Description and use of European euonymus in garden compositions
Content
General description of the plant
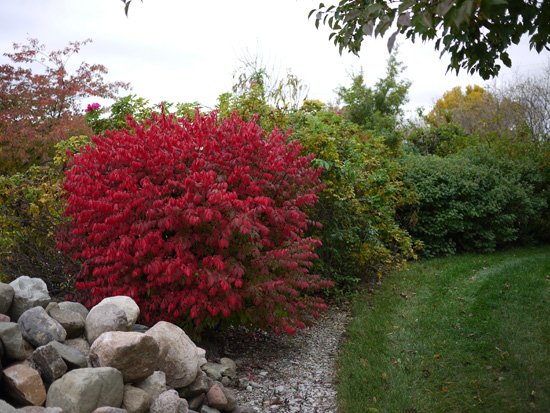
The European spindle tree (Euonymus europaeus) shrub is popular in our country. It thrives in central Russia and colder regions due to its frost resistance. In winter, the bushes attract attention with their brightly colored drooping fruits against the surrounding snowdrifts.
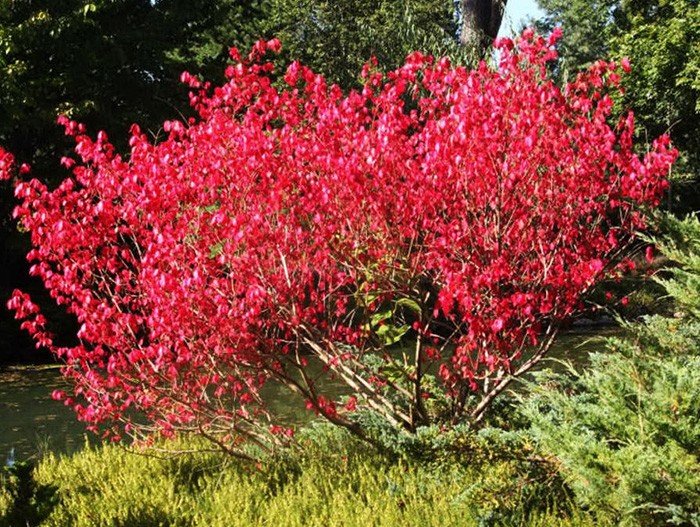
The plant is an evergreen deciduous plant with a decorative, lacy crown. It can grow as a shrub up to 3-4 meters tall or as a tree, reaching 5-6 meters in height at maturity.

Here is a brief description of the plant:
- The root system is shallow but branched.
- New shoots are initially green, but over the years they darken, becoming black and covered with small growths.
- The foliage is dark green, up to 10 cm long, oval-shaped, and smooth. By early autumn, it turns a variety of shades from yellow to red.
- The inflorescences are semi-umbel-shaped, collected from 5 greenish-white buds.
- The flowering period is from May to July, lasts about a month, and is not particularly decorative.
- The fruits, which ripen in October, resemble leathery capsules with four valves. They are the main attraction of the plant.
- The crown is lush and dense.
The main color scheme of the euonymus tree is formed not by the flowers, but by the fruitsDifferent varieties come in unique shapes and colors. The wood is hard and often used for small crafts. The charcoal obtained from burning it is used to make high-quality pencil leads.
When planted in a garden, European spindle tree becomes a magnet for insects that harm fruit crops. This fact can be useful in gardening.
Video: "A Brief Description of the European Euonymus"
This video presents the main characteristics of the ornamental plant.
Popular varieties of European euonymus
Wild species of this plant are found in the European part of the country, Crimea, and the Caucasus. Cultivated varieties number dozens, used in landscape design, singly and in groups. Here's a brief description of some varieties that thrive in the Moscow region climate.
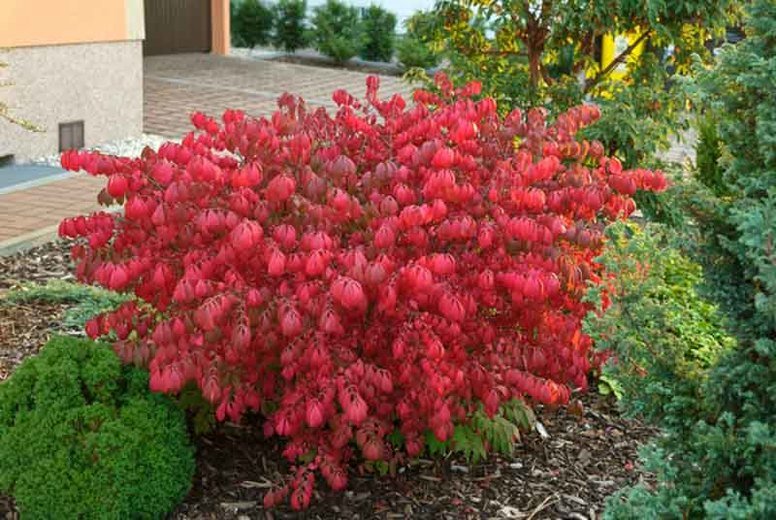
Red Cascade. It grows as a shrub or small tree. Its maximum height is 3.5 m. Its fall foliage is dark red, and its fruit is orange. It adapts well to new locations and tolerates air pollution, making it recommended for urban planting. There are up to 20 ornamental hybrids of this variety:
- Alba – medium height, white fruits;
- Aucubaefolia – green leaves with yellow spots;
- Atropurpurea – leaves with a lilac hue;
- Intermedia – berries are massive and red.
Sherwood. A tall (up to 5 m) shrub with a compact crown that grows vigorously in width. Leaves are up to 11 cm long and have a leathery surface. By mid-season, the leaves turn reddish-pink. The fruits are bright red capsules that ripen in September. When opened, they release orange seeds.
Nana. A low-growing, creeping shrub, approximately half a meter tall. The stem is prostrate, and the shoots root quickly upon touching the soil. The foliage is narrow. It blooms in July. The pinkish-yellow fruits appear in September.
- Sherwood
- Red Cascade
- Nana
Planting and caring for European euonymus
The plant is easy to grow and, if proper cultivation practices are followed, thrives even in unfavorable conditions, such as acidic soils, sun, or partial shade. Although self-pollinating, fruit set is best when several plants are present in the same plot.
Selecting and preparing a site
Euonymus is not picky about soil, but it is recommended to select:
- drained soil with an alkaline reaction;
- a well-lit place (the more light, the more saturated the color of the foliage and fruits).
Dig a hole large enough to accommodate the seedling's root system. Line the bottom with small stones and sand to improve drainage. Prepare fertile soil by mixing:
- peat (2 measures);
- turf (1 measure);
- sand (1 measure).
- lime or dolomite flour.

Step-by-step landing algorithm
New plants are usually planted in the fall, although spring is also possible. The step-by-step planting procedure is as follows:
- A mound of soil is poured into the prepared hole and the seedling is placed on top.
- The rhizome is straightened in all directions and then sprinkled with a fertile mixture.
- The seedling is watered with warm, settled water.
- The soil is compacted, ensuring that the root collar protrudes slightly above the surface.
Methods of reproduction
There are several methods:
- By seeds. A natural, albeit lengthy, method. First, they are kept wrapped in a damp cloth at a temperature of +10°C for three months, then lowered to +3°C. Sow in a mixture of leaf mold, sand, humus, and turf.
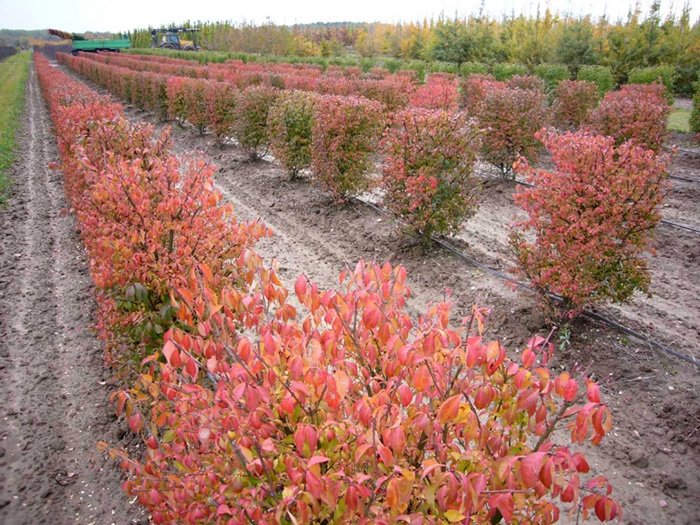
- Cuttings. In summer, branches are cut into cuttings up to 10 cm long and placed in fertile soil mixed with sand, where they take root within 45 days.
- Layering. In the spring, shoots growing near the ground are placed in the soil, dug into special trenches, secured, and covered with soil. The top should remain exposed to the air. The shoot will quickly take root.
- Root suckers. In the spring, shoots 40 centimeters or more tall are separated and transplanted to another location.
- By dividing the bush. Suitable for low-growing crops. Divide with a spade.
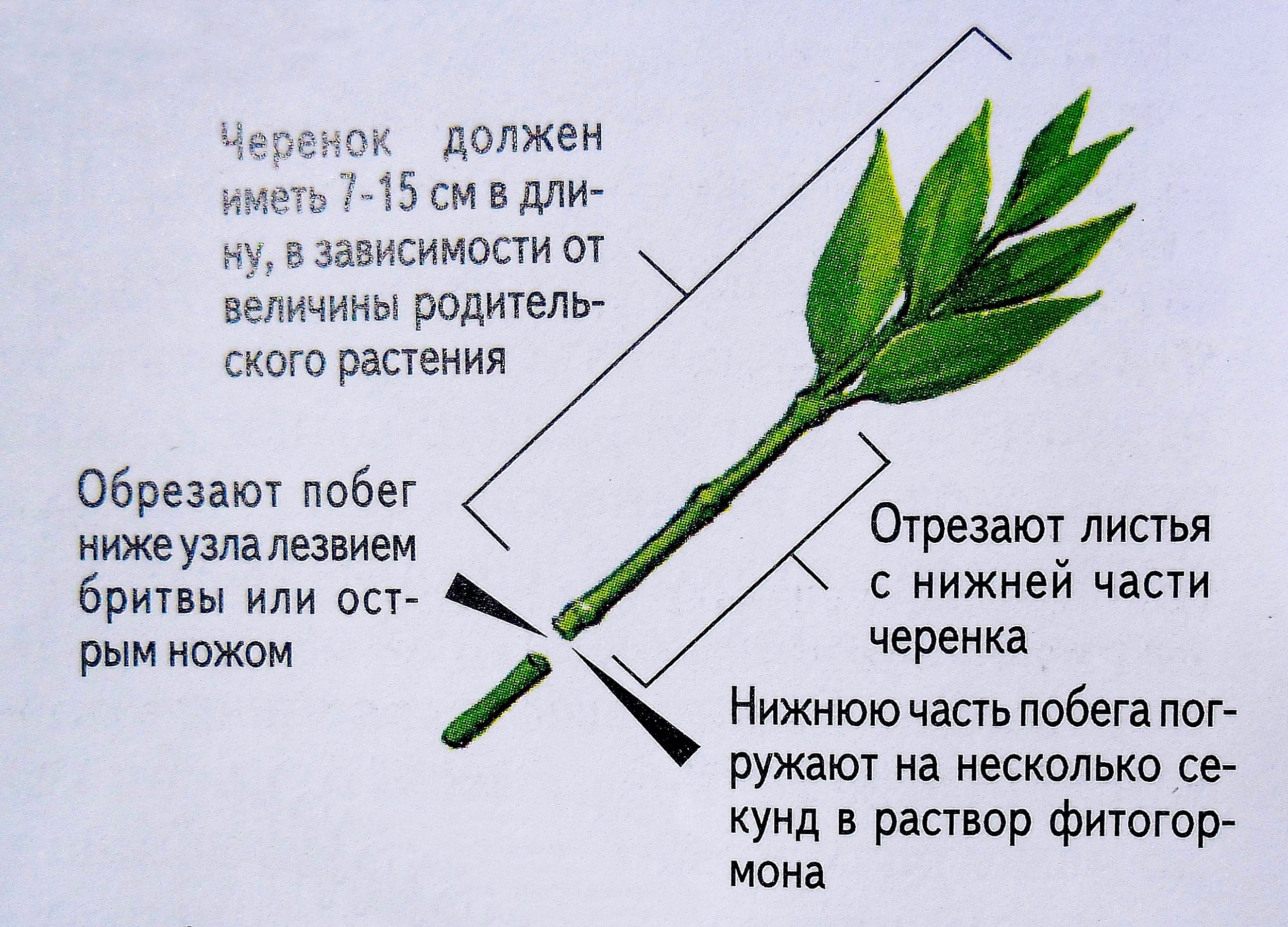
Watering, loosening and fertilizing
For the first seven days after planting, water every day, morning and evening. Subsequently, water sporadically, increasing only during summer droughts. Excess moisture is harmful to the plant, as the root system begins to rot. After each heavy rain and watering, loosen the soil around the tree trunk and mulch with peat.
Fertilizers should be applied:
- mineral - in spring and autumn;
- organic (ash, lime, fallen leaves) to reduce soil acidity.
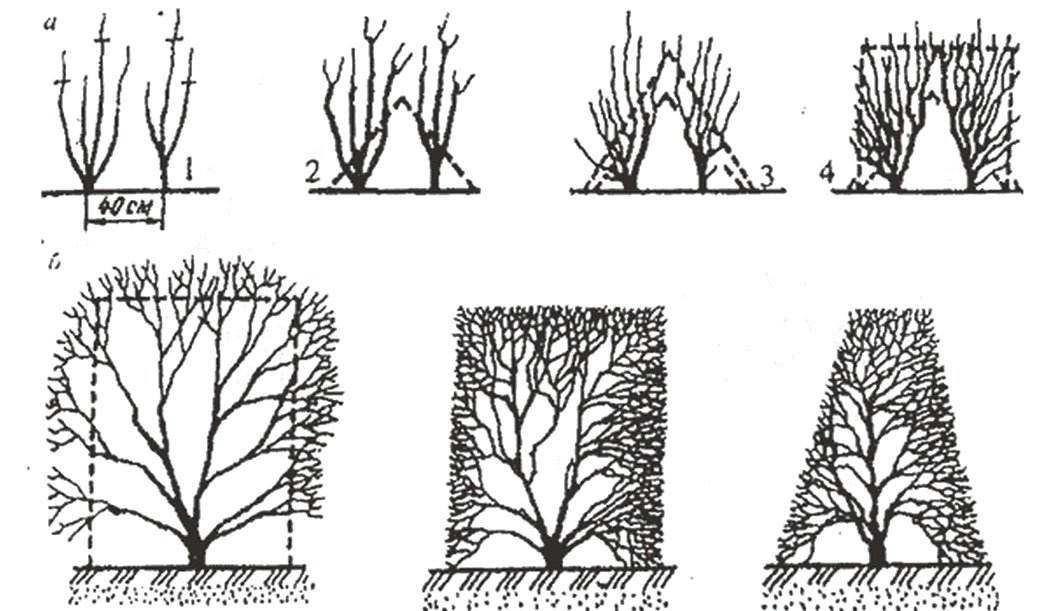
Pruning and haircut
If necessary, the bush can be given any shape, but a cone or ellipse is most often preferred. Don't be afraid to overdo it—a pruned bush will produce numerous new shoots. Pruning should be done twice:
- early spring, before flowering begins;
- in the fall, when the berries ripen.
During the procedure, the tops of the shoots are pinched, achieving the desired growth direction of the bush. Sanitary pruning is also performed, removing defective branches.
Features of wintering
Although a mature plant tolerates even severe frosts well, it still requires protection and care until it reaches 3 years of age. Before winter:
- apply fertilizers containing potassium and phosphorus;
- the ground around is hilled with dry peat or humus;
- The bush is covered with fabric (burlap, jute, etc.).
A pile of fallen leaves mixed with sawdust should be sufficient for a mature bush to grow under. If any shoots freeze over the winter, simply trim them off, and the bush will sprout new ones.
How to combat potential diseases and pests
European spindle tree has weak immunity to diseases and pests. Moreover, it has been observed that it attracts many pests, thereby protecting other crops. It is most often attacked by:
- spider mite;
- aphid;
- mealybugs;
- apple moth;
- hawthorn;
- scale insects;
- caterpillars.
Specialized universal insecticides are effective against most pests. Actellic and Aktara have proven effective. For mealybugs, it's recommended to spray the plant with Fito-Verm or Confidor.
The shrub also requires protection from diseases. The most dangerous are the following:
- Trunk rot. This fungal disease can destroy the entire bush. There is no treatment; the affected plant is dug up and burned. Preventative measures include spraying with Bordeaux mixture in the spring.
- Powdery mildew. Treatment includes Fundazol or colloidal sulfur.
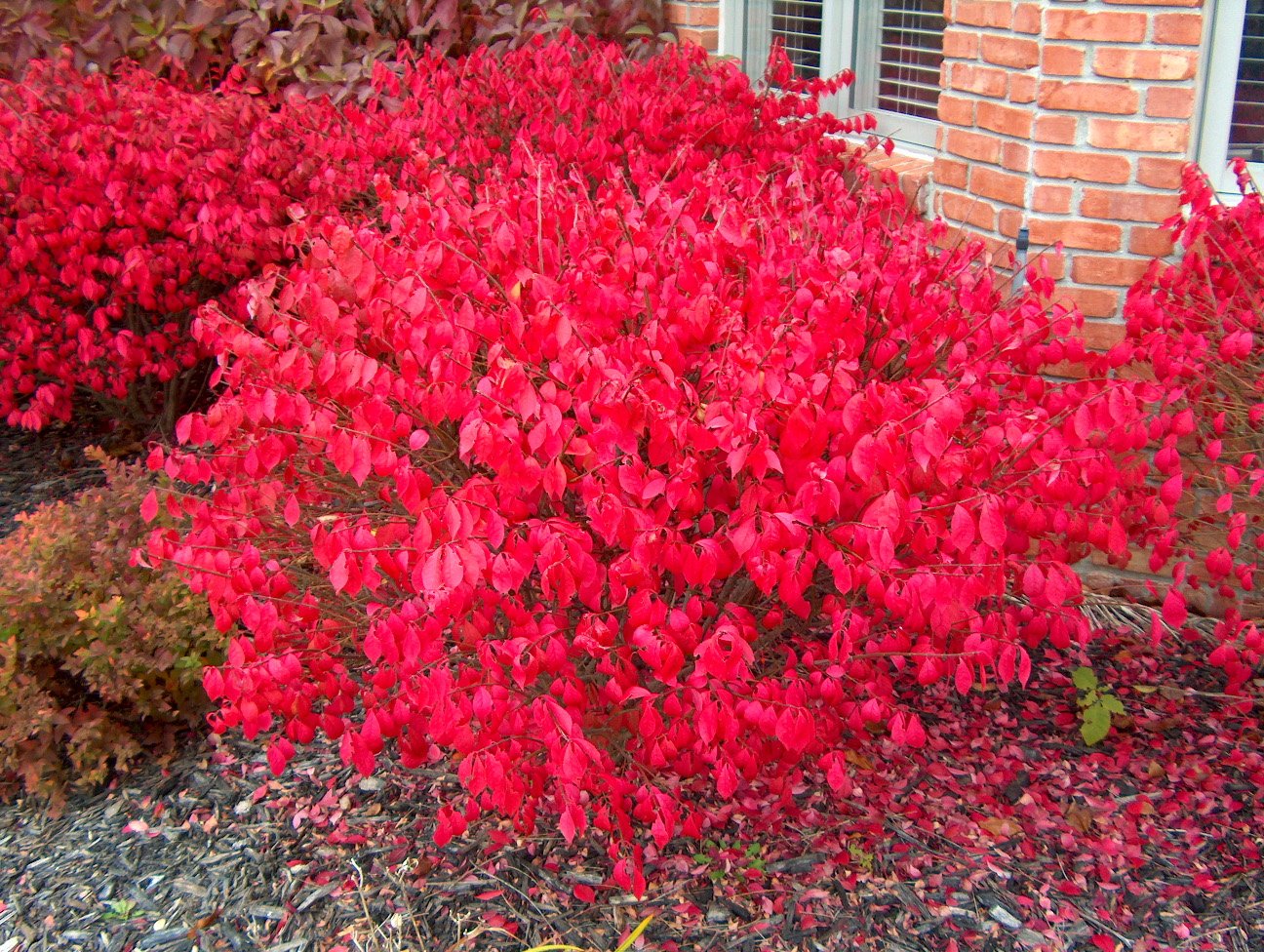
Use in garden compositions
A common use is as a hedge, as the plant can be easily pruned to any shape. Another option is growing isolated specimens, creating attractive accents in the autumn garden.
Dwarf and climbing varieties are used to line garden paths and create decorative arrangements. They are planted in pots and used to decorate arbors. Their variegated coloration makes an attractive backdrop when combined with coniferous groups, such as dwarf pines and junipers.
Isolated euonymus oases can cover infertile areas, while also strengthening the soil on loose slopes.

Reviews of European euonymus
"I planted two of them in my garden. They took root, survived the winter (I covered them), the fruit ripened, and the garden was simply transformed. The one in the sun has brighter foliage, while the second one's is more faded compared to the first."
"We read the reviews and planted Red Cascade as a hedge. Over the course of a few years, it's grown almost 4 meters—it completely blocked the view, and no intruder could get through. We have to trim it frequently to maintain its shape, but it still looks beautiful."
This plant is widely used in landscaping gardens and urban flowerbeds. It poses no danger and requires little care. Its vibrant foliage and variegated fruits will delight visitors until the first snow falls.



