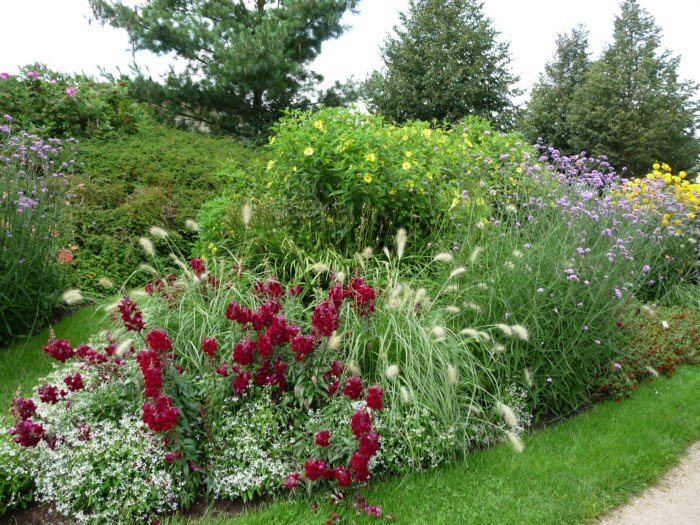
Detailed instructions for creating a mixed border with your own hands: photos and diagrams
Content
What is a mixborder?
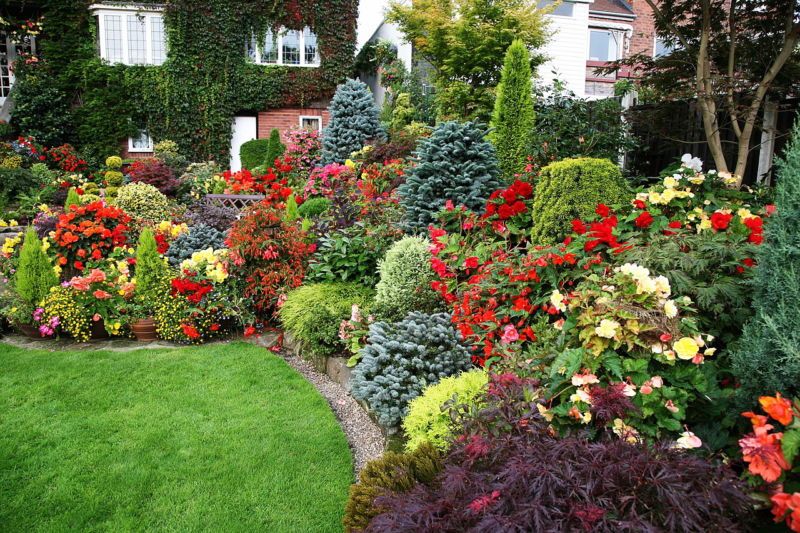
The term "mixborder" translates from English as "to mix a border." A mixborder is a composition without defined boundaries. In landscape design, this term refers to a free-form flowerbed composed of several types of greenery and flowers, combined according to a specific principle.
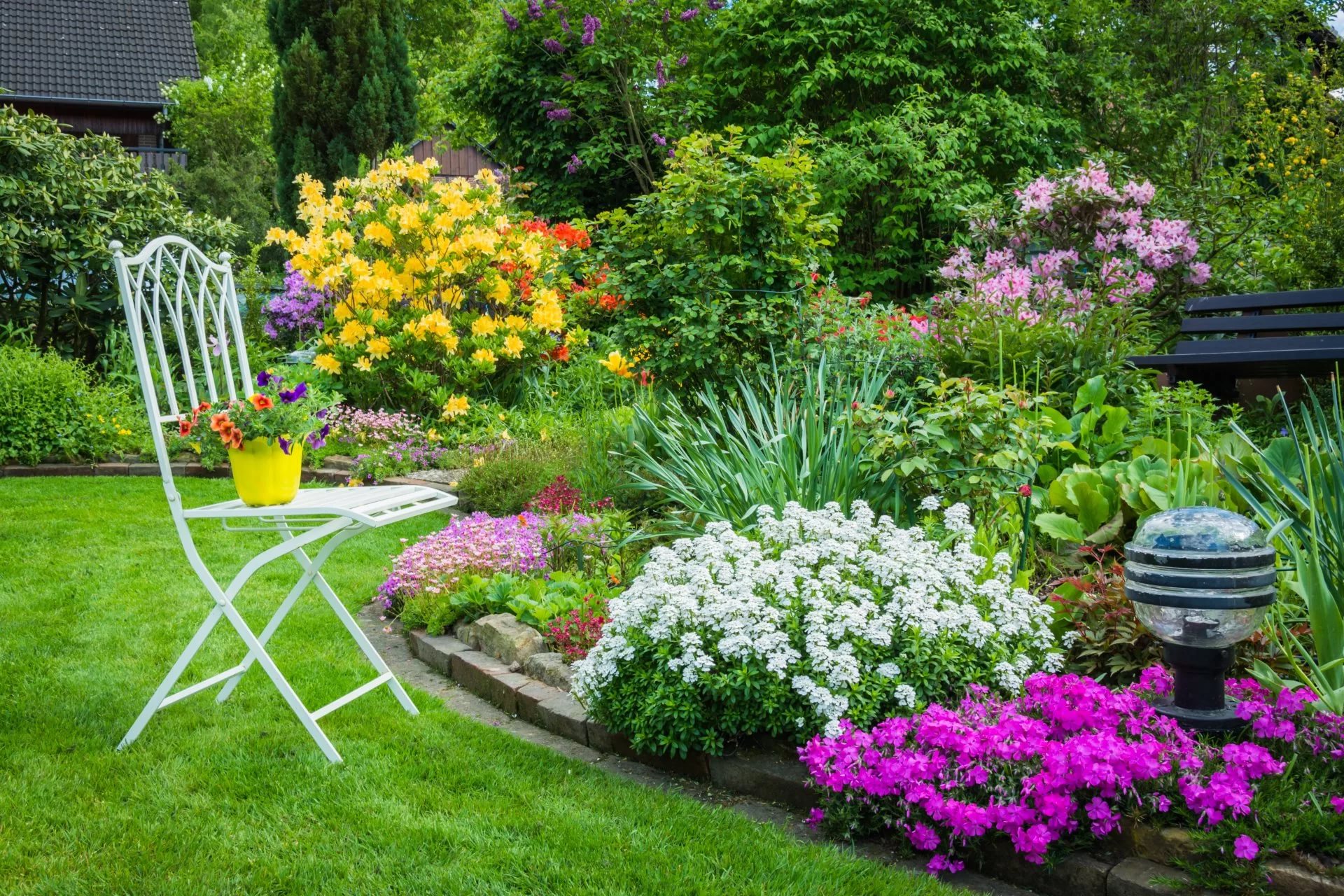

You can find ready-made schemes and examples of such compositions on the Internet. A mixborder differs from a simple flowerbed in that the plants in it are planted in a strict order, but it looks as if the composition was created by nature and grows on its own. All the lines flow smoothly into each other, greenery and shrubs form the background of the flowerbed, and bright flowers, planted in tiers, serve a decorative function and attract attention.
General rules for arranging mixborders
When arranging a flower bed, you should adhere to the following rules:
- the composition should look harmonious, without sharp corners;
- be of such a size that when leaving, you do not have to step on the front tiers to reach the flowers in the background;
- If the flower bed is located near a fountain or other architectural form, the height of the last tier should not obscure the object;
- For a flower bed located at the entrance to the house, you should not use honey plants so as not to attract insects;
- the composition should not be too colorful and chaotic - it is optimal to combine 5-6 plants of different species and flowering periods;
- The boundaries of the flower bed should be clear - the easiest way to achieve this is by framing it with decorative materials: stones, wood, gravel, colored chips;
- The composition should be visible - there is no point in planting it in hard-to-reach places.

Video: "Perennial Mixed Garden"
In this video, experts explain how to choose flowers for mixed planting.
Location options
Creating any flowerbed begins with choosing a location. Designers often suggest the following options:
- at the facade of the house
- along the perimeter of the fence
- in the center of the lawn
- on a hill or slope;
- near the paths;
- in the corner of the plot (sometimes this is necessary).
A flower bed near the house should be low and elegant. Ideally, this space would be planted with roses of various varieties. Peonies, hydrangeas, or phlox in delicate shades would be suitable for the middle tier. Hostas can be planted along the edge to add a touch of greenery to the arrangement.
Clematis can be planted against the fence in the background. Ferns and a few conifers can be placed below, along with bright nasturtiums at the bottom. A shaded corner can be decorated with mallows, daylilies in the middle tiers, and chickweed or chickweed at the bottom.
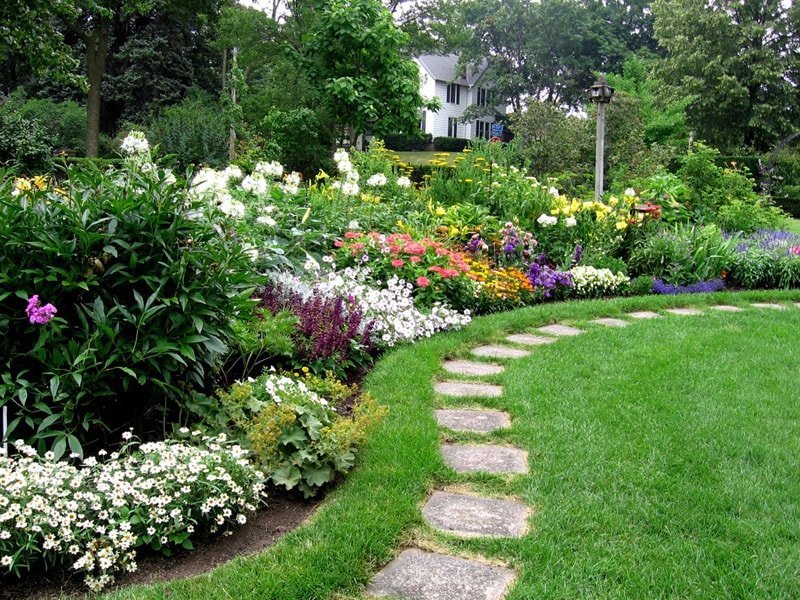
Flowering shrubs framed by lilies, carnations, and phlox look stunning on a lawn. Several low-growing perennials are suitable for edging paths: boxwood, hosta, stachys, saxifrage, and pansies.
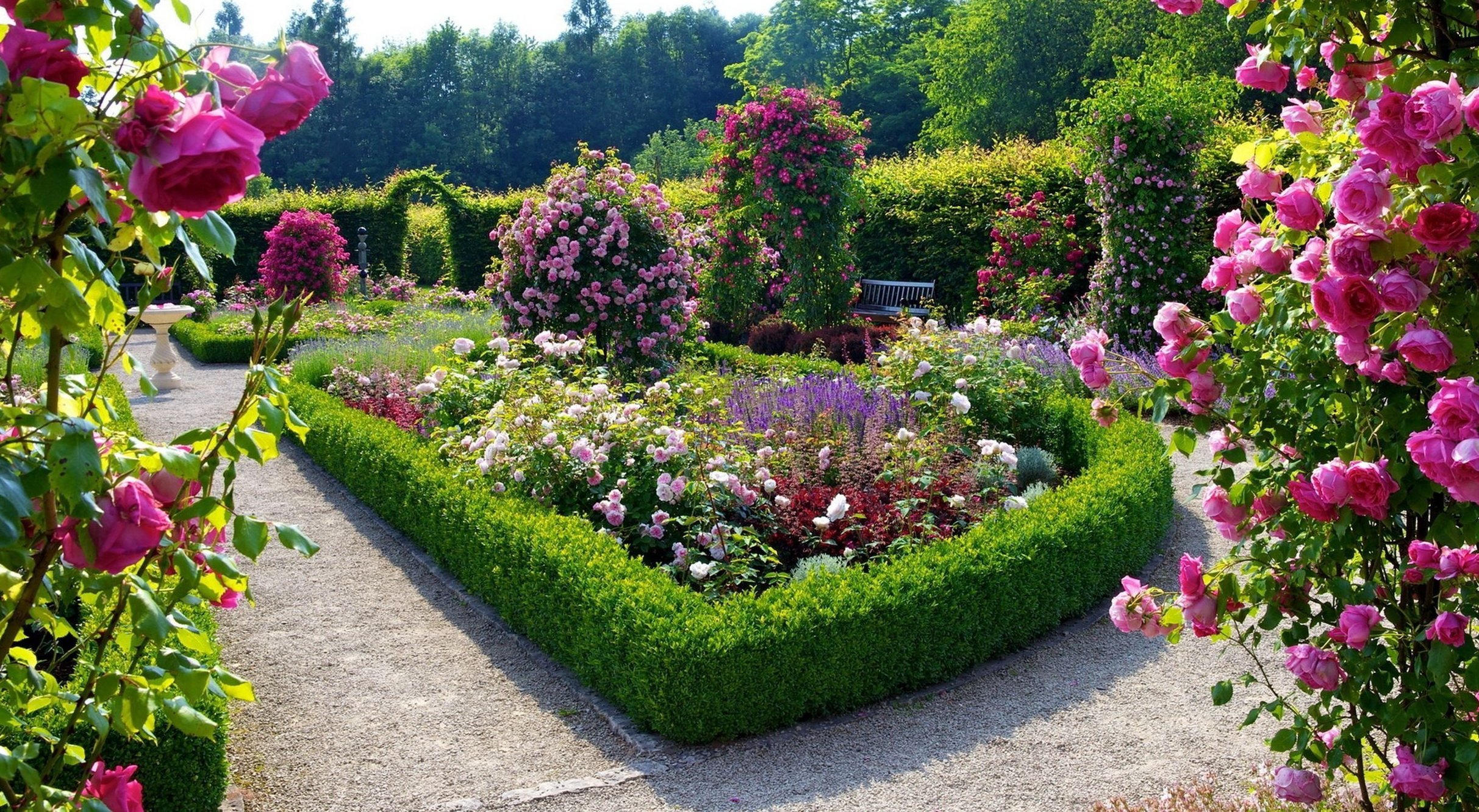

Mixborder styles
Depending on the type of dominant flora, flower beds differ in style:
English, or garden
The main principle of creating such a flowerbed is austerity and naturalness. It harmoniously combines common garden and wildflowers, artistically pruned shrubs, and conifers. An English flowerbed is arranged along paths or walls. It is characterized by an abundance of greenery and restrained color palettes, so delicate bellflowers, delphiniums, daisies, rosemary, and low-growing roses are often planted against a backdrop of arborvitaes, boxwoods, and ornamental shrubs.
Meadow
This option features an abundance of wildflowers growing in their natural environment: a meadow or field. Grasses typically serve as the background, with the lower tiers filled with daisies, cornflowers, poppies, chicory, and flax.
Rustic, or country
The style is based on the use of lushly blooming plants typically found in country gardens: phlox, peonies, mallows, rudbeckia, chrysanthemums, and dahlias. Beneficial herbs (mint, rosemary) and even berry bushes are used as a green backdrop.
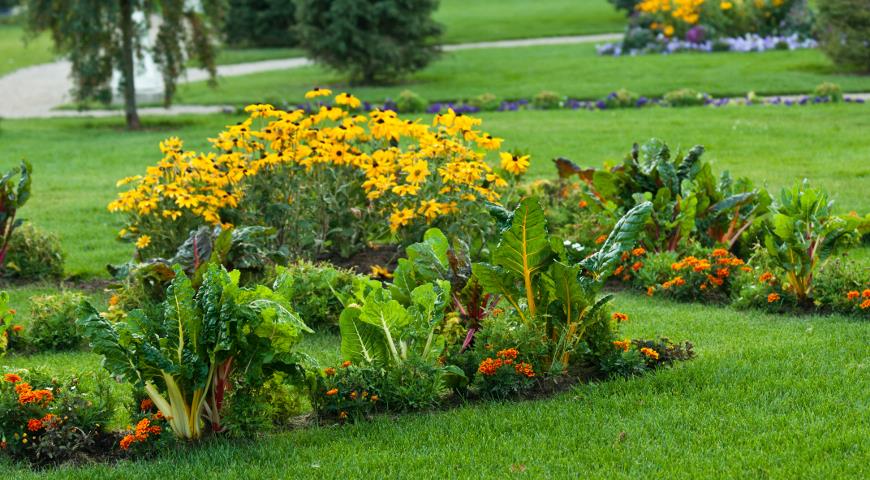
Garden
This option can be considered a variation of the "country" style. The only difference is that the flower arrangement is complemented by berries and vegetables: strawberries, tomatoes, various varieties of cabbage and lettuce. For added color, vibrant flowers such as marigolds and calendula are planted among the vegetables.
Shrub
This flowerbed design includes perennial shrubs with varying foliage shapes and colors, both flowering and evergreen, retaining their beauty year-round. A small tree may be included, but only one, as an accent.
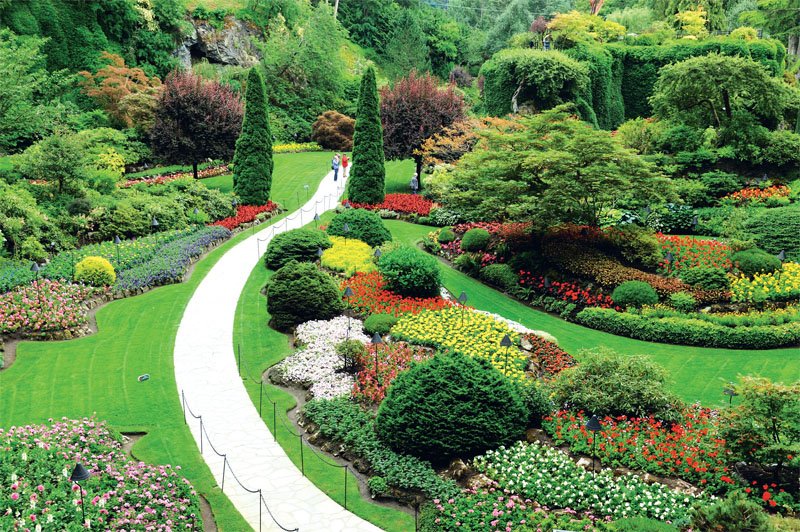
Coniferous
A composition of conifers is a surefire choice for any garden. They look elegant and fresh year-round and require little maintenance. Ideally, combine four to five species of varying heights: arborvitaes, firs, low-growing junipers, and cypresses. Deciduous shrubs can be added to complement this arrangement.
Mixed or collectible
As the name suggests, the composition consists of several specimens collected by the gardener. These are typically rare or exotic plants, making this flowerbed unique.
- Coniferous
- Mixed
- Garden
- Rustic
- English
- Meadow
Color scheme
Flower beds are also divided into types depending on the color scheme:
Monochrome
This involves using a single color but in varying shades. Most often, these flowerbeds are done in yellow, violet-blue, or pinkish hues.
Polychrome
Use a variety of complementary plants, but no more than five. In this color scheme, a green background forms the base, while white and brightly colored flowers create accents. It's worth noting that white is the last color to fade at dusk, so it's best used in the frame of the composition.
Contrasting
Consisting of contrasting colors, such as white and green, yellow and blue, or gray and red, contrasting flower beds are typically small and used to create a bold accent within a space.
Try creating a composition of blue, purple, and white flowers. They look very vibrant against the greenery.
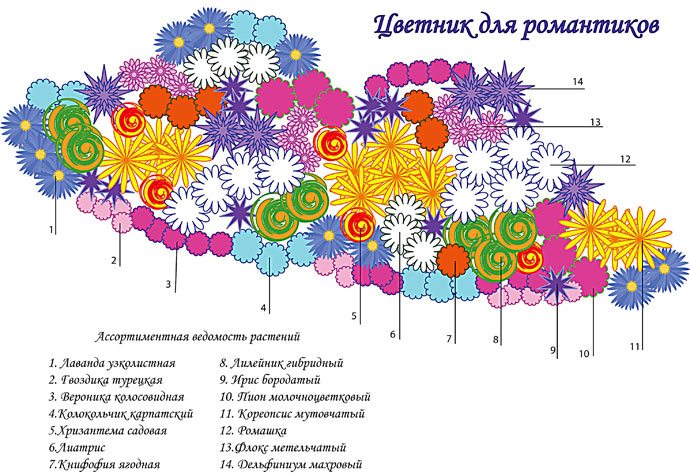
Selecting plants for a flower bed
When selecting elements of a composition, you should adhere to the following principles:
- You need to choose flowers with different flowering periods so that they replace each other and the flowerbed blooms continuously;
- correctly arrange plants by height - the difference between tiers should not be more than 20 cm;
- plants in the upper tier should not be higher than 1.5 m;
- the leaves should match in texture and color scheme;
- You cannot use plants with rapidly growing roots - they will crowd out the rest;
- take into account the acidity of the soil, humidity, and shading of the area - these indicators should be suitable for all plants in the composition;
- focus on perennials - they overwinter in the ground and do not require complex care;
- Fill the gaps between plantings with ground cover plants.

Care instructions
To maintain the beauty and decorativeness of the flowerbed, it is necessary to carry out the following procedures:
- Watering. The frequency of watering depends on the weather, but it's important to ensure the soil doesn't dry out too much. During the first year, until the plants become established, water regularly. It's best to use a watering can to prevent the water pressure from washing away the soil.
- Loosening the soil. This procedure will prevent crusting on the soil. Once the cover crops have established themselves, loosening will no longer be necessary.
- Weeding. A properly planted flowerbed has no room for weeds to grow, but while the plants are small, they need to be removed regularly.
- Fertilizers. Potassium and phosphorus fertilizers are applied in the summer to promote lush flowering. Compost can be added to the soil in the fall.
- Trim faded blooms. This should be done throughout the summer, as wilted buds can seriously spoil the appearance of a flowerbed.
- Formative pruning (for ornamental bushes).
A tiered flowerbed is the most popular landscape design element today. It can transform a space, create a striking accent, and attract attention. What's more, creating one yourself is quite easy. The key is to choose the right plants so they bloom throughout the season.






