Rules for planting and growing early grapes of the Augustin variety
Content
- 1 History of variety selection
- 2 Description and characteristics of the Augustine grape
- 3 Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- 4 Video: "A Detailed Description of the Augustine Grape"
- 5 Rules for planting and caring for grapes
- 6 Diseases and pests, methods of control and prevention
- 7 Reviews from winegrowers
History of variety selection
The Augustin grape, a popular choice among gardeners, was developed by crossing the Villard Blanc and Pleven varieties. From its parent grapes, the new fruit and berry variety inherited its resistance to extreme weather conditions and high immunity to most bacterial and fungal diseases. The breeding work was carried out on horticultural farms located in warm and sunny Bulgaria.

There are also other names for the variety, the most common of which are Phenomenon, Pleven Stable and V 25/20.
Description and characteristics of the Augustine grape
Adapted to the warm and mild southern climate, Augustin attracted the attention of winegrowers from across Russia. Today, this variety is grown not only in the south, but also in the central and northern regions.
Description of the vine and bunches
Augustine tends to grow vigorously. This vigorous shrub is widely used in landscape design to decorate entrance areas, garden arbors, arches, and columns.
The sturdy yet highly flexible stems have a beautiful, "freckled" reddish-brown bark. Young and mature shoots are resistant to wind and other weather conditions. The leaves are dark green and rounded, with three or five lobes. The edges of the leaf blades are jagged.
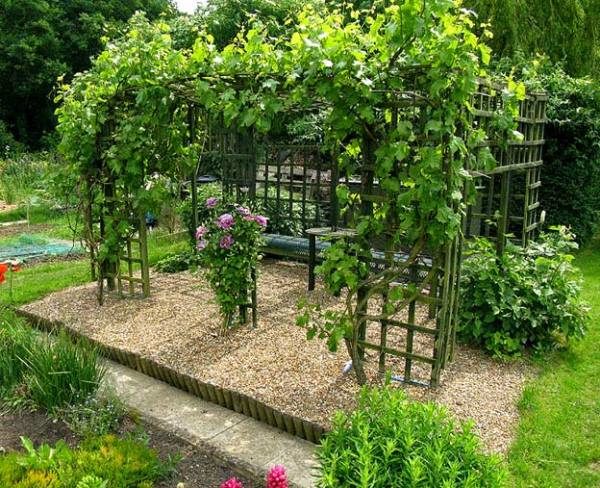

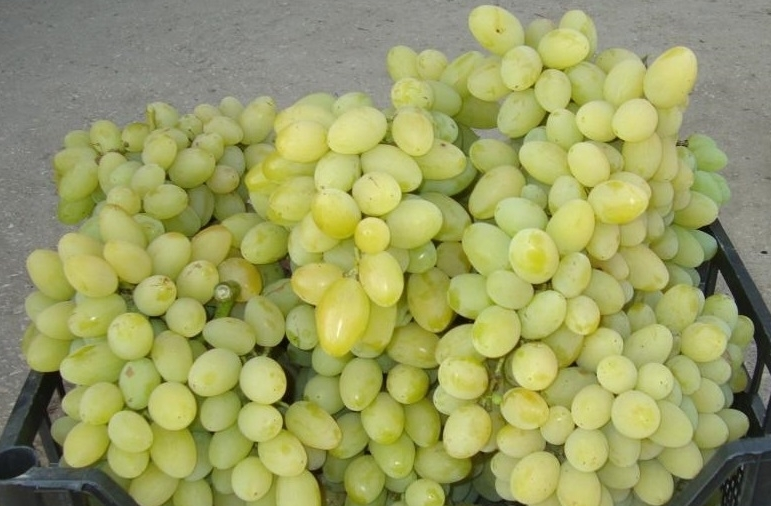
The clusters have a regular, elongated conical shape. Some grapes often have lateral branches. The cluster structure is moderately loose, with visible spaces between the berries. The weight of a single bunch ranges from 500 to 1200 g.
Characteristics of berries
The berries of this variety are large, elongated-oval in shape. The average weight of a ripe fruit is 5-8 g. Augustine grapes are transparent, amber-yellow in color, with a characteristic white bloom. The skin is thick, but its texture does not affect the taste.
The dense, fleshy pulp has a rich, harmonious flavor. This variety is characterized by a high sugar content—approximately 17 g per 100 ml. The acidity is insignificant – no more than 7 g per 1 liter of freshly squeezed juice.
Productivity and fruiting
Augustin is an early-bearing variety. It takes 110-117 days from fruit set to harvest. In most regions of Russia, harvesting occurs in mid-August. The berries are resistant to cracking and retain their flavor and marketability for 10-14 days.
The average yield of this variety is 60 kg of ripe and juicy berries per mature bush. Augustine is a table grape variety. The harvested fruit can be eaten fresh or used to make juices, compotes, homemade wines, and dried fruits.

Drought resistance, frost resistance
The crop's drought tolerance is above average. Excess soil moisture leads to root rot.
The variety is highly frost-resistant. Augustine tolerates temperatures down to -24°C. However, this fruit and berry crop reacts negatively to sudden temperature fluctuations. Decreased fruiting and reduced yields are observed.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
The Augustine variety has many positive qualities. Unfortunately, however, it also has some drawbacks.
- high decorative value of the bush;
- early ripening of fruits;
- self-pollination;
- high yield;
- universal use of berries;
- high transportability;
- excellent winter hardiness;
- disease resistance.
- the presence of large seeds in fruits;
- shedding and cracking of berries during prolonged precipitation;
- the tendency of the vine to be overloaded.
Video: "A Detailed Description of the Augustine Grape"
This video presents the main varietal characteristics of the crop.
Rules for planting and caring for grapes
Experienced gardeners claim that the Augustine grape is easy to care for and undemanding of growing conditions. Let's take a closer look at the cultivation techniques for this fruit and berry crop.
Recommended timeframes
This variety is suitable for both spring and fall planting in open ground. Spring planting offers more advantages: rapid adaptation and root establishment before frost sets in. Seedlings planted in early spring begin fruiting sooner.
Site and soil requirements
Augustine's yield depends on the amount of sunlight the vine receives. The plant prefers full sun and does not respond well to shade or even partial shade.
Augustine produces fruit well in loose, fertile soil with a neutral pH. The plant can be grown in black soil and loamy soils.
Methods of reproduction
Few people know that the Augustine variety can be propagated not only by seedlings and cuttings, but also by layering. The outer shoots of the grape vine should be bent down to the ground and secured in several places with metal staples. At the secured points, the vines are covered with soil mixed with fertilizer. Young shoots can be separated only when they have developed several healthy leaves.
- Propagation by seedlings
- Propagation by cuttings
- Propagation by layering
Watering and fertilizing
Despite its good drought tolerance, the plant requires periodic soil moisture. Watering frequency depends on soil type, weather, and the plant's developmental stage.
Grapes are watered more generously during the spring growth period and at the flowering stage.
You can fertilize a grape bush according to the following scheme:
- in early spring – with nitrogen-containing agents;
- a couple of weeks before flowering begins – with superphosphates;
- at the stage of berry ripening – with potassium and phosphorus compounds.
Pruning and pinching of side shoots
The grapevine is not pruned during the first year. Beginning in the second year, shaping is performed. Young vines are left with 6 to 12 buds. Old and damaged branches are also removed.
During the growing season, pinch out the side shoots. No more than 5–6 leaves should be left above the newly formed cluster. Leaves from the second and third rows should be completely removed.
Preparing crops for winter
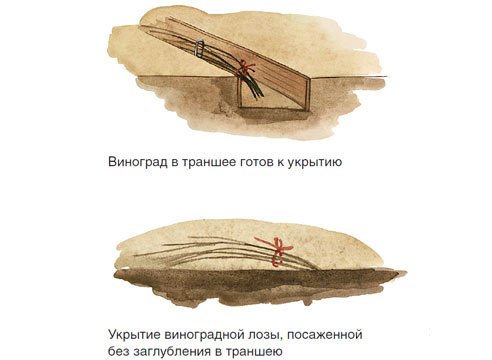
A sudden change in temperature can cause the rhizome and young vines to freeze. For this reason, it's recommended to insulate the plant for the winter. The root zone of the bush is insulated with peat, river sand, and dry fallen leaves. The vines are gathered into bundles and covered with agrofibre and sprinkled with pine branches.
Diseases and pests, methods of control and prevention
Augustine is resistant to most fungal and bacterial infections. To prevent powdery mildew and mildew, periodically spray the shrub with a Bordeaux mixture solution.
The variety is susceptible to nailworms and phylloxera. To control the insects and protect the plant, use Fitoverm, Actellic, and Fozalon.
Reviews from winegrowers
"The Augustin grape is one of my favorite varieties. It produces abundant fruit and the berries taste amazing. And it doesn't require much time or attention to care for."
"Since our dacha is located in a sunny spot, shade was a pressing issue. When choosing between ornamental and fruit-bearing shrubs, we opted for the versatile Augustin grape. Now we have a beautifully decorated garden gazebo with grape vines and a bountiful harvest of delicious berries."
The agricultural practices described in this article will help any novice winegrower master the planting and cultivation of the table grape variety Augustine. As is well known, proper planting and care are the key to abundant fruiting and high yields.



