The benefits of growing the large-fruited raspberry variety Pride of Russia
Content
- 1 History and characteristics of the Pride of Russia raspberry
- 2 Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- 3 Video: "Introducing the Super-Large-Fruited Raspberry 'Pride of Russia'"
- 4 Features of agricultural technology for the Pride of Russia raspberry
- 5 Diseases and pests, methods of control and prevention
- 6 Reviews from gardeners
History and characteristics of the Pride of Russia raspberry
The name of Professor and biologist Viktor Valerianovich Kichina is familiar to virtually every gardener. The "Pride of Russia" raspberry is another of his creations. In 1992, the scientist crossed the Stolichnaya variety with the hybrid form Shtambovy-20. Six years later, in 1998, a new super-large-fruited variety was developed, named "Pride of Russia," or "Ispolin."
Description of the bush
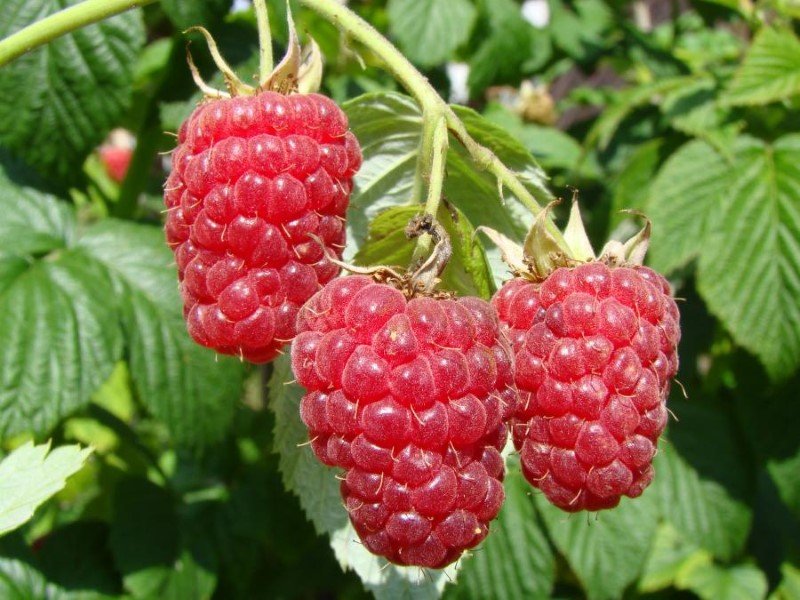
The Pride of Russia raspberry is classified as a medium-sized fruit tree. The mature bush reaches no more than 1.8 m in height. The bush is strong, vigorous, and compact. It produces no more than 10 replacement shoots and approximately 5-6 root suckers. One-year-old shoots are slightly pubescent and lack a waxy coating. The bark is a rich green. Two-year-old shoots are brown. A distinctive feature of this variety is the absence of thorns on both young and mature branches.
The leaves of this variety are eye-catching with their beautiful dark green color. The outer surface of the leaf blade is glossy. The plant is often used for landscaping in gardens or home areas.

Consumer qualities of fruits
The Ispolin variety produces very large berries. The average ripe fruit weighs 10–12 g. Their shape is perfectly conical. Due to the close contact with the core, the berries do not fall off when they reach harvestable maturity. The raspberries have a sweet and tart flavor, with a subtle aroma.
Productivity and fruiting
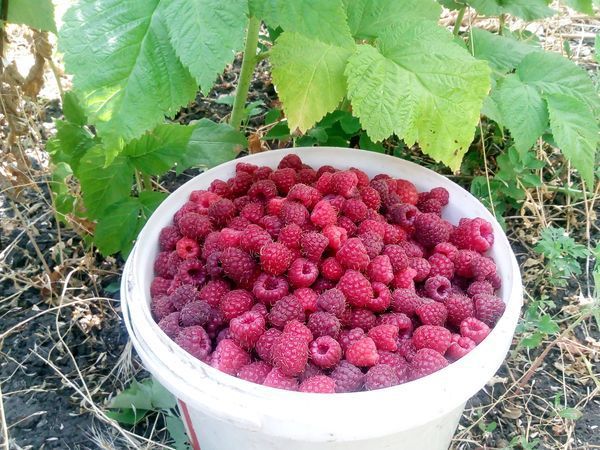
What's so special about the Pride of Russia berry? Its key advantages include early ripening and high yield. The first berries are harvested in the second ten days of June. With fruiting up to six times per season, a single bush yields approximately 5 kg of large berries.
Application of fruits
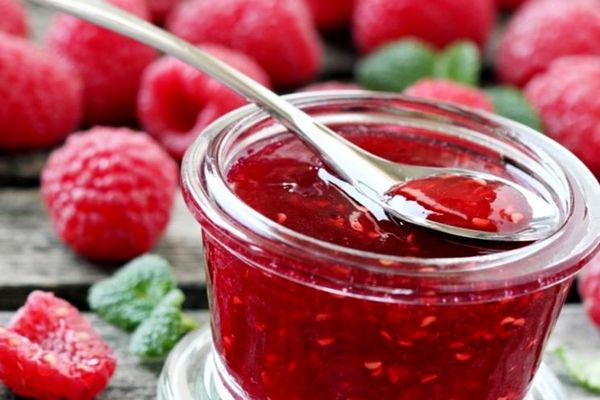
The juicy berries are eaten fresh and canned. The Ispolin variety is often used to make juices, fruit drinks, compotes, pastilles, berry candies, and a variety of desserts.
- The berries are large and conical in shape.
- The variety is characterized by high productivity.
- The harvested crop is used to make jam.
Drought resistance, frost resistance
The shrub is highly drought-resistant. This super-large-fruited variety can survive without additional watering for up to 30 days. The Pride of Russia raspberry can withstand temperatures as low as -28°C and as low as -32°C. It can be grown in gardens in Siberia and the Urals.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- rapid adaptation of seedlings;
- high level of drought resistance;
- excellent winter hardiness;
- absence of thorns and decorative nature of the bush;
- early ripening;
- amazing consumer qualities of berries;
- increased productivity;
- universal use of fruits;
- high transportability.
- loss of taste when there is too much moisture in the soil;
- dependence of fruiting on precipitation and the amount of nutrients in the soil.
Video: "Introducing the Super-Large-Fruited Raspberry 'Pride of Russia'"
This video explains what berry bushes look like and where they grow.
Features of agricultural technology for the Pride of Russia raspberry
Any fruit crop requires time and attention from gardeners. Knowing and applying the right agricultural practices for a specific plant increases fruiting and yield.
Landing rules
Raspberry seedlings can be purchased at gardening stores or nurseries. When inspecting the plants, pay attention to the condition of the roots, shoots, and leaves. The seedling should look fresh and healthy.
The Pride of Russia is best planted outdoors in the fall. Fall planting has one huge advantage: the young plant has time to strengthen well over the winter. With the arrival of spring, the plant begins to grow vigorously. To prevent a seedling planted in unprotected soil from dying from hypothermia, it is carefully insulated for the winter. The bush is covered with dry fallen leaves, covered with agrofibre, and then insulated with pine branches.

The Ispolin variety is a sun-loving fruit crop. For a raspberry patch, choose a sunny but wind-protected area of the garden. Blackberry and currant bushes, as well as barberry, garden roses, and juniper, are considered the best neighbors. However, it's best to avoid grapes, jasmine, sea buckthorn, and elderberries.
The Pride of Russia raspberry prefers heavy soil. Ideally, loam or black soil with low or neutral pH is ideal.
Watering, mulching and fertilizing
Fruit and berry bushes are watered 1-2 times a week. 30 to 40 liters of water are required per square meter of soil. Raspberries are watered with settled, room-temperature water. The optimal time for watering the soil is in the morning before sunrise or in the evening at sunset.
To maintain optimal moisture levels, mulch the soil with hay, straw, or peat. Black spunbond mulch can also be used.
Soil fertility affects the fruiting and yield of the crop. Ispolin raspberries can be fertilized according to the following schedule:
- In spring, apply mullein diluted in water (500 ml of organic fertilizer per 10 liters of water). No more than 5 liters of fertilizer are required per square meter. Nitrogen-containing fertilizers are often used instead of organic fertilizer.
- In summer, use complex potassium-phosphorus mixtures or diluted bird droppings with urea. For every 10 liters of solution, use 2 tablespoons of urea.
- Autumn – a nutrient mixture of superphosphate (30 g), ammonium nitrate (15 g), potassium salt (20 g) and water (10 l).
Pruning stages
Raspberry bushes require pruning. In the spring, sanitary and formative pruning is performed. Sanitary pruning involves removing shoots weakened by winter. Crown shaping, in turn, prevents the bush from becoming overgrown. No more than eight replacement shoots and about five root suckers are left on each bush.

Shelter for the winter
Frost-resistant raspberries are susceptible to winters with little snow and sudden temperature fluctuations. To prevent young shoots from freezing, the plant should be insulated for the winter. The branches of the fruit bush are gathered in bunches and carefully bent to the ground. The vines are covered with agrofibre or burlap.
Raspberry bushes grown in southern Russia require no shelter. Preparing for winter involves watering and mulching the root zone with a mixture of peat, sawdust, and coarse river sand.
Diseases and pests, methods of control and prevention
One of the most important aspects of growing fruit crops is pest and disease control. Unfortunately, the Giant has weak resistance to the pathogens that cause septoria, rust, and root canker.
Maintaining a watering schedule, proper fertilizing, and timely pruning are the best disease prevention measures. If septoria leaf spot or rust cannot be avoided, use fungicides such as Topsin-M, Antracol, Topaz, Magnicur Star, and Fital. A cure for root canker is unlikely. To prevent infection of other plants, the affected bush is dug up along with the roots and burned.
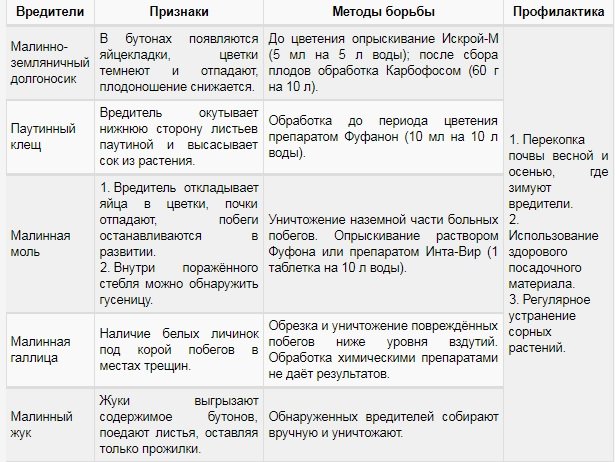
The variety is susceptible to attacks by raspberry beetles, raspberry moths, spider mites, strawberry weevils, and raspberry stem gall midges. Effective pest control methods are described in the table below:
Reviews from gardeners
"I've been growing raspberries for many years, but I can confidently say that my favorite variety is 'Pride of Russia.' The plant is resistant to extreme weather conditions and frost."
"Unfortunately, we rarely visited our dacha last year. Lack of time and attention negatively impacted the 'Pride of Russia' raspberry bush we grew in the garden. The bush became overgrown, fruiting decreased, and the berries became small. I'll try to revive it with pruning and fertilizing."
Compared to other fruit and berry crops, the Pride of Russia raspberry variety is highly adaptable and easy to grow. With proper watering and timely fertilizing, it produces a bountiful harvest of large, juicy berries.



