Growing Dogwood—Practical Recommendations for Planting, Propagation, and Care
Content
What does dogwood look like?
Dogwood is a tall fruit-bearing shrub. The average height of this pyramidal bush is 3 meters, although some cultivated specimens have reached 8–9 meters. The bushy or tree-like plant has yellow-green shoots. As it matures, the branches become woody.
The leaves are a beautiful, rich green with a slight sheen. The underside of the leaf is matte, a shade lighter. The leaf blade is elongated and pointed. During flowering, the shrub is covered in lush, beautiful yellow inflorescences.
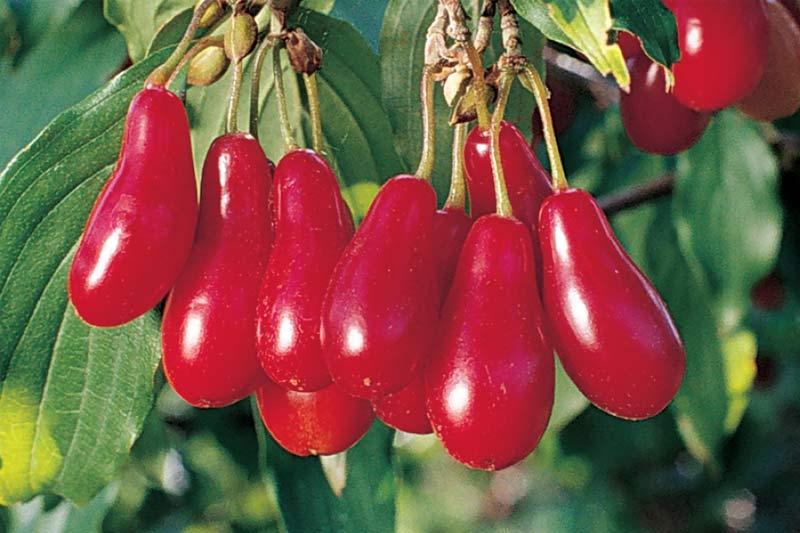

The skin of ripe berries is colored predominantly red.
The elongated berries come in red, white, and yellow. The average fruit weight is 8 g and length is 40 mm. The skin is dense and slightly firm, the flesh is juicy and rich. The flavor has a hint of tartness, with a tart aftertaste. As the berries ripen, so does the sugar content.
Video: "Peculiarities of Growing Dogwood"
In this video, experts explain how to grow fruit from a seed.
Types and varieties of dogwood
Gardeners in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus, where dogwood has taken root particularly well, have come to appreciate the following high-yielding species and varieties of this fruit crop:
- Lukyanovsky - up to 50 kg;
- Vladimirsky – up to 60 kg;
- Eugenics – up to 50 kg;
- Vydubitsky – up to 60 kg;
- Coral Brand – up to 40 kg.
The indicated yield figures are typical for mature fruit-bearing crops.
Planting dogwood
Dogwood is considered a fruit crop that is undemanding to growing conditions. However, improper planting can negatively impact the plant's growth and development. Let's figure out how to plant a dogwood tree correctly.
Optimal timing and choice of location for planting
The optimal time for planting dogwood is throughout the growing season. If planting is planned for the fall, check the weather forecast in advance.
As for site selection, the plant thrives even in rocky soil. It grows best on an exposed northeast-facing site. It's recommended to avoid marshy areas, lowlands, and areas with a high water table. Dogwood prefers partial shade, well-drained soil that is rich in oxygen, calcium, and alkaline.

The optimal period for planting dogwood is the entire growing season.
How to select and prepare seedlings
For rapid rooting, seedlings with 2-3 root branches are best. The main root should be at least 30 cm long. The tree should be free of cracks and other damage. If the seller allows you to make a small cut in the bark, pay attention to the color of the wound. Green indicates high viability, brown indicates low viability.
Preparing the seedling involves thoroughly moistening the root system. If planting in open ground is delayed, the seedling should be buried at an angle in a shady area.
Step-by-step planting process
First, dig a 30x50 cm planting hole. Expanded clay, pebbles, and crushed stone are placed at the bottom of the hole. The optimal drainage layer is about 15 cm. Then, add a layer of soil and plant the tree. The plant's root system is pre-soaked in a clay slurry. The area around the tree trunk is mulched to retain moisture.
Dogwood is highly sensitive to fertilizer. Experienced gardeners do not recommend using compost, manure, or any mineral fertilizers when planting.
How to care for dogwood
Caring for fruit crops includes a number of simple, but very important measures for the normal functioning of the plant:
- Watering is carried out along a circular furrow formed around the edge of the tree trunk. The frequency of watering is determined by the moisture content of the topsoil.
- After each watering, mulch the soil with sawdust, hay or freshly cut grass.
- Loosening the soil and removing weeds helps enrich it with oxygen. However, loosening the soil should be shallow, as young rhizome shoots are found at a depth of 5–8 cm.
- Nitrogen and phosphorus are used as fertilizers during the first half of the growing season. Potassium-rich fertilizers are applied during the second half of the growing season.
- Systematic pruning is one of the care rules. Old shoots are cut back to the ground to stimulate the growth of new shoots.
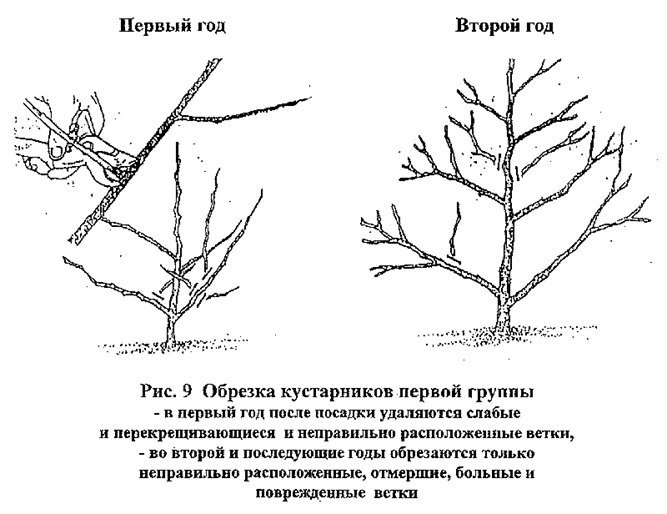
Fruit bush pruning scheme
Propagation of dogwood
Gardeners propagate fruit crops using vegetative methods and very rarely use the seed method.
Growing from seed
Seed propagation of dogwood is used by breeders to select the best varieties. Before sowing, selected dogwood seeds are planted 2.5–3 cm deep in moist moss or sawdust. Stratification lasts from 12 to 28 months.
Stratified seeds germinate within a year, while unstratified seeds germinate after 5–10 years. First-year seedlings reach 30–40 mm in height, while second-year seedlings reach 100–150 mm. Once they reach two years of age, the young seedlings are transplanted into open ground.
Propagation by cuttings
How to grow dogwood from cuttings? To propagate this fruit tree, use green cuttings taken early in the morning from 5-6-year-old bushes. Woody branches don't take root well and are often susceptible to disease.
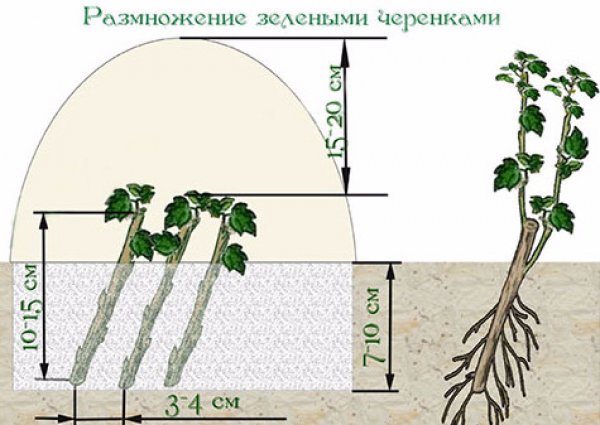
Propagation of dogwood by green cuttings
The cutting must have a formed growth point and at least two pairs of developed leaf blades. Before planting, the cutting is placed in a 3% heteroauxin solution for 6-12 hours. Then, the plant is rinsed with water and planted in the soil at an acute angle. The soil is covered with washed river sand and covered with plastic film. After 20-25 days, the first roots appear. During this period, the gardener removes the plastic film and begins "hardening off" the plant. The strengthened cuttings are planted in open ground the following fall.
Propagation by grafting
Dogwood budding is done in August or September. A branch of a wild tree is used as the rootstock. Using a sharp pruning knife, a cross-shaped cut up to 30 mm deep is made in the rootstock. The scion is placed into the resulting "hole."
The scion must have a well-developed bud with a piece of bark and a leaf stalk.
The scion is attached to the rootstock with budding tape or regular office tape. If the procedure was performed correctly, the leaf petiole will fall off the scion within 15–20 days. The tape is removed in early October.
Propagation by layering
To propagate fruit trees by layering, use a one-year-old, arching stem that is positioned almost horizontally to the soil surface. This procedure is carried out in the spring, after applying a complex mineral fertilizer to the soil.
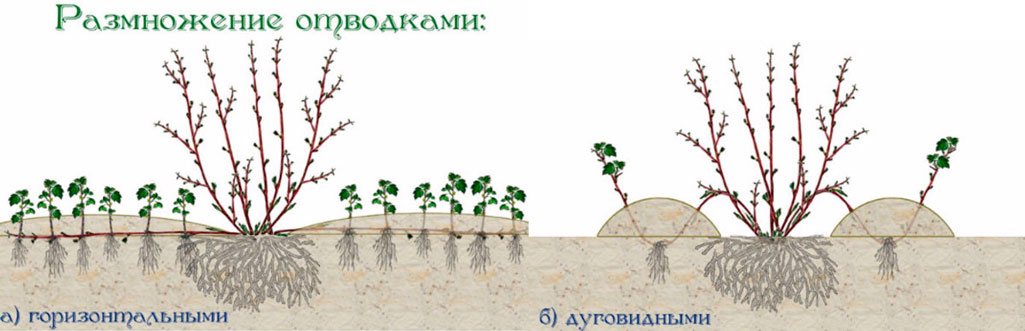
Propagation of fruit bushes by layering
The bent stems are placed in shallow furrows and covered with nutrient-rich soil. The first shoots that appear are half-covered with soil. When the branches have grown 1.5–2 times their original height, the procedure is repeated. The layers are separated from the parent plant in the fall or the following spring.
Propagation by dividing the bush
Bush division is used as a method of dogwood propagation only when replanting is necessary. The optimal time for this operation is spring (before the buds begin to swell) or early fall.
The bush is dug up, old and damaged shoots are removed, and the soil is carefully removed from the root shoots. The plant is then divided into several equal parts. Before planting, the root system is carefully inspected, and dead, damaged, and rotten shoots are removed.
Harvest timing
Harvest timing is determined by many factors. The climate zone and fruit variety play a significant role. On average, the period from the end of flowering to the beginning of fruit ripening takes 100 to 150 days.
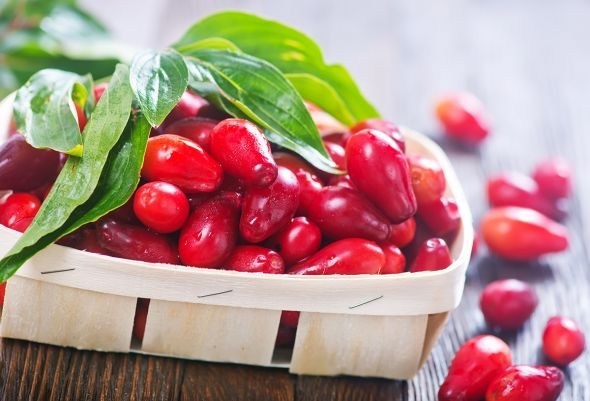

The harvest time depends on the variety of crop being grown.
Early-ripening plants are harvested in June, while mid-ripening plants are harvested in August and September. Late-ripening fruit crops yield fruit in late autumn – early November.
As the tree matures, its yield increases. According to experienced gardeners in the Moscow region, a 10-15-year-old shrub can yield 10 to 25 kg of ripe berries. A 20- to 30-year-old tree produces around 40 to 60 kg of healthy fruit. The most productive trees are those that are over 40 years old. The average yield of an "old" dogwood is 100 to 110 kg.
Rich in vitamin C, organic acids and essential oils in dogwood berries are used to normalize blood pressure, eliminate signs of anemia, remove heavy metals from the body, and strengthen the immune system.



