Growing and beneficial properties of red sea buckthorn, or silver sea buckthorn
Content
- 1 Description of berry crops
- 2 Nutritional value and calorie content of berries
- 3 Pharmacological properties of red sea buckthorn
- 4 The intricacies of growing silver sea buckthorn
- 5 Picking and harvesting berries
- 6 Video: "Red Sea Buckthorn Jam"
- 7 Uses of red sea buckthorn fruits
- 8 Contraindications and possible harm of berries
Description of berry crops
Shepherdia is a perennial deciduous shrub belonging to the small Elaeagnaceae family. The slender, intertwining shoots are covered with rough gray bark and small spines. The plant reaches 3-5 m in height. The leaves are small (2-6 cm), oval, rounded at the tip, gray-green, covered with a light silvery bloom, and pubescent beneath.
The shrub blooms in early spring. The flowers are pale, petalless, and consist of four sepals. The plant is dioecious—female bushes require pollination by male plants. Fruiting begins in the third or fourth year. The yield is approximately 15 kg per bush.
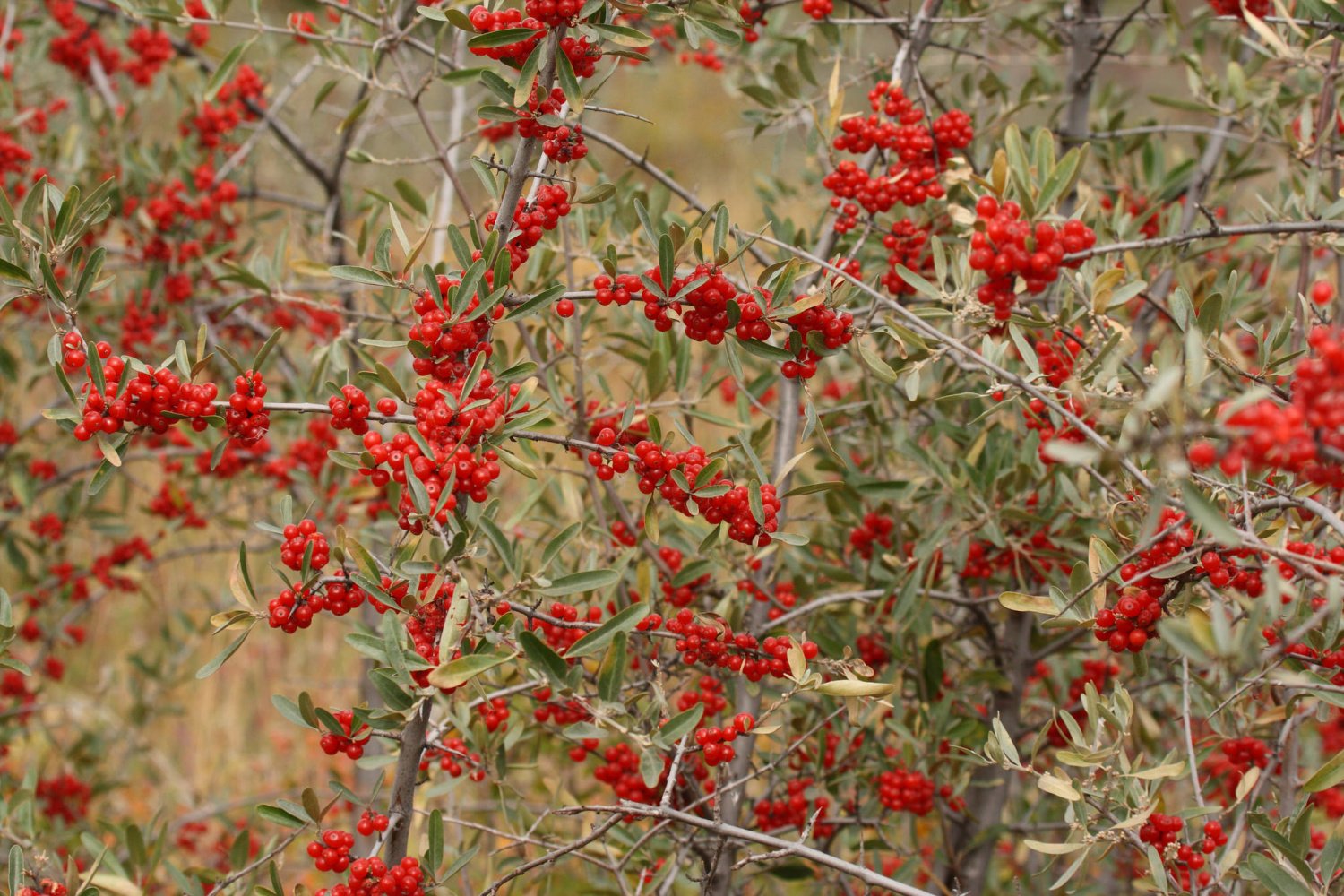

The sea buckthorn's wide growing range is due to its high winter hardiness. It easily tolerates temperatures down to -45°C and can be cultivated in all regions except the Far North. In the wild, it is found only in North America and Canada.
The Elaeagnaceae family includes only three genera of plants: oleaster, sea buckthorn, and, of course, shepherdia.
Nutritional value and calorie content of berries
Shepherdia berries are spherical drupes of orange-red or purple color. They grow on branches like sea buckthorn and remain fruit for a long time. The skin is thin but firm, with numerous white spots visible on the surface. The fruit pulp is tender, sweet and sour, and slightly sticky. Inside is a small, flattened seed.
The benefits of sea buckthorn lie in its rich vitamin content and the organic acids, tannins, and anthocyanins it contains. Its vitamin C content surpasses that of citrus fruits. It also contains vitamins A, E, and PP. The calorie content of the fruit is low—28 kcal/100 g. This amount contains 1.5 g of protein, 3.7 g of carbohydrates, and virtually no fat (0.2 g).
Pharmacological properties of red sea buckthorn
The Canadian guest has the following effects on the body:
- improves immunity and tone;
- strengthens the walls of blood vessels, prevents the development of hypertension and atherosclerosis;
- improves the functioning of the visual apparatus;
- normalizes the functioning of the intestines and stomach;
- reduces the risk of developing heart disease;
- relieves inflammatory processes;
- improves skin condition;
- has a moderate diuretic and choleretic effect.
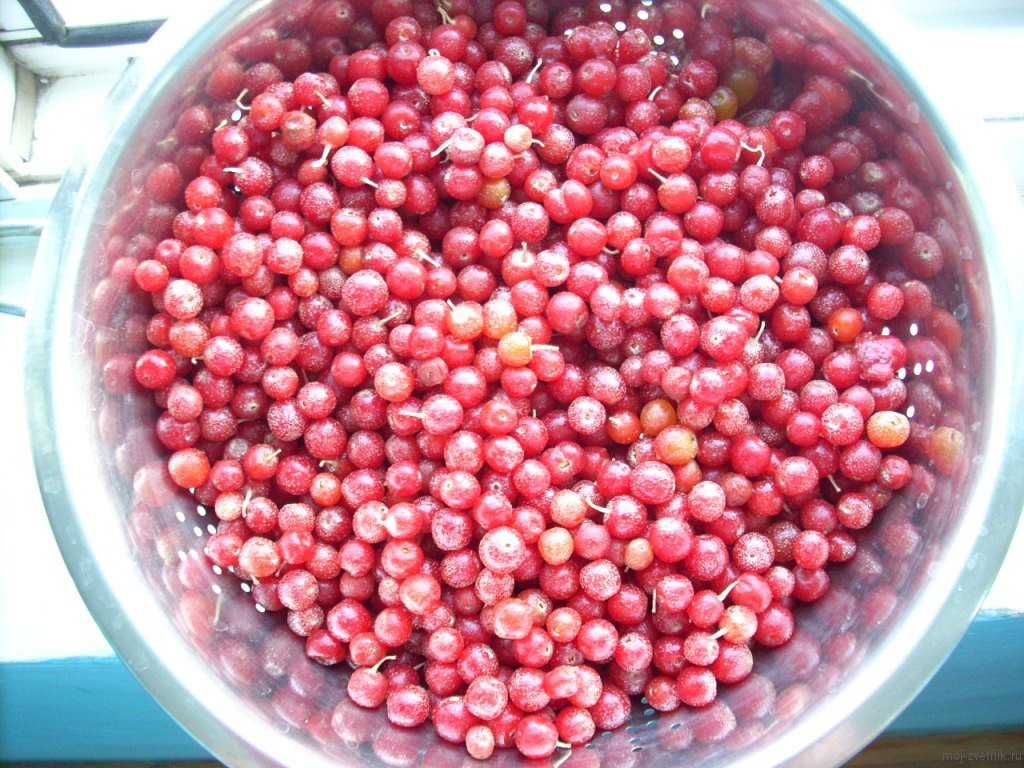

The intricacies of growing silver sea buckthorn
There are some nuances that should be taken into account when growing the crop.
Landing rules
The shrub can grow in any soil, from sandy to saline, as long as the site is sunny, as this will yield sweeter fruits. The plant doesn't like overwatering, so the groundwater level should be no closer than 1 meter from the surface.
The best time to plant is spring, when the soil has thawed but the buds have not yet begun to open. Seedlings are planted in the standard manner, spaced 1.5-2 meters apart.
Since the plant is dioecious, it's important to plant both male and female plants at the same time, in a roughly 4:1 ratio. They can be distinguished by their buds: those of female plants are pointed and flattened, while those of male plants are round and covered with small scales.
Shepherdia is propagated in the following ways:
- By seeds. Sow at a depth of 2-3 cm in late autumn. Seedlings emerge in mid-April. By September, when they reach a height of 10-15 cm, they are transplanted to a permanent location.
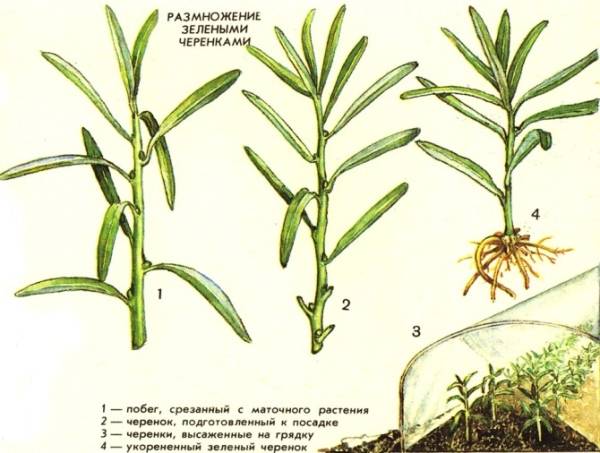
- Cuttings. Green summer cuttings 10-15 cm long with 2-3 buds are planted in a sandy-peat substrate at a depth of 3-4 cm. By September, they will have developed roots, after which they can be replanted.
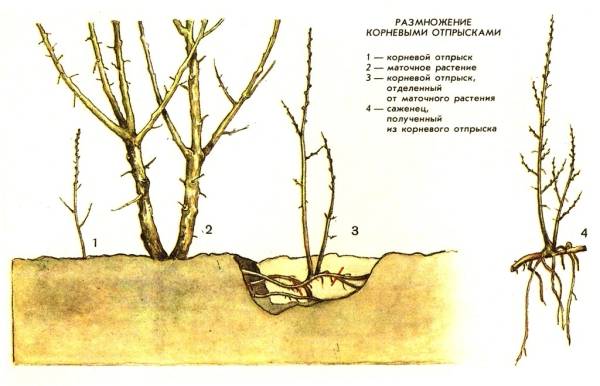
- Root suckers. Every year, young offspring appear around the bush. These can be carefully separated and replanted.
- Germination of seeds
- Propagation by green cuttings
- Propagation by root suckers
Caring for berry bushes
Care for the plant involves loosening the soil around the trunk, fertilizing, and pruning. Watering is only necessary during unusually hot weather; rainfall is sufficient during normal periods. To prevent weeds, the soil around the plant is mulched.
Shepherdia is fed in spring and midsummer. For spring feeding, use humus, ammonium sulfate, or urea. During fruiting, apply ash, superphosphate, or potassium sulfate.
Sanitary crown thinning is performed annually, and formative pruning is done every 2-3 years. Main shoots are shortened to 2-2.5 m, and side shoots are used to create a bushy shape. After 7-8 years, the bush's growth slows. From this age, only rejuvenating pruning is performed, every 4-5 years.

The plant tolerates severe frosts without any problems. Only young, non-fruiting seedlings require winter protection around the trunk.
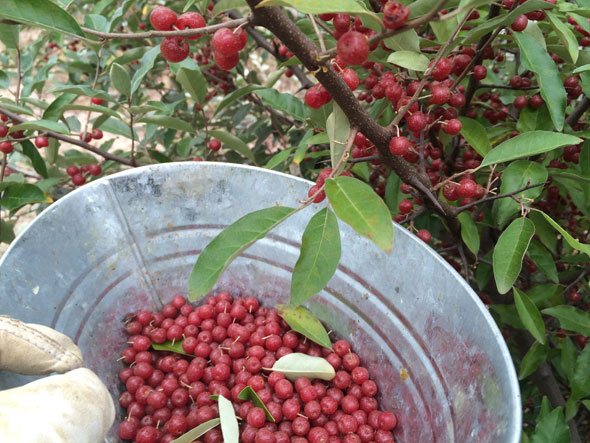
Picking and harvesting berries
The berries are harvested in September, but after the first frost, they become sweeter and fall off naturally—just lay plastic wrap under the bush and shake the branches. In September, the berries cling tightly to the branches and are picked with the roots attached, increasing their shelf life. The only drawback is that the shoots are thorny, and the berries are easily crushed in the hands.
The harvested crop is used primarily for preserves. To preserve their medicinal properties, the berries are ground with sugar. They are also frozen and used to make various jams and compotes. Dried and cured sea buckthorn berries are popular.

Video: "Red Sea Buckthorn Jam"
This video shows how to make a delicious and healthy dessert at home.
Uses of red sea buckthorn fruits
Fresh sea buckthorn is rarely consumed due to its astringency and bitter taste, but it is widely used in cooking and cosmetology.
Cooking
The fruits can be used to make delicious and slightly spicy dishes, the recipes for which are presented below:
- Jam. Layer washed berries (1 kg), sprinkle with sugar (700 g), and leave for 2-3 hours until the juice appears. Bring to a boil, then simmer for 5 minutes. Pour into sterilized containers.
- Mousse. Squeeze the juice from 350 g of fruit, add 0.5 cups of sugar, bring to a boil, and bring to a boil. When the mixture has cooled slightly, add lemon juice, honey (1 tablespoon each), and agar-agar diluted according to the instructions. Pour into molds and refrigerate.
- Mors. Lightly mash berries (0.5 kg), add 2 liters of boiled water, bring to the boil, and heat thoroughly. Add 300 g of sugar, remove from the heat, and let cool.
- Sauce. Chop 200 g of berries, pour the mixture into a saucepan, and bring to the boil. Stir constantly, adding salt, sugar, spices to taste, and a little flour for thickening. The chilled sauce goes well with meat and poultry.
Traditional medicine
Sea buckthorn fruits are used to treat respiratory infections, vascular and cardiac conditions, and to boost immunity. Freshly squeezed juice is highly effective, helping quickly recover from serious illnesses and physical exertion.
Decoctions and infusions of dried fruits are recommended as a diuretic and for cold prevention. To prepare the drink, pour a tablespoon of the dried fruit into a glass of boiling water and let it steep for 15-20 minutes. Drink daily, morning and evening.
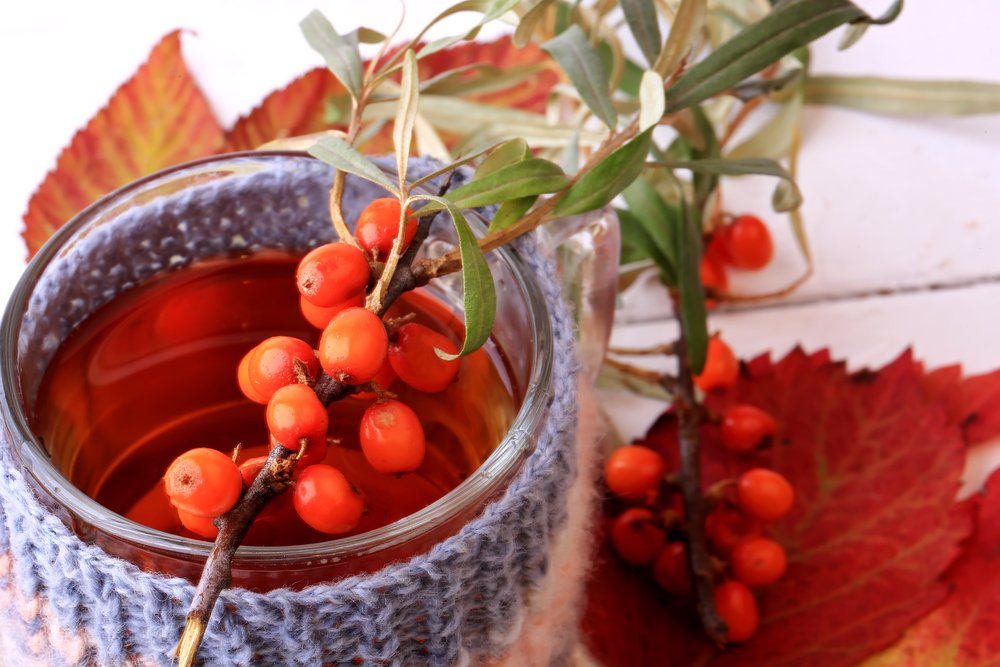

A tincture made from fresh fruit helps strengthen the immune system. Fill a jar halfway with fruit, add vodka or cognac, and let steep for at least 7 days. Then drain the liquid, add honey to taste, and let steep for another 3-4 days.
Shepherdia oil is used to treat skin and gastrointestinal conditions. To prepare it, grind the dried berries, add olive oil in a 1:2 ratio, stir, and let sit in a dark place for about 10 days. Take 1 teaspoon 20 minutes before meals; it can also be applied topically.
Contraindications and possible harm of berries
The main contraindications to eating fresh fruits:
- acute and chronic liver diseases;
- gastrointestinal diseases in the acute stage;
- early childhood.
Because the berry is red, people with allergies should avoid it. It may also be harmful to those with an individual intolerance.
Besides its medicinal value, sea buckthorn bushes are also a great way to decorate a garden. The silvery foliage and vibrant fruits look stunning against greenery and other plants, and there's no need to worry about freezing in winter.