Overview of mineral fertilizers: classification, application rules, compatibility table
Content
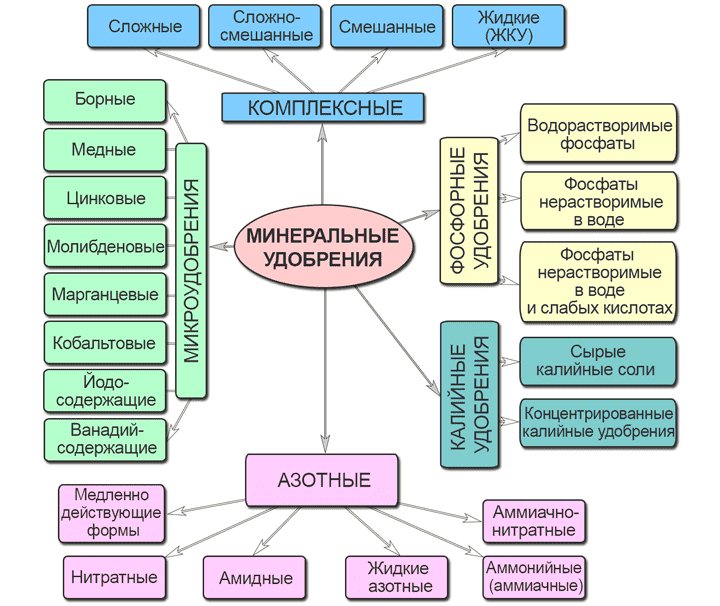
What are mineral fertilizers?
So, what types of mineral fertilizers are there, and what are they exactly? They are inorganic elements essential for the normal growth and development of plants. However, it's important to note that mineral fertilizers are not universal fertilizers; they have a rather specific purpose.
Mineral fertilizers are generally simple fertilizers containing only one element. However, complex compounds are also available. The latter include, for example, chemical compounds of potassium and nitrogen. It's important to remember that these fertilizers must be applied with extreme caution.
In general, the appropriateness of using each individual type of mineral fertilizer depends on the type of soil and the effect you ultimately want to achieve.And although some gardeners believe that such fertilizing is not necessary at all and even harmful, if everything is done correctly, the positive effect will not be long in coming.
Video "Types of Mineral Fertilizers"
This video presents various types of mineral fertilizers and describes how to use them.
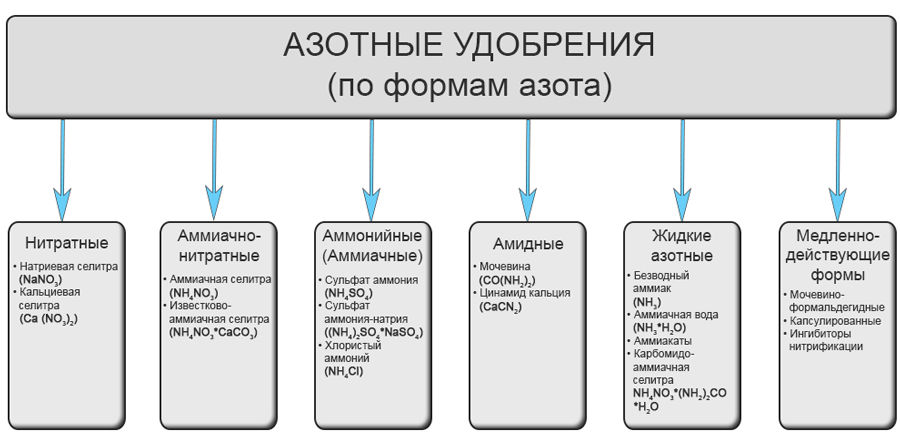
Nitrogen
The main element of such nutrient supplements is nitrogen. They are used to promote the growth and development of the above-ground parts of plants. They can also be used when symptoms of nitrogen deficiency appear in plant tissue. This manifests itself in poor growth, small leaves, and underdeveloped inflorescences. Nitrogen deficiency also causes leaves to lighten and lose their rich pigmentation. In these cases, nitrogen-based fertilizers, of which there are several varieties, should be used.
Ammonia
Ammonium nitrate is a type of fertilizer widely used for fertilizing vegetables and grain crops. It is highly acidic and consists of two main components: one that dissolves immediately, while the other dissolves over time, providing a comprehensive and long-lasting effect. Adding potassium or phosphorus increases its effectiveness, as these elements are highly compatible.
Nitrate
Nitrogen takes the form of an acid that dissolves very easily in water, forming a nutrient solution. These fertilizers are recommended for use in the fall and spring. However, the dosage must be calculated correctly, as large amounts of nitrate-containing fertilizers can contribute to the accumulation of nitrates in the human body. However, in small amounts, they have a positive effect. They are typically used to strengthen vegetable crops.
Amide
This is urea, which is the most potent nitrogen concentrate. It is used to increase the yield of fruit trees and berry bushes. There are two application methods: apply it directly to the soil during tillage, or add it to water and apply it during irrigation. Keep in mind that this fertilizer is extremely acidic.
Potassium
Potassium is an essential element for all plants. It increases yield, extends the shelf life of fruits, and improves their taste. Potassium also makes plants more resistant to various diseases. Potassium is often used in combination with other elements rather than in its pure form.
Potassium chloride
This is a natural fertilizer, although its properties are controversial. This is because it contains several elements that are both harmful and beneficial. Chlorine, which is harmful to certain garden crops, is one of its components. On the other hand, in addition to chlorine, this fertilizer contains nutrients essential for plant growth and development.
Potassium chloride is added in the fall so that all the chlorine has time to wash out by the time spring arrives.
Potassium sulfate
This highly concentrated fertilizer is an excellent alternative to the previous option. Potassium sulfate is used to feed plants that are sensitive to chlorine. It is applied during the growing season to enhance vegetative processes.
Potassium salt
The fertilizer contains kainite, potassium chloride, and sylvinite. Its spectrum of action is identical to that of potassium chloride. Potassium salt is applied only in the fall.
Phosphorus
This variety promotes abundant flowering and accelerated fruit formation. Fertilizer is typically applied either in the fall or early spring. The key issue is that phosphorus is poorly soluble in water, so the effect only becomes apparent 1.5–2 months after application.
Simple superphosphate
This fertilizer contains gypsum and sulfur and can be used on any soil type. It can be used both dry (simply sprinkled into the holes) and liquid. Its primary application is for fruit trees and berry bushes.
Double superphosphate
The spectrum of action is similar to the previous one, but the amount of phosphorus in this fertilizer is 2–3 times greater.

Phosphate rock flour
Rock phosphate flour dissolves slowly in water and is a quarter phosphorus. It is used only for acidic soils, as only this type of soil allows plants to absorb phosphorus. If applied in large quantities, it can provide plants with nutrients for several years to come.
Complex
These are mixed fertilizers, which increases the concentration of useful elements.
Nitroammophoska, or nitrophosphate
This fertilizer contains potassium, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. Plants absorb these elements seamlessly, which is a definite plus. Nitrophosphate is suitable for all soil types and has a positive effect on all plants.
Nitrophoska
The fertilizer contains phosphorus, potassium, and nitrogen, in roughly equal amounts. It is often used as a primary fertilizer for all plants. If the soil is too heavy, nitrophoska is applied in the fall, and if it is light, in the spring.
Ammophos
It contains no chlorine or nitrates, but it does contain phosphorus and nitrogen in large quantities. It's perfect for vegetables, fruits, and berries.
Diammophos
Key components: nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. It also contains many beneficial microelements, including magnesium, zinc, and iron. Suitable for all types of plants.
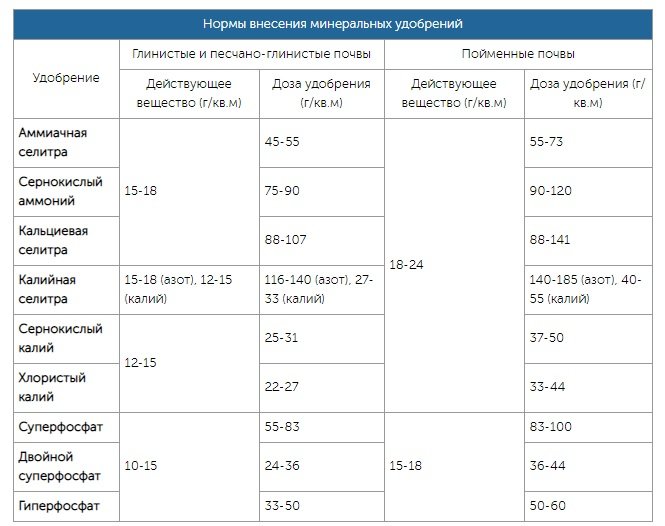
General rules for applying mineral fertilizers
To achieve the desired effect, you need to carefully follow the rules for applying these fertilizers. As you may have already noticed, some of them require extremely careful application.
The key to success when working with mineral fertilizers is strict adherence to the rules for applying these fertilizers.
So, what can and cannot be done:
- Never use the same container you use for preparing food to prepare the solution. It's best to purchase a separate container for further use in preparing the fertilizing solutions.
- It is best to store the fertilizers themselves in vacuum packaging.
- If caking occurs, pass the fertilizer through a sieve before diluting with water.
- Strictly adhere to the dosage indicated by the manufacturer.
- Fertilizers should be applied directly to the plant's roots and avoid contact with the above-ground parts. Either do this very carefully or rinse the plant afterward.
- Dry fertilizers are placed in the top layer of soil so that they quickly reach the root zone.
- Don't forget to wet the soil before carrying out the procedure.
- If there is a lack of nitrogen in the soil, it must be added.
- Clay soils will require more fertilizer.
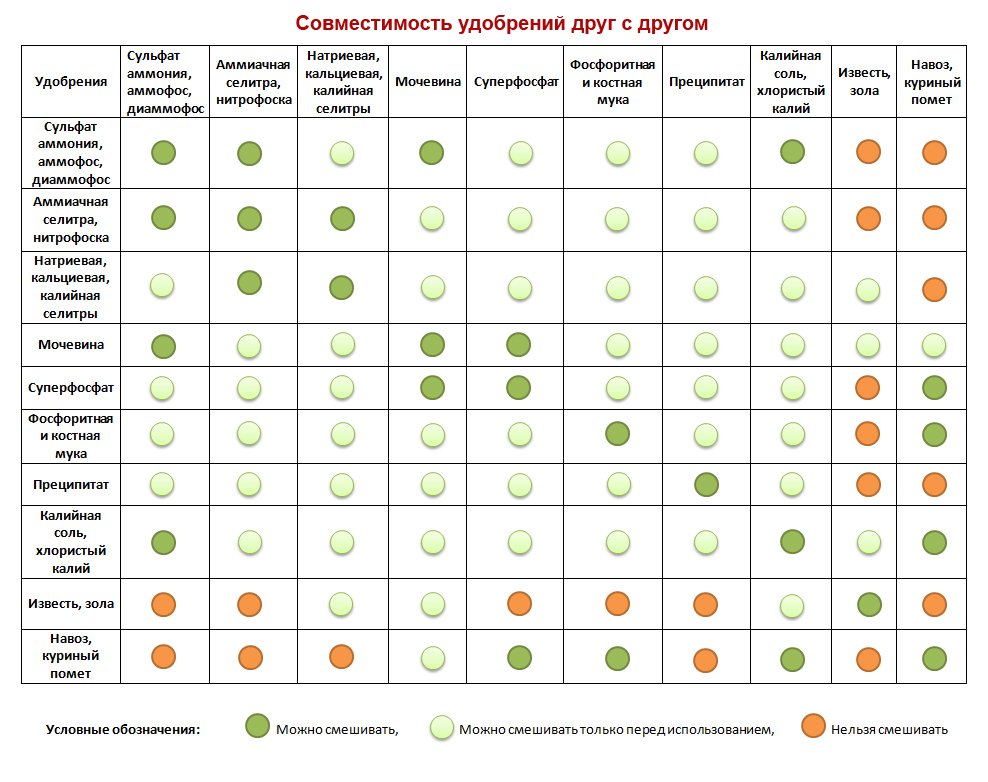
- Do not overuse mineral fertilizers and alternate them with organic ones.
- If foliar feeding is necessary, do it in early spring.
- When applying mineral and organic fertilizers simultaneously, the amount of mineral fertilizers is reduced by a third of the norm.
- It is best to use granular fertilizers.
Benefits and harms in the garden and vegetable garden
Benefit:
- They enrich the soil with useful elements.
- Increase crop yields.
- They help to increase plant immunity, protecting against diseases.
- Effective at low temperatures.
- Easy to transport.
- They are more affordable and convenient than organic ones.
As for harm, mineral fertilizers can have a negative impact on the human body. However, this only occurs if the dosage is exceeded.
As we can see, mineral fertilizers are a very useful tool in the home. Despite the stereotypes about their health risks, when used correctly and in the right dosages, they have a positive effect on plants. Use them wisely.



