- In a small greenhouse, to make efficient use of space, it is better to plan the beds along the edges, and the central part is reserved for a path;
- to ensure integrity and maintain the shape of the beds, they are equipped with a fence;
- the soil in greenhouses should be moderately moist, this should be monitored especially carefully during the winter period;
- Due to the high humidity in the room, all materials used for fencing, paths, boxes, shelves, and partitions must withstand these conditions. Materials in contact with the ground are treated with special anti-rot agents.
For earthworks
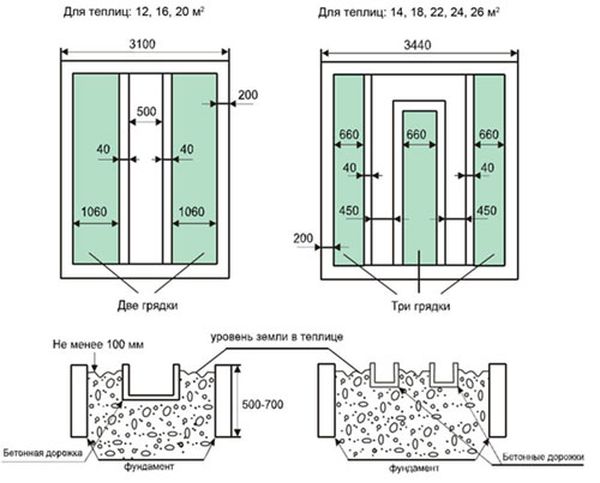
Setting up a greenhouse inside requires specific conditions for excavation work. The main goal when allocating space is to use the available space efficiently. The number of beds directly depends on the size of the greenhouse. For a small greenhouse, they are arranged along the edges or in a "U" shape with a path in the middle. For larger greenhouses, three beds with paths between them are used.
The middle bed can be double-wide, as it can be accessed from both sides.
Garden bed landscaping begins with laying polyethylene on the bottom. This will help retain soil moisture and serve as thermal insulation. A 20 cm layer of drainage is poured directly onto the film, followed by prepared soil appropriate for the specific plant species. Due to the high humidity, paths should be made of appropriate materials: gravel, paving slabs, brick, etc. Their width should be calculated to allow for comfortable cultivation of the beds and the ability to carry equipment and various loads without damaging the plants. Further arrangement of the greenhouse interior involves installing shelving and partitions.
Use of shelving and partitions
Why are partitions needed? They are designed to isolate different, incompatible crops, as well as plants with different temperature and humidity requirements. Partitions can be equipped with doorways and vents for ventilation. Polycarbonate is an excellent material for their manufacture. A less expensive option is polyethylene stretched over a frame.
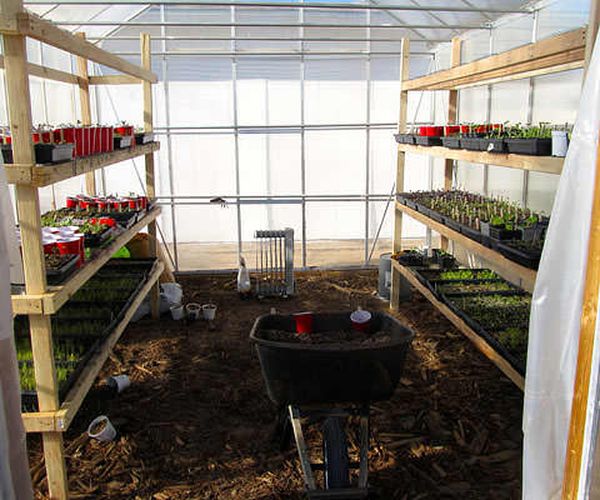
Greenhouse shelving is an alternative to raised beds. It's used for growing low-growing plants (strawberries, flowers, some vegetables, and seedlings). Plant boxes are placed directly on the shelving. The lower tier is reserved for crops that tolerate some shade, while the upper tiers are for sun-loving plants.
When installing shelving, a clever space-saving trick can be found in placing it above the garden beds. Shelving can be made from timber or metal profiles. This design is simple, so you can build it yourself.
Utility room
If the greenhouse is large enough, it's a good idea to include a utility room with shelving. This way, tools and everything needed for work will be close at hand. This room can also be used to house a heating boiler.
We'll be glad if our advice on how to set up a greenhouse is useful to you.