What to do if your tomatoes have white spots on their leaves: the main causes
Content
Reasons for occurrence
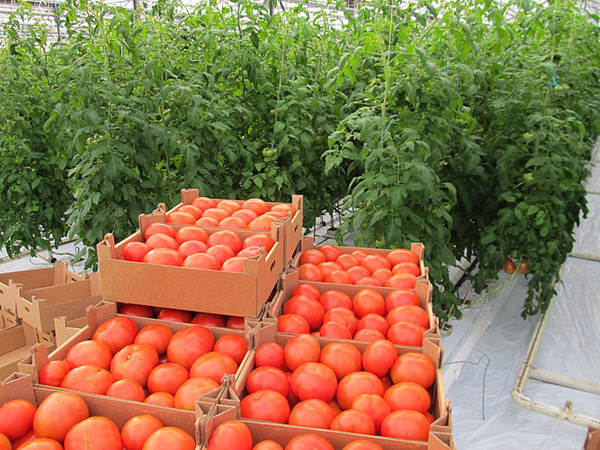
Gardeners prepare seeds for planting, fussing over them, germinating, watering, turning, transplanting, and fertilizing the seedlings. But when it's time to enjoy healthy plants in anticipation of the harvest, spots can appear on the leaves.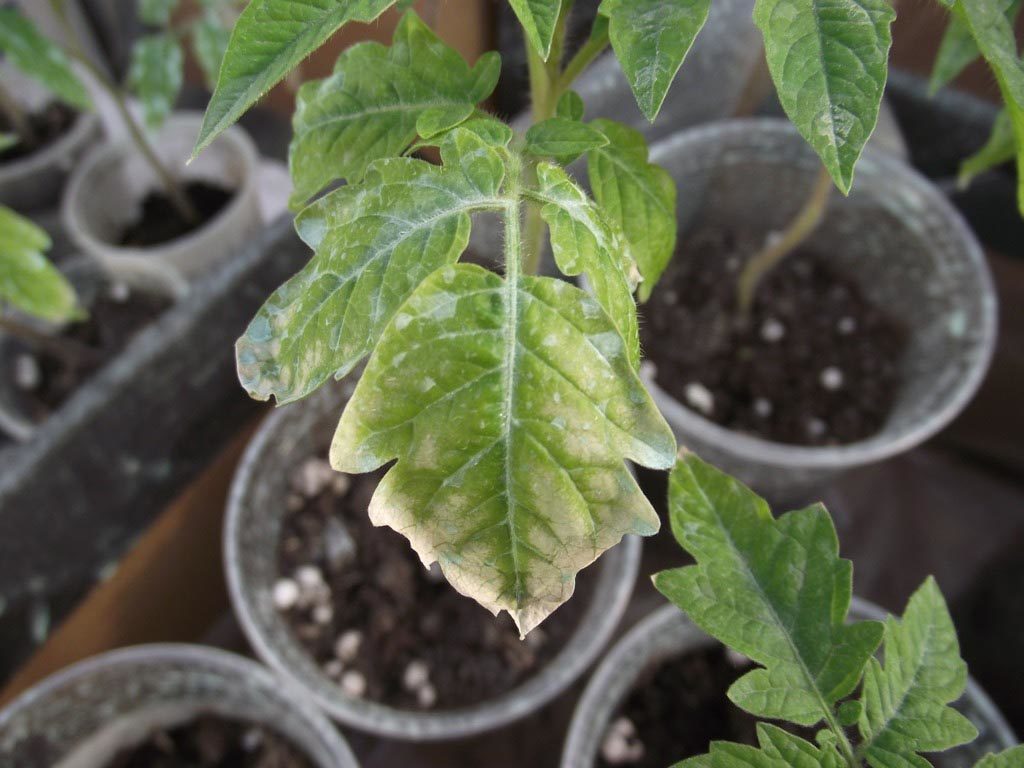
Of course, this is cause for concern, as it means something is wrong. The spots can be white and dry, have a border, or be covered with a whitish coating. They can be dark or light, sunken or raised above the leaf surface. It's important to examine them carefully and recall any recent history of the plants; this will help identify the spots and determine their cause.
Sometimes it happens that seedlings are growing well, looking healthy, but as soon as they are brought out into the sun or a few days after planting in the garden, white irregular spots appear. These spots often appear on the upper leaves, or all the leaves may turn white, leaving only the stems green. This is most likely sunburn. It occurs when direct sunlight hits an unhardened plant, especially if the plant is wet and exposed to the sun. It's very unpleasant, but not fatal; in most cases, the plant can recover and continue growing.
It's much worse if white spots on tomato leaves are caused by disease. If cloudy white spots with dark edges start on the lower leaves and then spread, and if they leave a grayish coating, it's most likely septoria leaf spot, a very dangerous fungal disease. If left untreated, black spots will appear in the center of the white spots, the leaves will darken and fall off, and the disease will spread to other leaves, stems, and fruits. The plant could have become infected if the soil was poorly prepared, leaving spores in the soil. The seed material could also be contaminated, which is why seeds should be treated before sowing. Septoria leaf spot usually develops in July, as it is triggered by high humidity and extreme heat.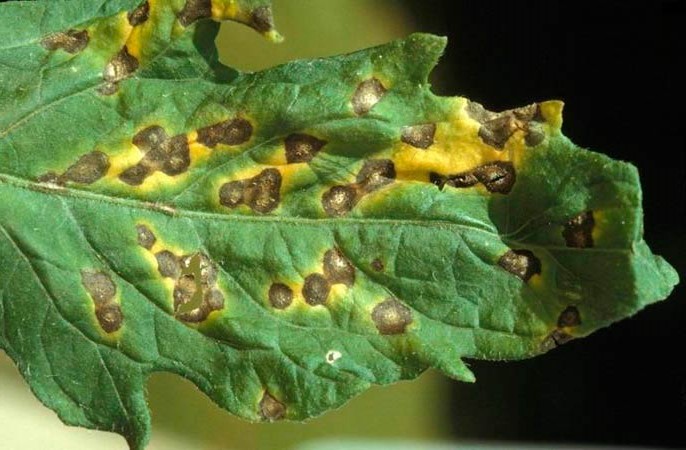
Spots can appear on tomato leaves as a result of other diseases, but they will have a different appearance. With Cladosporiosis, spots are olive-green on top and brown underneath. A mossy or velvety coating on the underside of the leaf indicates a fungal infection. A whitish coating appears on leaves with powdery mildew, but it is located on the underside.
A viral disease called mosaic also covers leaves with spots, which are usually multi-colored - light and dark green shades, and can also be whitish or almost black.
Video: "Tomato Seedling Problems"
This video will tell you about possible problems and diseases of tomato seedlings.
Control measures
Once the cause is identified, you can combat the problem. If the spots are the result of sunburn, shading the plants will help. If the burn appears on seedlings that have been moved outdoors, adjust the "walking" schedule. First, air the plants early in the morning, then later during the day, starting with shady areas, exposing the young plants to sunlight for short periods of time, gradually increasing the time spent outside.
Epin can help manage the situation and quickly get the plant back into shape. You can apply it in the evening; it will help the seedlings survive the stress and return to normal.
If the spots are caused by a fungal disease, it's not so easy to treat. Early detection can help save the plant by removing the affected leaves. Septoria can enter the plant either from the soil or from the seed, so removing some leaves can lead to further losses, increasing the risk of infection for other plants. If an adult plant is infected, it should be removed and destroyed as soon as possible. If signs are detected on seedlings, you can try treating them with Fitosporin. Dilute the product according to the package directions and apply several applications. If the plants continue to receive proper care and a balanced diet, the disease may be gone for the rest of the summer.
If mosaic is detected, the affected plants should be removed as soon as possible. Cladosporiosis can be controlled using "Zaslon" or "Barrier." Affected leaves are removed and the plants are treated. Powdery mildew can be controlled using "Zineba," "Trichodermin," and "Gaupsin."
Preventing occurrence
To prevent sunburn from affecting tomatoes, you need to gradually acclimate your seedlings to sunlight from the very beginning, from the first days of their life. Vegetable growers who wait until they've grown stronger and then expose them to sunlight before planting them in the ground are doing the wrong thing. This should be done as early as possible; this will eliminate the risk of sunburn and allow the plant to gain more strength and energy. If you miss the time, you'll have to apply lutrasil for shade after planting, but this type of tomato grows more slowly.
To prevent fungal diseases, it is necessary to carefully select planting material and disinfect seeds and soil.
Video: "Tomato Diseases and Pests"
This video will tell you about the most common tomato diseases and pests.



