Description of the highly immune pear variety Feeria
Content
Description and characteristics of the variety
The Feeria pear variety is the result of crossing two remarkable cultivars—Talgarskaya Krasavitsa and Docherya Zari. It is a late-ripening winter variety with a mixed yield. The fruit can be stored for a long time in cold rooms and special storage chambers. The pears are quite wind-resistant and do not shatter or fall off. Their flavor remains consistent and is unaffected by harvest time. The variety is characterized by its resistance to adverse weather conditions, pests, and diseases. Feeria is also resistant to low temperatures, tolerates frosts well, and does not require winter cover.
A medium-sized tree, approximately 2 m tall, with a drooping, broadly pyramidal crown with moderate foliage. The branches are fairly thick, smooth, and gray with a brownish tint. The shoots are arched. The buds are medium-sized and perfectly conical. The leaf blade is small, with a smooth, glossy surface of a rich green color. The leaflet is slightly concave, the base is flattened, and the margin is pointed.
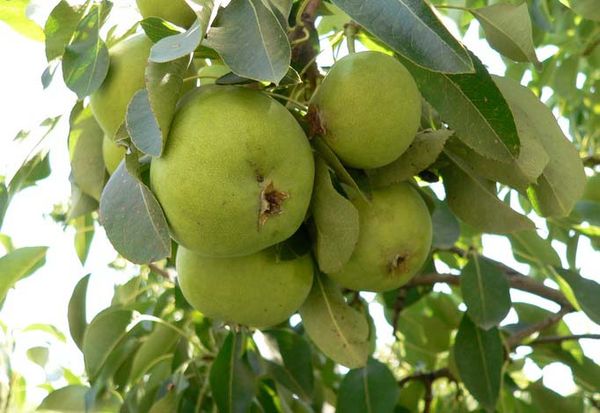
The fruits are quite large, weighing over 200 g in optimal climatic conditions. A classic, slightly elongated shape with smooth, buttery skin. The skin color changes as the fruit ripens: from bright green with a light coral blush to deep yellow with a raspberry tint. The flesh is white, slightly oily, tender and sweet. The aroma is subtle.
A description of the variety would be incomplete without mentioning the fruit's excellent chemical composition. The pear contains not only vitamins and microelements but also beneficial acids, including ascorbic acid. The pear begins to bear fruit in the fifth to sixth year. The trees are generally characterized by high yields.
Features of cultivation
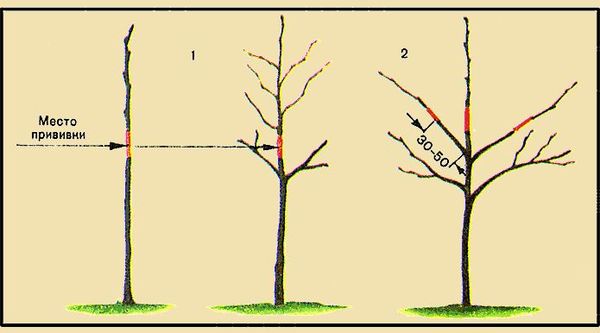
Grafting is considered the most effective method of propagating Feeria. Pear trees can be grafted onto both cultivars and wild pear or quince seedlings. The Lyubimitsa Yakovleva and Fevralsky Souvenir varieties are ideal rootstocks. Minimal pruning is recommended before fruiting begins. In the first few years, pruning is done to establish proper branching and crown formation. Mature trees are pruned in the spring for sanitary and rejuvenating purposes. Proper pruning regulates growth vigor, ventilation, and light access to all branch levels. Excessive crown density leads to smaller fruits.
Additionally, tree trunks are cleared of calluses and dead bark. Preventative treatment is recommended to prevent diseases and pests. The tree should be sprayed several times a year: in early spring, before and after flowering. Areas with damaged bark or cracks should be treated especially carefully, as these are where parasites most often breed and fungal spores overwinter.
Before wintering, sanitary pruning and whitewashing of trees is carried out, and the remaining fruits are collected from the tree.
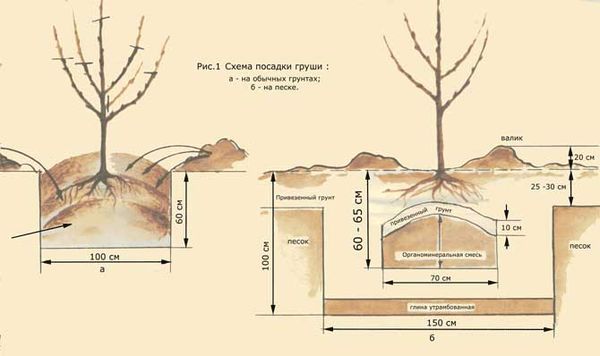
Young trees are best wrapped in burlap or simple canvas to protect them from rodents. During severe frosts, young trees can also be covered with spruce branches. Water the trees as needed, depending on the amount of rainfall. Watering can be done by sprinkling or in trenches dug around the tree trunk.
During the flowering period, the plant is fed with nitrogen-containing fertilizers. These are diluted with water and added during irrigation. In the fall, potassium and phosphorus-containing fertilizers are used. The main issue facing gardeners is harvest time. The fruit must reach the required ripeness for the pear to achieve its full range of flavors. However, leaving the fruit on the vine for too long is also not recommended.
Advantages and disadvantages
The Feeria pear is one of those varieties that has virtually no drawbacks.
This tree is rightly considered the best specimen bred from this pair of "parents." The only drawback is the reduced fruit size due to excessive crown density. This can be remedied with timely and regular pruning. Let's look at the advantages of Feeria in more detail:
- high degree of resistance to various climatic conditions, frost resistance;
- lack of susceptibility to diseases such as black cancer, scab, cytosporosis, fruit rot, rust, powdery mildew and other fungal diseases;
- resistance to parasites and pests: green aphids, pear moths, leafhoppers, mites, leaf rollers;
- wind-resistant fruits - they do not crumble or fall off;
- high degree of preservation of fruits in cool rooms and special chambers, good transportability;
- The excellent taste and chemical composition of pears make them suitable for both fresh consumption and processing.
Certainly, Feeria is a tree that is worthy of your garden and efforts.
Video: "Formation of the pear damage"
This video will show you how to properly shape the crown of a pear tree.