What is boric acid used for for cucumbers?
Benefit
First of all, it's worth noting that boron, when present in sufficient quantities in plants and soil, can increase yields severalfold. It also extends the shelf life of fruits, which is especially important for tomatoes and cucumbers at the end of the season, before the canning stage has begun. Plants also show increased disease resistance when boron is applied to the soil in adequate quantities as a fertilizer.
Boric acid shows good results on podzolic, forest, and chernozem soils. If you have a swampy area with excess carbonates, boric acid treatment will help stabilize the pH balance and normalize all micronutrient levels in the soil. Boron also promotes fruit set in tomatoes and cucumbers, increasing their productivity and improving their flavor.
The use and foliar application of boric acid to plants is essentially harmless, as boron is classified as a Class IV hazard, meaning it's the lowest. For example, contact with human or animal skin has no negative effects, and it only affects certain insects, such as cockroaches and ants. However, despite all the benefits for vegetation, an excess of this micronutrient can be harmful to plants. Typical symptoms include yellowed leaves curling inward and quickly falling off.
If there is a shortage of boron-containing chemical compounds, the plant develops a weak root system, its above-ground part withers, and becomes more vulnerable to dry and brown rot. In this case, boron fertilization will help strengthen the plant’s immunity.
Application
Fertilization with boric acid is usually done mid-season, often through foliar feeding or spraying. This fertilizer is especially beneficial for apple trees, tomatoes, and cucumbers.
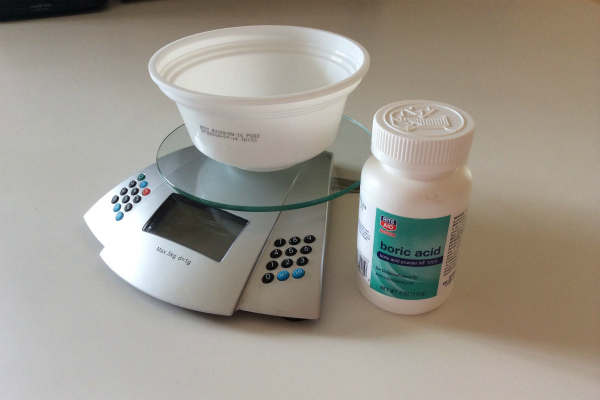
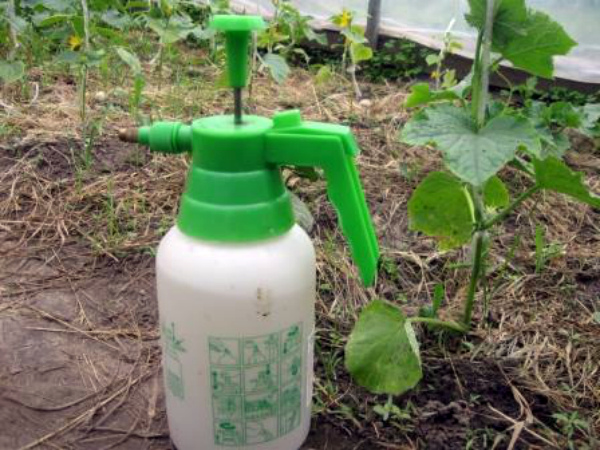
Foliar feeding is done with a boric acid solution: a quarter teaspoon of the solution is mixed with 1-2 grams of potassium permanganate and potassium permanganate in 1 cup of water. It is applied before flowering to stimulate vegetative processes. Once fruiting begins, cucumbers require a large amount of minerals to support growth and development, so they can be sprayed once a week with a solution of mineral fertilizers containing boron. For this purpose, you can use dissolved boric acid at a rate of ¼ teaspoon per 10 liters of water.
At the beginning of the season, before planting, boron is used to treat seeds. Dissolve 1 g of boric acid in 1 liter of water, then soak the seeds in the resulting solution for 10-13 hours. You can also spray the seeds with diluted boric acid shortly before planting to stimulate good germination and subsequent rooting.
Note for beginning gardeners: Fertilizing with boron-containing fertilizers should be done either early in the morning, when it's not too hot, or late in the evening, when it's no longer too hot. It's best to wait until dry, windless weather allows the fertilizer to be absorbed better.
Fertilizing the soil with this solution before planting tomatoes will create a so-called "safety cushion"—a reserve of nutrients for the initial period of rooting in a new location and subsequent vigorous growth. You can use 10 grams of boron-containing substances per 10 liters of water, and then water the beds.
Spraying and fertilizing plants will be helpful not only during flowering but also as additional support while the plant establishes itself in its new location. Boron fertilizers should be applied no more than once every 2-3 weeks to prevent over-fertilization.
It's important to remember that no fertilizer can replace proper, comprehensive soil fertilization. Therefore, boron-based fertilizers should only be used after ensuring they don't become the sole source of nutrients. Add organic and mineral fertilizers to the soil before planting to ensure fertile soil.
Another use for boron fertilizers is ant control. Garden ants are often a nuisance, damaging fruit and aggressively defending their territory. To kill two birds with one stone, use boron traps: this way you'll feed your plants and get rid of these pesky insects. Boron compounds affect the ants' intestines, and after absorption, their peripheral nervous system is paralyzed. Within a few hours, you'll be rid of any ant colony. Given the substance's tendency to accumulate in the body, it also affects the reproductive system, preventing ants from reproducing. This leads to the rapid demise of the colony. The presence of boron microelements in the soil serves as a preventative measure, preventing new insects from establishing their nests on your property.
Video: "Feeding Vegetables with Boric Acid"
This video will show you how to make a boric acid solution for feeding cucumbers and tomatoes, as well as how to properly deliver it to the plants.