Description and cultivation features of the Rouge Cardinal clematis variety
Content
History of selection and description
Clematis Rouge Cardinal belongs to the group of late large-flowered species. The variety was developed in 1968 by the French breeder A. Girault.
The parent varieties are Lanuginosa and Viticella. The hybrid, the result of a breeding experiment, has actively participated in international flower shows. For example, the clematis "Rouge Cardinal" was awarded the highest prize and a gold medal at the Dutch Ornamental Flowering Crops Exhibition.
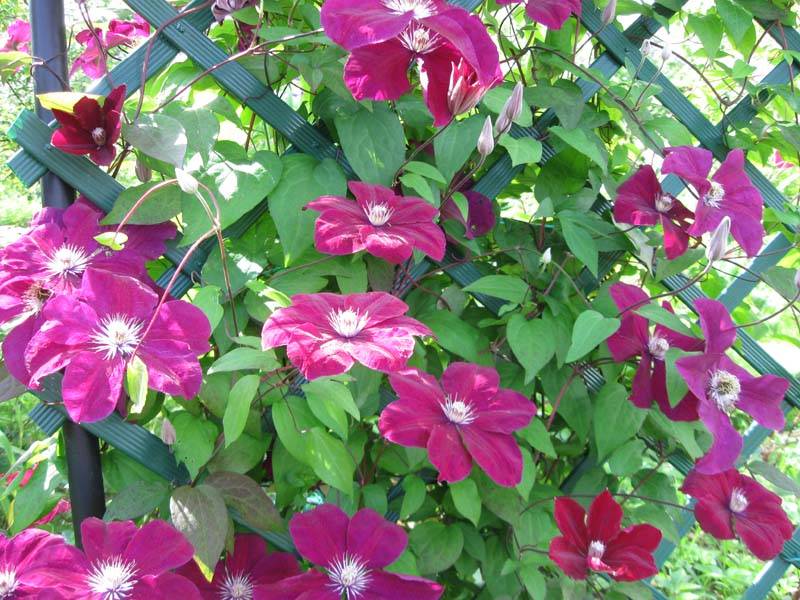

Rouge Cardinal is a vine-like shrub characterized by abundant flowering and undemanding growing conditions. It is actively used in gardening and landscape design for landscaping and decorating various buildings.
Appearance of the bush
The maximum height of a mature bush is 3 m. As it grows, this perennial forms a vertical vine. It can be grown in containers.
The young vine is green. The leaves are medium-sized, pinnately compound, and trifoliate. The leaf blades are dark green and leathery.
Features of flowering
Rouge Cardinal is a late-blooming garden plant. The first buds open around midsummer. With favorable weather conditions and proper care, the flowering period can extend until early October.
A distinctive feature of this cultivar is its abundant flowering. Buds form on the current year's vines. The flowers are velvety, large, and cross-shaped. The average diameter of a bud when open is 15 cm. This cultivar features a rich purple-red flower color, while the stamens are light yellow. The plant maintains the juiciness and vibrancy of its buds even when exposed to direct sunlight.
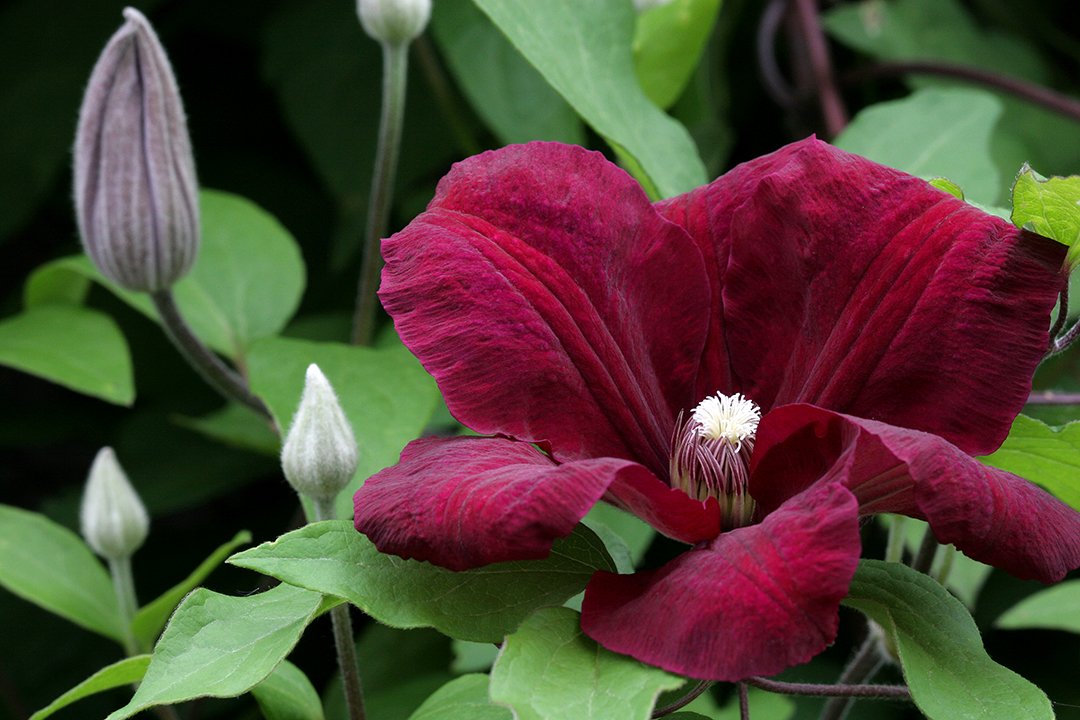

Frost and drought resistance
The variety has average drought tolerance. This perennial responds equally negatively to both insufficient and excessive moisture. A properly established watering regimen will help prevent frequent illnesses or death of this ornamental shrub.
Rouge Cardinal is suitable for growing in northern regions. As noted in the variety description, this vine-like shrub tolerates temperatures as low as -30°C.
Video “Botanical description of clematis Rouge Cardinal”
This video presents the varietal characteristics of this ornamental crop.
Planting and caring for clematis Rouge Cardinal
Gardeners and landscape designers prefer to work with low-maintenance plants, including the clematis Rouge Cardinal. Let's look at the basic rules for cultivating this ornamental plant.
Recommended planting times
Clematis is one of the few perennials that can be planted outdoors in spring, summer, and fall. Experienced gardeners recommend fall planting. This allows the plant time to adapt to the new growing conditions before the first frost.
In spring, when the weather becomes consistently warm, young vines begin to grow actively.
Selecting a suitable location and planting material
Clematis thrives in light, fertile soil with moderate acidity. Heavy or salty soil is not the best option for growing this perennial. In such an environment, the ornamental shrub grows poorly and flowers poorly.
Seedlings of cultivar clematis should be purchased from specialized gardening stores and nurseries. Plants labeled "caper" are known for their rapid adaptation. This designation indicates that the planting material was stored refrigerated. The root ball of the seedling is packed in moist soil.

Propagation methods and planting algorithm
A 60x60x60 cm planting hole is prepared 3-4 weeks before planting. A drainage layer of crushed red brick or expanded clay is required. Organic fertilizer is added to the planting hole to improve soil fertility.
Place the seedling in the center of the planting hole. Cover the rhizome, root collar, and 5–10 cm of the stem with soil. Install a support next to the buried clematis seedling. After planting, water and mulch the plant. Shade the young bush for the first few days.
Mature clematis (5 years or older) are propagated by division. Carefully dig up one side of the bush and separate the root section. It's best to remove the severed root along with the growing medium. This will allow the transplanted perennial to adapt more quickly to its new environment.
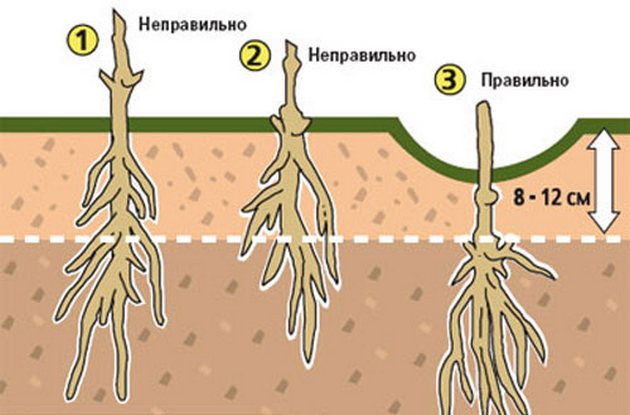
Watering and mulching
Clematis prefers moderate watering. Water the plant at least once a week. Apply 10–20 liters of water to a young plant, and 20–40 liters to a mature plant. Once the water has been absorbed, loosen the soil. Don't forget to periodically remove any weeds that may emerge from the ground.
Mulching the soil will help prevent weed growth. You can mulch the perennial with hay, straw, peat, or black agrofibre.
Fertilizing the bush
Flowering plants require additional feeding. Clematis can be left unfertilized for the first year. Subsequently, fertilize according to the following schedule:
- in spring during the period of active growth – nitrogen-containing preparations;
- at the stage of bud formation – complex mineral mixtures with a high content of potassium and phosphorus;
- in autumn after flowering – superphosphates.
Rouge Cardinal is periodically fed with organic matter. Crushed chalk, wood ash, compost, or rotted manure are used for fertilization.
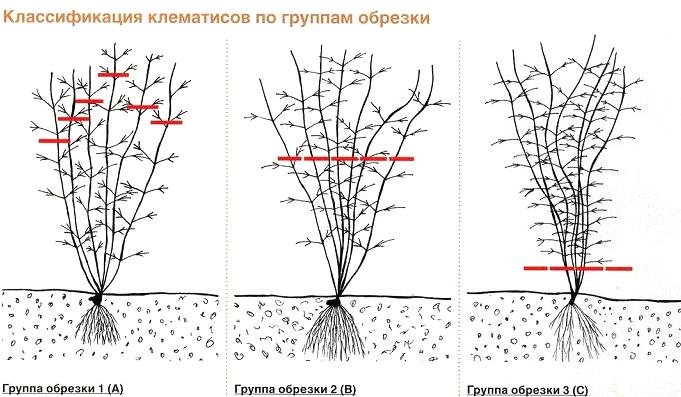
Clematis pruning rules
One of the most important agricultural practices is pruning. During the growing season, broken, weather-damaged, and dried shoots are removed.
Rouge Cardinal belongs to the third pruning group of vine-like shrubs. This means the plant requires complete pruning of its vines for the winter. Experienced gardeners recommend leaving two to three pairs of above-ground buds intact.
Covering shrubs for winter
Preparing for winter begins with insulating the root zone. The base of the clematis is covered with dry fallen leaves, river sand, peat, hay, or straw. The upper part is left untouched until the temperature drops below freezing. The plant must undergo a hardening-off phase.
The above-ground portion of the bush is wrapped with medium-density agrofibre. In severe frosts, the bush can be additionally insulated with pine branches.
Diseases and pests: control and prevention
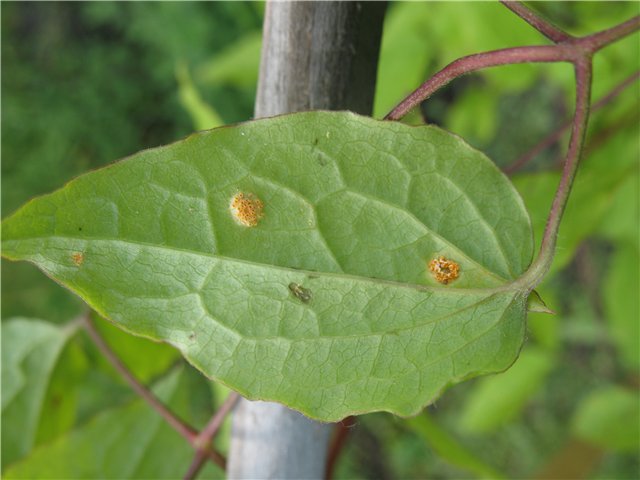
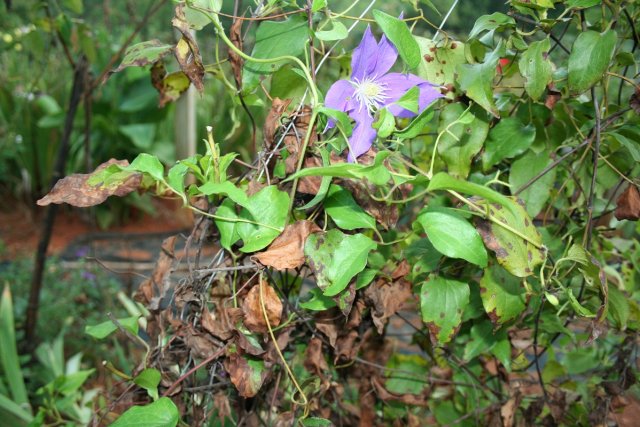
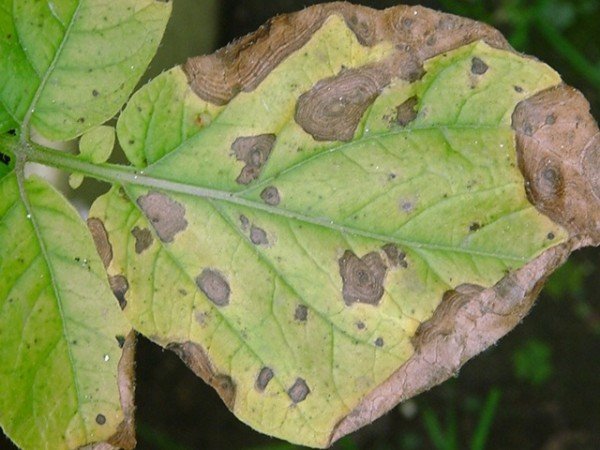
This perennial is resistant to most fungal diseases. It can occasionally be affected by rust, fusarium, and leaf spot. For prevention and treatment, use fungicides such as Horus, Skor, Radomil Gold, and Maxim.
Dangerous pests for this variety include nematodes, midges, and spider mites. To control these insects, use a garlic or soap solution. In case of widespread pest infestations, use the insecticides "Aktara" and "Aktellik."
- Traces of rust
- Signs of fusarium
- Leaf spot
Reviews from flower growers
"I really like vine-like shrubs, including the clematis Rouge Cardinal. This perennial requires minimal care but delights with its abundant and lush blooms."
"For the past few years, I've been eagerly awaiting midsummer, as that's when the clematis Rouge Cardinal blooms. I'd like to highlight its beautiful and long-lasting blooms."
The large-flowered clematis Rouge Cardinal is an ideal solution for landscaping a garden plot. This beautifully flowering shrub can be used to decorate arches, open and semi-closed garden arbors, fences, and other enclosures.



