Secrets to Successfully Growing the Very Early Julian Grape Variety
Content
History of variety selection
The Yulian grape is the brainchild of Rostov-based amateur breeder Vasily Kapelyushin, who has conducted over 75 successful experiments in developing new varieties and hybrids of fruit and berry crops. Yulian is the result of cross-pollination between the Kesha and Rizamat varieties.

Varietal characteristics and description of the Julian grape
Presented at the Golden Bunch 2001 competition, the Julian grape was awarded top prizes in the categories of Best Private Selection and Best Table Grape.
Appearance of the bush
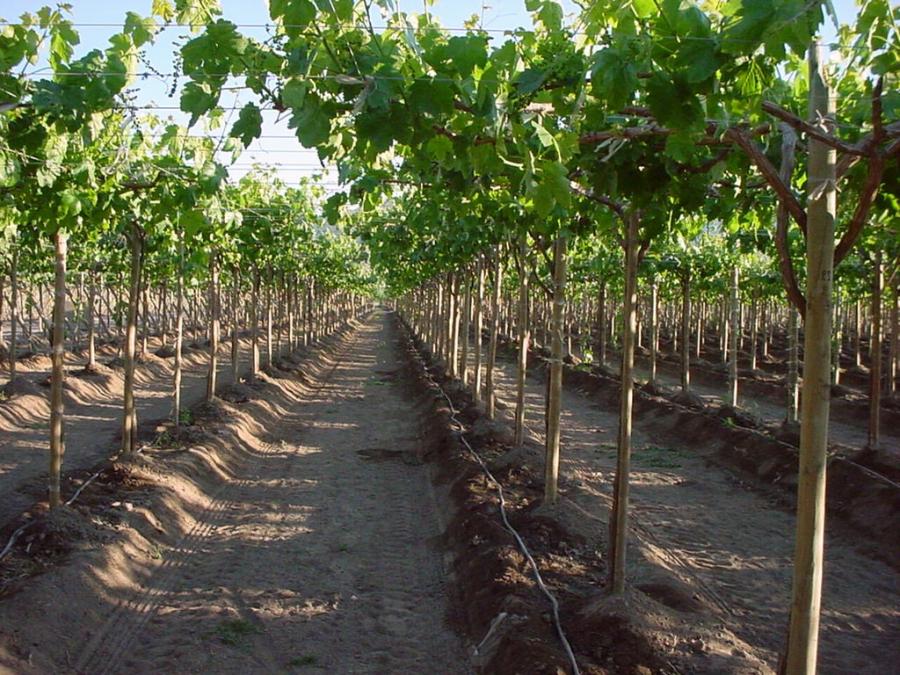
This medium-sized bush is prone to vigorous growth, allowing shoots to mature along their entire length, which is especially important for northern regions. The shoots are spreading and vigorous. The root system, accordingly, is characterized by abundant branching and rapid growth.
The bark of mature vines is a beautiful rich brown, while young shoots are light green. The leaves are rounded-heart-shaped and a pleasant olive-green color.
Description of bunches and fruits
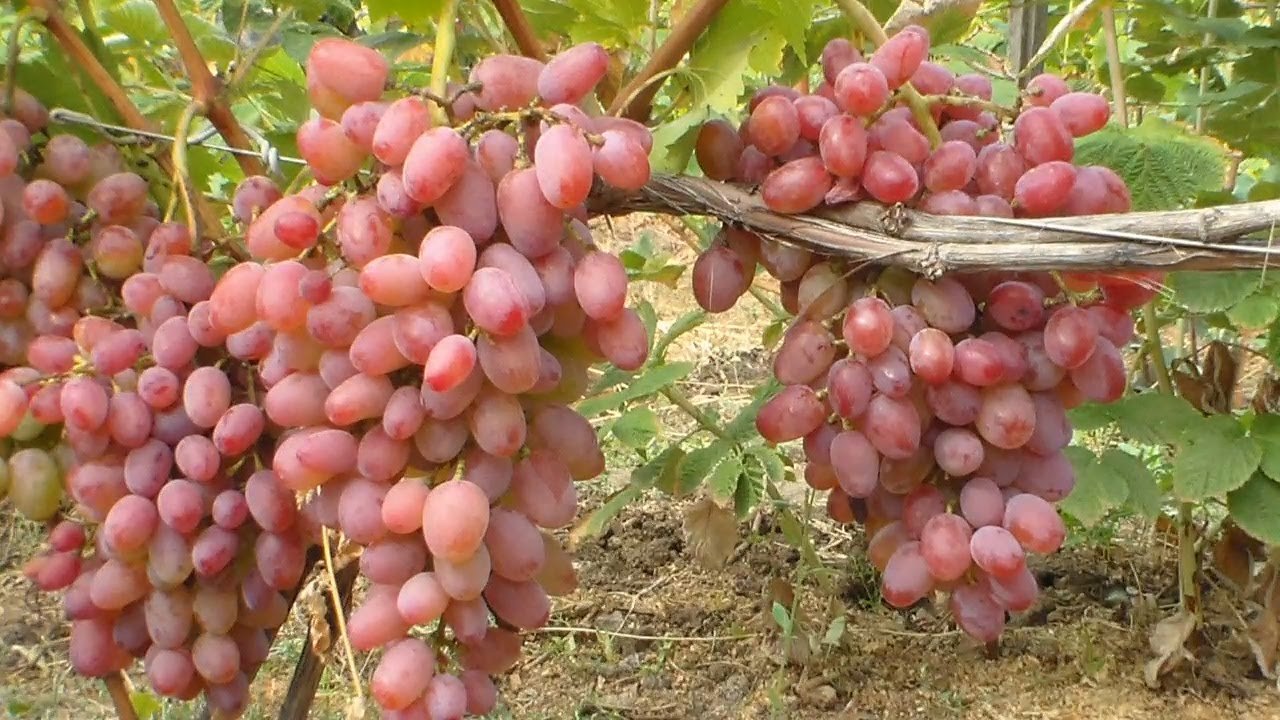
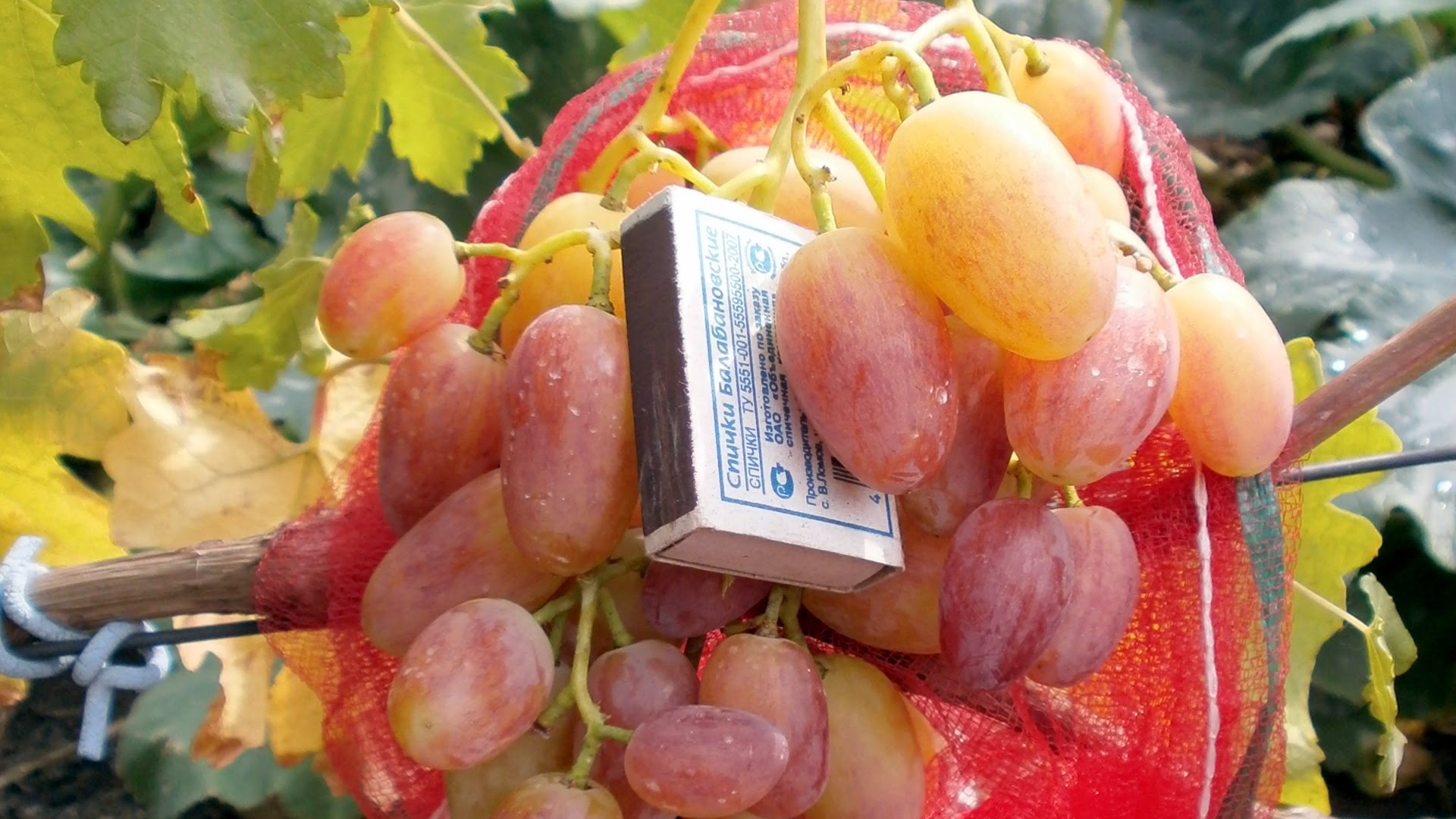
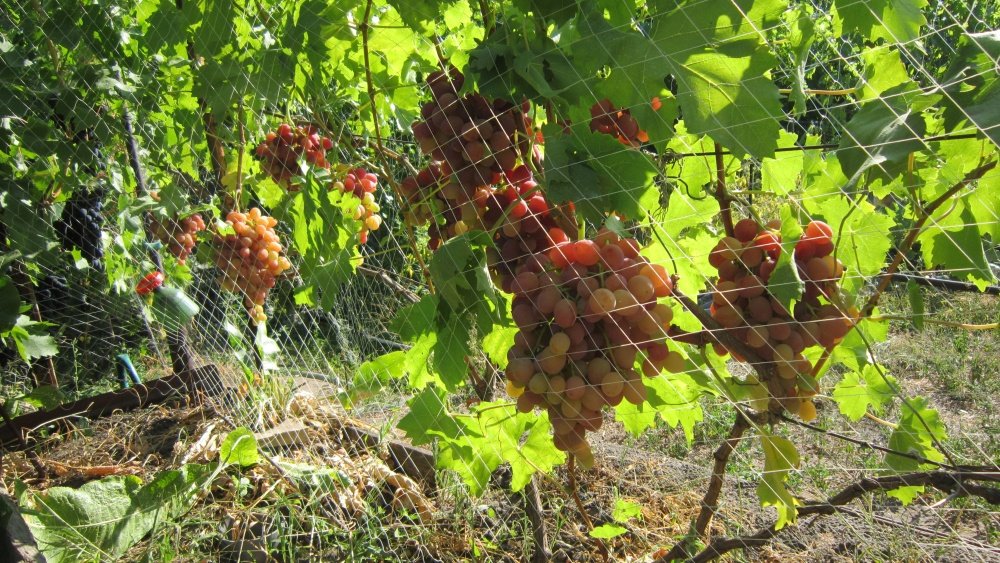
The clusters are cylindrical-conical in shape. Because the berries, formed on long stalks, are loosely packed together, the cluster structure is loose. Traditionally, cluster weight ranges from 700 g to 1 kg. Under favorable weather conditions and proper care, specimens weighing 1.5–2 kg have been observed.
The berries are characterized by a nipple-shaped, pointed shape. They weigh 15–20 g. The skin color ranges from light pink to pinkish-purple, which is considered the standard for the parent variety, Rizamat. It's worth noting that the thin skin is practically imperceptible when eaten. The flesh is dense, firm, and has a slight crunch. The fruits of the Julian variety are distinguished by a sweet taste with a strawberry aftertaste. They also have a subtle muscat aroma.

Productivity and fruiting
Yulian is considered an early-ripening variety. It takes 95–110 days from flowering until the berries reach harvestable maturity. The harvest period and duration depend on the climate zone. In the south, the first harvest occurs in mid-July. In the central and northern regions, harvesting occurs in August.
The yield depends on the chosen pruning method. For example, if up to 45 buds are left on a bush, the average yield will be 30–35 kg.
Application of fruits
Thanks to its amazing flavor, Julian grapes are eaten fresh. The fruit can also be used to make juices, compotes, and jams.
The crop is distinguished by its high transportability and long shelf life. For this reason, Julian is often grown on an industrial scale for export.
Drought resistance, frost resistance
Despite good drought tolerance, soil moisture deficiency can negatively impact fruit production. Dreaming of a bountiful harvest? Monitor soil moisture levels.
As noted in the variety description, Yulian's winter hardiness ranges from -23 to -26°C. The plant is suitable for growing in the south. Grapevines grown in the central and northern zones are covered for the winter.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
To form a subjective opinion about the Julian grape variety, familiarization with its disadvantages and advantages will help.
- early ripening;
- consistently active fruiting;
- good yield;
- interesting taste and universal application;
- amazing product qualities;
- long-term storage;
- high transportability;
- excellent winter hardiness;
- resistance to cracking.
- demanding of the growing site;
- decreased crop yields in the absence of heat and active sun.
Video "Description of the Julian grape"
This video will introduce you to the main varietal characteristics of the crop.
Rules for planting and growing Julian grapes
Julian grapes are considered an easy-to-care-for fruit and berry crop. However, following a few agricultural practices will help improve the plant's viability.
Recommended timeframes
This variety is suitable for spring and fall planting in open ground. The first option is preferable for regions with early and cold winters. The second option, fall planting, is often used in southern regions.
Planting tips
A sunny, but sheltered from wind and drafts, area of the garden is ideal for cultivating this variety. It's best to plant the seedling on a south or southwest-facing surface.
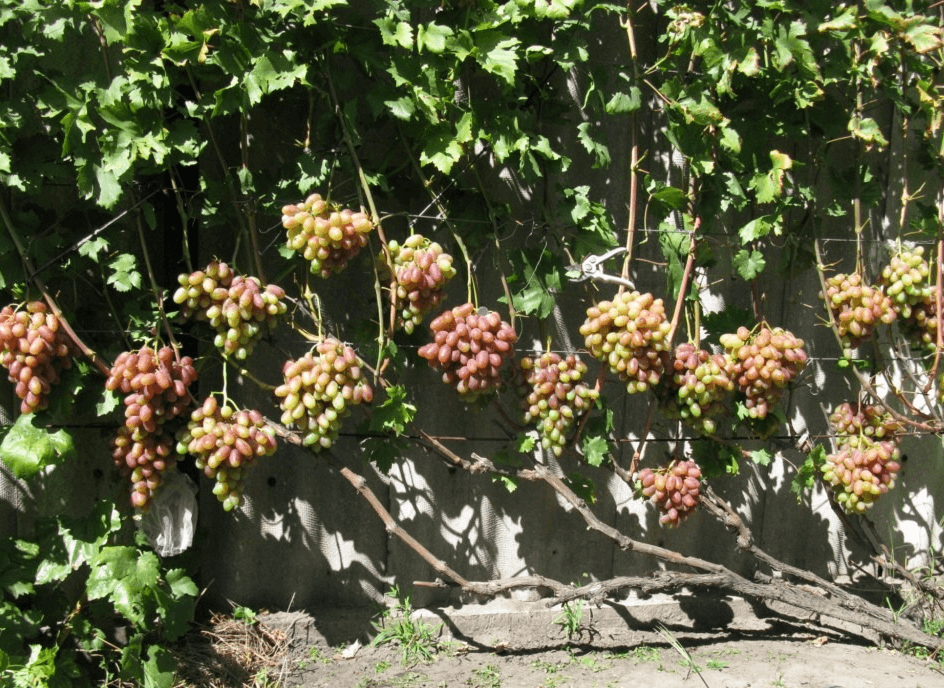
The soil should be light, nutritious, and slightly acidic. Liming can help reduce acidity. For example, 200 g of lime per 1 m² of soil is needed.
When selecting planting material, inspect the plant for bark damage and signs of rot. A seedling suitable for planting should have at least three large root shoots, several leaves, and buds. The cut end of the root shoot should be white, and the cut end of the trunk should be light green.
Planting holes for grapes are prepared 10-14 days in advance, with a distance of 2.5-3 meters between them. The bottom is lined with expanded clay and broken brick. For better rooting, the seedlings are planted in soil mixed with humus.
Watering regime and fertilizing rules
Moisture-replenishing irrigation is carried out twice per season: before flowering and after harvest. During the fruiting period, grape vines are watered every 3-4 days. The amount of water is determined by weather conditions.
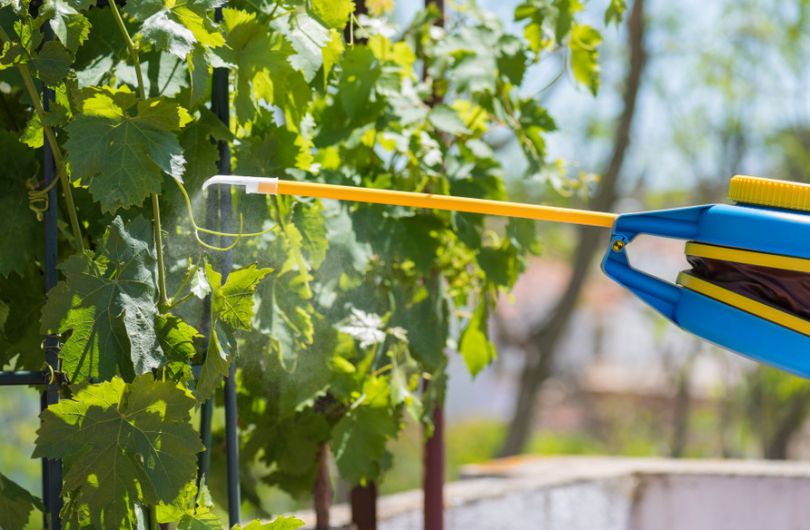
To increase fruit set, the plant is fed with potassium-phosphorus mixtures. Foliar feeding is done by spraying the vines with a solution of Plantafol.
Every spring, rotted compost is added under the grape bush. The nutrient layer should be at least 4–5 cm deep.
The need for pruning
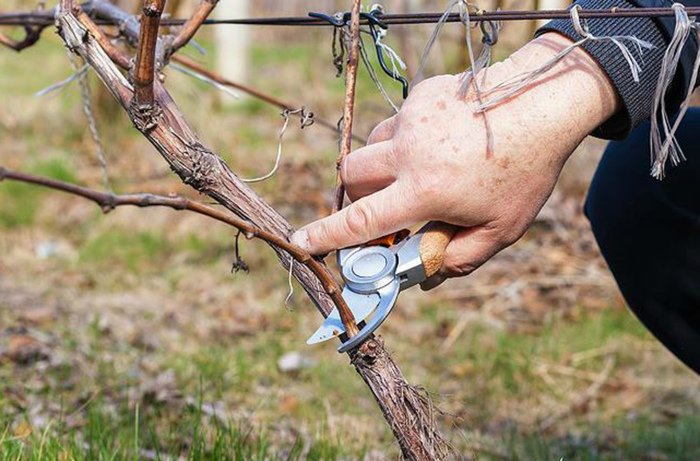
One of the essential care procedures for the Julian grape is vine pruning. Seven to ten buds are left on the current year's shoots. This pruning is best done in early spring before active sap flow begins.
During the growing season, branches that are dry, damaged by weather, or injured by insects should be removed.
- Drip irrigation system for vineyards
- Foliar feeding
- Pruning grape vines
Preparing crops for winter
To prevent the vines from freezing, the plant needs to be insulated. Burlap, agrofibre, white polypropylene bags, pine branches, spruce branches, or dry fallen leaves are used as covering materials. Vineyards grown in the south are not covered for the winter.
Typical diseases and pests
The Yulian variety is resistant to most fungal and bacterial infections, but unfortunately, it has weak resistance to Alternaria. To protect the plant, use a 2% Bordeaux mixture, as well as Topaz, Hom, and Kurzat.
The main pests of this variety are wasps and birds. For this reason, experienced gardeners recommend using netting and special bags for the bunches.

Reviews from gardeners
"I've been growing Julian grapes for many years. I'd like to point out that they're one of the most low-maintenance fruit and berry crops."
"Our region can grow almost any grape variety, but I prefer Julian. Its main advantages include early fruiting and abundant yields."
The Julian grape is highly sought after by professional winegrowers and amateur gardeners. It is prized for its marketable qualities and amazing fruit flavor, abundant fruiting, and good survival rate.



