The intricacies of planting and growing large-fruited strawberries of the Asia variety
Content
- 1 History of the variety's appearance
- 2 Description and characteristics of Asia strawberries
- 3 Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- 4 Video "Description of Asian Strawberries"
- 5 Features of planting and caring for Asian strawberries
- 6 Diseases and pests, methods of control and prevention
- 7 Reviews from gardeners
History of the variety's appearance
The Asia strawberry is considered a relatively new variety. It was developed in 2005 by Italian breeders at New Fruits. The variety was originally intended for commercial cultivation in northern Italy. However, the berries' amazing flavor and attractive appearance attracted the attention of amateur gardeners. Today, the berry is grown in many European countries, as well as in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus.

Description and characteristics of Asia strawberries
In Italy, the berry is grown in peat bags using Dutch agricultural techniques. Russian gardeners and summer residents prefer to grow it both outdoors and indoors.
Plant characteristics
This variety grows large, spreading, upright bushes with a robust and well-developed root system. It is characterized by large, richly green leaves. The leaf surface is glossy and slightly wrinkled. The leaf edges are corrugated and ragged.
Commercial and taste qualities of berries
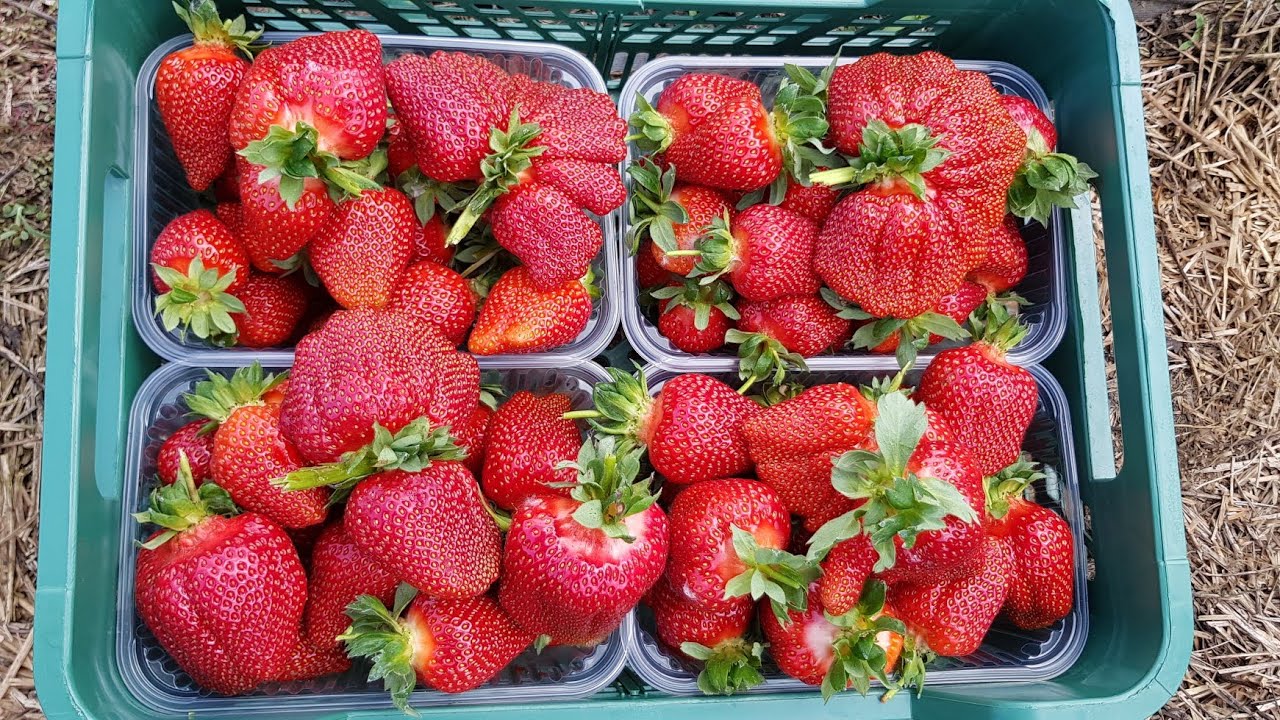
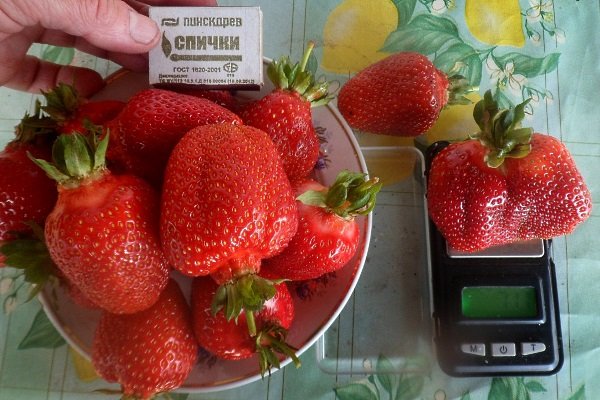
The Asia strawberry is considered a large-fruited variety. The average ripe berry weighs 45 g, but specimens weighing 80–110 g are not uncommon. The fruit's shape can be diamond-shaped, comb-shaped, or elongated-conical. Despite its large size and weight, there are no hollows. The flesh is juicy and sweet, with a hint of garden strawberry aroma. Berries that reach harvestable maturity are a beautiful blood-red hue.
Collection, yield and application
Asia is a mid-early variety with a prolonged fruiting period. The first berries begin to ripen in early June. Harvesting can continue until early July. Yields depend on the region's climate and compliance with the cultivar's recommended agricultural practices. On average, a single bush yields 1–1.2 kg of edible fruit.
The berries are eaten fresh, frozen, and used to make desserts and sweet drinks. Asia is often used for the production of fruit and berry wines and liqueurs.

Drought and frost resistance
The variety has average drought tolerance; without adequate moisture, the fruit loses its marketable quality. Therefore, soil moisture levels must be carefully monitored.
The crop's winter hardiness is modest. It can withstand temperatures as low as -15°C. Strawberries are susceptible not only to frost but also to sudden temperature fluctuations.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
A favorite among many gardeners, the Asia strawberry has many advantages. However, it's important to remember that every garden-grown crop also has its drawbacks.
- high yield;
- early ripening;
- long fruiting;
- amazing commercial and taste qualities of berries;
- universal application;
- high transportability;
- resistance to bacterial diseases.
- poor winter hardiness;
- high demands on the growing site;
- low resistance to fungal infections;
- deterioration of taste when grown indoors.
Video "Description of Asian Strawberries"
This video shows the commercial characteristics of the fruits of this variety.
Features of planting and caring for Asian strawberries
The Asia strawberry is often called an easy-to-grow fruit crop. This statement is not entirely accurate, as the variety's yield is influenced by growing conditions and plant care.
Recommended timeframes
For regions with cold climates, spring planting is preferable. This should be done before flower stalks begin to form, and the average daily temperature should be at least 10°C.
In the central and southern regions, seedlings can be planted in both spring and fall. Fall planting periods range from the second half of August to the second ten days of September.
Selecting a location and soil
Asiatic jasmine is demanding when it comes to its growing location. The chosen garden site should be protected from wind and drafts. The plant prefers full sun with some shade at midday. A slope or flat terrain (not a lowland!) facing south or southwest is ideal.

Loose, fertile, and highly aerated soil is suitable for growing this crop. The soil pH should be neutral. A high water table is undesirable for this fruit and berry crop.
Landing algorithm
Prepare the planting holes or beds for strawberry bushes 10–15 days in advance. Before planting, disinfect the soil with a copper sulfate solution. Maintain a 70–75 cm spacing between rows and 30–35 cm between holes.
A small mound is formed in the center of each hole. The plant is planted into the mound, carefully straightening the roots. The growing point, called the "heart," should be level with the ground surface.
The plant can be propagated by seeds, side shoots, and division. The easiest method is by side shoots. On plants that are two years old, all flower stalks are removed to provide the side shoots with nutrients. The shoots are pressed to the ground and secured with metal staples. Once the plant has established roots (around mid-July), the rosette can be separated from the mother plant.
- Propagation by seeds
- Rooting of stepchildren
- Dividing the bush
Watering mode
Since the variety has average drought tolerance, soil moisture should be maintained. Watering frequency is determined by the weather and climate of the region. For example, in southern regions, where summers are typically hot and dry, beds are watered every 2–3 days. If there is a prolonged drought, watering frequency can be increased. After the water has been absorbed, loosen the top layer of soil.
Strawberries can be mulched with hay, straw, or black agrofibre. Mulch maintains soil moisture and prevents weed growth.
How and when to feed
It's no secret that you can increase the yield of garden plants by using organic and mineral fertilizers. The following fertilizing regimen is suitable for Asia strawberries:
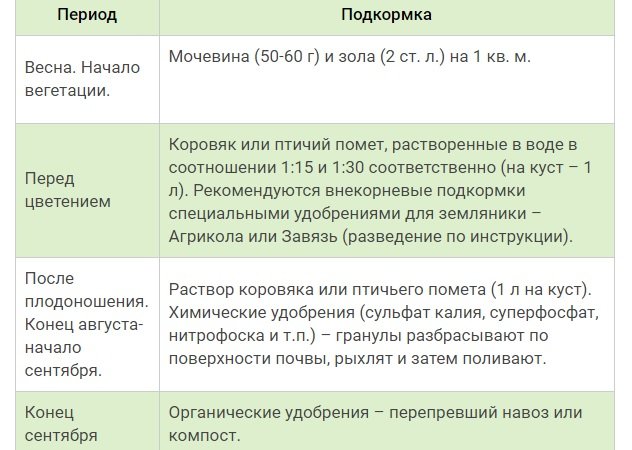
Diseases and pests, methods of control and prevention
The plant often suffers from infestations of aphids, nematodes, sawflies, weevils, and strawberry mites. To control insects, use Chlorophos and Karbofos, and to prevent them, use finely ground laundry soap diluted with water.
Unfortunately, the crop has weak immunity to brown spot, gray mold, and powdery mildew. Strawberries can be treated with fungicides such as Topaz and Bayleton.
Reviews from gardeners
"The Asia strawberry was a sensation for me. Delicious, large berries with minimal care. I recommend it to everyone."
"I really liked the large fruits of the Asia strawberry. I decided to try growing them at my dacha. The experiment was a success, and the variety took root. The only caveat is to carefully cover the beds for the winter."
Juicy and sweet, the Asia strawberry will delight you with a bountiful harvest if you follow the above-described cultivation practices. Growing this berry is a breeze for both professionals and amateur gardeners.



